Instant messaging (IM) technology is a type of synchronous computer-mediated communication involving the immediate (real-time) transmission of messages between two or more parties over the Internet or another computer network. Originally involving simple text message exchanges, modern IM applications and services tend to also feature the exchange of multimedia, emojis, file transfer, VoIP, and video chat capabilities.
An anonymous P2P communication system is a peer-to-peer distributed application in which the nodes, which are used to share resources, or participants are anonymous or pseudonymous. Anonymity of participants is usually achieved by special routing overlay networks that hide the physical location of each node from other participants.
The Invisible Internet Project (I2P) is an anonymous network layer that allows for censorship-resistant, peer-to-peer communication. Anonymous connections are achieved by encrypting the user's traffic, and sending it through a volunteer-run network of roughly 55,000 computers distributed around the world. Given the high number of possible paths the traffic can transit, a third party watching a full connection is unlikely. The software that implements this layer is called an "I2P router", and a computer running I2P is called an "I2P node". I2P is free and open sourced, and is published under multiple licenses.
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a private communication system in which only communicating users can participate. As such, no one else, including the communication system provider, telecom providers, Internet providers or malicious actors, can access the cryptographic keys needed to converse. End-to-end encryption is intended to prevent data being read or secretly modified, other than by the true sender and recipient(s). The messages are encrypted by the sender but the third party does not have a means to decrypt them, and stores them encrypted. The recipients retrieve the encrypted data and decrypt it themselves. Because no third parties can decipher the data being communicated or stored, for example, companies that provide end-to-end encryption are unable to hand over texts of their customers' messages to the authorities.
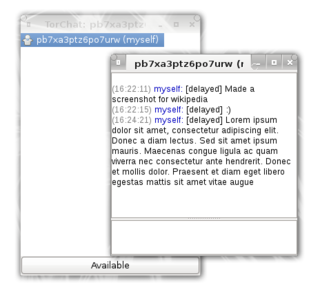
TorChat was a peer-to-peer anonymous instant messenger that used Tor onion services as its underlying network. It provided cryptographically secure text messaging and file transfers. The characteristics of Tor's onion services ensure that all traffic between the clients is encrypted and that it is very difficult to tell who is communicating with whom and where a given client is physically located.

Jami is a SIP-compatible distributed peer-to-peer softphone and SIP-based instant messenger for Linux, Microsoft Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android. Jami was developed and maintained by the Canadian company Savoir-faire Linux, and with the help of a global community of users and contributors, Jami positions itself as a potential free Skype replacement.
Silent Circle is an encrypted communications firm based in Washington DC. Silent Circle provides multi-platform secure communication services for mobile devices and desktops. Launched October 16, 2012, the company operates under a subscription business model. The encryption part of the software used is free software/open source and peer-reviewed. For the remaining parts of Silent Phone and Silent Text, the source code is available on GitHub, but under proprietary software licenses.
The Dark Mail Alliance is an organization dedicated to creating an email protocol and architecture with end-to-end encryption.

Twister is a decentralized and experimental peer-to-peer microblogging program which uses end-to-end encryption to safeguard communications. Based on BitTorrent and Bitcoin-like protocols, it has been likened to a distributed version of Twitter.

Tox is a peer-to-peer instant-messaging and video-calling protocol that offers end-to-end encryption. The stated goal of the project is to provide secure yet easily accessible communication for everyone. A reference implementation of the protocol is published as free and open-source software under the terms of the GNU GPL-3.0-or-later.
TextSecure was an encrypted messaging application for Android that was developed from 2010 to 2015. It was a predecessor to Signal and the first application to use the Signal Protocol, which has since been implemented into WhatsApp and other applications. TextSecure used end-to-end encryption to secure the transmission of text messages, group messages, attachments and media messages to other TextSecure users.

Open Whisper Systems was a software development group that was founded by Moxie Marlinspike in 2013. The group picked up the open source development of TextSecure and RedPhone, and was later responsible for starting the development of the Signal Protocol and the Signal messaging app. In 2018, Signal Messenger was incorporated as an LLC by Moxie Marlinspike and Brian Acton and then rolled under the independent 501c3 non-profit Signal Technology Foundation. Today, the Signal app is developed by Signal Messenger LLC, which is funded by the Signal Technology Foundation.

Threema is a paid cross-platform encrypted instant messaging app developed by Threema GmbH in Switzerland and launched in 2012. The service operates on a decentralized architecture and offers end-to-end encryption. Users can make voice and video calls, send photos, files, and voice notes, share locations, and make groups. Unlike many other popular secure messaging apps, Threema does not require phone numbers or email addresses for registration, only a one-time purchase that can be paid via an app store or anonymously with Bitcoin or cash.

Signal is an open-source, encrypted messaging service for instant messaging, voice calls, and video calls. The instant messaging function includes sending text, voice notes, images, videos, and other files. Communication may be one-to-one between users or may involve group messaging.

Matrix is an open standard and communication protocol for real-time communication. It aims to make real-time communication work seamlessly between different service providers, in the way that standard Simple Mail Transfer Protocol email currently does for store-and-forward email service, by allowing users with accounts at one communications service provider to communicate with users of a different service provider via online chat, voice over IP, and videotelephony. It therefore serves a similar purpose to protocols like XMPP, but is not based on any existing communication protocol.
Tuta, formerly Tutanota, is an end-to-end encrypted email app and a freemium secure email service. The service is advertisement-free; it relies on donations and premium subscriptions. As of June 2023, Tutanota's owners claimed to have over 10 million users of the product. The company announced a transition to 100% renewable electricity in March 2019. This decision coincided with employee participation in Fridays for Future protests. On 1st October 2024, Tuta launched its standalone encrypted calendar app. Tuta Mail has recently integrated post-quantum cryptography features through its new protocol - TutaCrypt replacing standard encryption methods like RSA-2048 and AES-256 for its newly created accounts after March 2024.
Autocrypt is a cryptographic protocol for email clients aiming to simplify key exchange and enabling encryption. Version 1.0 of the Autocrypt specification was released in December 2017 and makes no attempt to protect against MITM attacks. It is implemented on top of OpenPGP replacing its complex key management by fully automated exchange of cryptographic keys between peers.

Conversations is a free software, instant messaging client application software for Android. It is largely based on recognized open standards such as the Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) and Transport Layer Security (TLS).
xx messenger is a cross-platform decentralized encrypted instant messaging service developed by PrivaTegrity Corporation and running on a blockchain called xx network. Messages are delivered over a variety of mix network first described in 2016. Users can send one-to-one and group messages, which can include voice notes and images.