
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the water, on ice (iceboat) or on land over a chosen course, which is often part of a larger plan of navigation.

The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in British and American shipbuilding traditions the construction is dated from this event.
A Bruce foil is a variant of the leeboard, consisting of a foil typically mounted on an outrigger and always set at an angle to provide both lateral and vertical force. It was invented by Edmond Bruce in the early 1960s, and first published in the Amateur Yacht Research Society publication in April 1965.

Dinghy sailing is the activity of sailing small boats by using five essential controls:
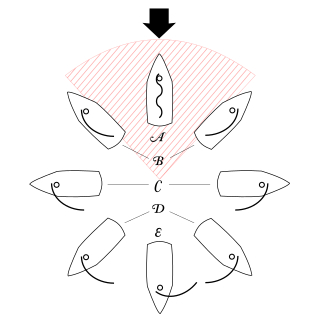
A point of sail is a sailing craft's direction of travel under sail in relation to the true wind direction over the surface.

A daggerboard is a retractable centreboard used by various sailing craft. While other types of centreboard may pivot to retract, a daggerboard slides in a casing. The shape of the daggerboard converts the forward motion into a windward lift, countering the leeward push of the sail. The theoretical centre of lateral resistance is on the trailing edge of the daggerboard.

A spinnaker is a sail designed specifically for sailing off the wind from a reaching course to a downwind, i.e. with the wind 90–180° off bow. The spinnaker fills with wind and balloons out in front of the boat when it is deployed, called flying. It is constructed of lightweight fabric, usually nylon, and is often brightly colored. It may be optimised for a particular range of wind angles, as either a reaching or a running spinnaker, by the shaping of the panels and seams.

A centreboard or centerboard (US) is a retractable keel which pivots out of a slot in the hull of a sailboat, known as a centreboard trunk (UK) or centerboard case (US). The retractability allows the centreboard to be raised to operate in shallow waters, to move the centre of lateral resistance, to reduce drag when the full area of the centreboard is not needed, or when removing the boat from the water, as when trailering. A centreboard which consists of solely a pivoting metal plate is called a centerplate. A daggerboard is similar but slides vertically rather than pivoting.

Proas are various types of multi-hull outrigger sailboats of the Austronesian peoples. The terms were used for native Austronesian ships in European records during the Colonial era indiscriminately, and thus can confusingly refer to the double-ended single-outrigger boats of Oceania, the double-outrigger boats of Island Southeast Asia, and sometimes ships with no outriggers or sails at all.
A leeboard is a form of pivoting keel used by a sailboat in lieu of a fixed keel. Typically mounted in pairs on each side of a hull, leeboards function much like a centreboard, allowing shallow draft craft to ply waters fixed keel boats cannot. Only one, however, the leeward, is used at a time, as it does not get lifted from the water when the boat heels under the force of the wind.
Ballast is used in ships to provide moment to resist the lateral forces on the hull. Insufficiently ballasted boats tend to tip or heel excessively in high winds. Too much heel may result in the vessel capsizing. If a sailing vessel needs to voyage without cargo, then ballast of little or no value will be loaded to keep the vessel upright. Some or all of this ballast will then be discarded when cargo is loaded.

The winged keel is a sailboat keel layout first fitted on the 12-metre class yacht Australia II, 1983 America's Cup winner.
A foil is a solid object with a shape such that when placed in a moving fluid at a suitable angle of attack the lift is substantially larger than the drag. If the fluid is a gas, the foil is called an airfoil or aerofoil, and if the fluid is water the foil is called a hydrofoil.

A canting keel is a form of sailing ballast, suspended from a rigid canting strut beneath the boat, which can be swung to windward of a boat under sail, in order to counteract the heeling force of the sail. The canting keel must be able to pivot to either port or starboard, depending on the current tack.

In sailing, heaving to is a way of slowing a sailing vessel's forward progress, as well as fixing the helm and sail positions so that the vessel does not have to be steered. It is commonly used for a "break"; this may be to wait for the tide before proceeding, or to wait out a strong or contrary wind. For a solo or shorthanded sailor it can provide time to go below deck, to attend to issues elsewhere on the boat or to take a meal break. It is also used as a storm tactic.

A sailing hydrofoil, hydrofoil sailboat, or hydrosail is a sailboat with wing-like foils mounted under the hull. As the craft increases its speed the hydrofoils lift the hull up and out of the water, greatly reducing wetted area, resulting in decreased drag and increased speed. A sailing hydrofoil can achieve speeds exceeding twice the wind speed.
Weather helm is the tendency of sailing vessels to turn towards the source of wind, creating an unbalanced helm that requires pulling the tiller to windward in order to counteract the effect.

Forces on sails result from movement of air that interacts with sails and gives them motive power for sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and sail-powered land vehicles. Similar principles in a rotating frame of reference apply to wind mill sails and wind turbine blades, which are also wind-driven. They are differentiated from forces on wings, and propeller blades, the actions of which are not adjusted to the wind. Kites also power certain sailing craft, but do not employ a mast to support the airfoil and are beyond the scope of this article.

A sail is a tensile structure—made from fabric or other membrane materials—that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails may be made from a combination of woven materials—including canvas or polyester cloth, laminated membranes or bonded filaments—usually in a three- or four-sided shape.
The Bristol Caravel 22, sometimes called the Bristol 22 Caravel, Sailstar Caravel, or just the Caravel 22, is an American trailerable sailboat that was designed by Halsey Chase Herreshoff as a cruiser and first built in 1968. It is named for the class of sailing ship.













