Related Research Articles

Messier 26, also known as NGC 6694, is an open cluster of stars in the southern constellation of Scutum. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764. This 8th magnitude cluster is a challenge to find in ideal skies with typical binoculars, where it can be, with any modern minimum 3-inch (76 mm) aperture device. It is south-southwest of the open cluster Messier 11 and is 14′ across. About 25 stars are visible in a telescope with a 150–200 mm (6–8 in) aperture.

Zeta Geminorum is a bright star with cluster components, distant optical components and a likely spectroscopic partner in the zodiac constellation of Gemini — in its south, on the left 'leg' of the twin Pollux. It is a classical Cepheid variable star, of which over 800 have been found in our galaxy. As such its regular pulsation and luminosity and its relative proximity means the star is a useful calibrator in computing the cosmic distance ladder. Based on parallax measurements, it is approximately 1,200 light-years from the Sun.

X Sagittarii is a variable star and candidate binary star system in the southern constellation of Sagittarius, near the western constellation boundary with Ophiuchus. It has a yellow-white hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.54. The star is located at a distance of approximately 950 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −10 km/s. The star has an absolute magnitude of around −2.85.

Zeta Sculptoris, Latinized from ζ Sculptoris, is a multiple star system in the constellation Sculptor. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of 5.04. The annual parallax shift is 6.49 mas, which yields a distance estimate of about 500 light years from the Sun. It is moving further away with a radial velocity of +8.6 km/s. Zeta Sculptoris is near the Blanco 1 cluster as viewed from Earth, although parallax measurements indicate it to be substantially closer.

Sigma Sculptoris, Latinized from σ Sculptoris, is a binary star in the southern constellation of Sculptor. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +5.54. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 14.04 mas as seen from Earth, it is located about 232 light years from the Sun.
Tau Sculptoris is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Sculptor, about 8° to the east-southeast of Alpha Sculptoris. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of +5.69. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 14.42 mas as seen from Earth, it is located around 230 light years from the Sun.
39 Boötis is a triple star system located around 224 light years away from the Sun in the northern constellation of Boötes. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, yellow-white hued star with a combined apparent magnitude of 5.68. The system is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −31 km/s.

Xi Cancri is a spectroscopic binary star system in the zodiac constellation of Cancer. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +5.15. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is roughly 370 light-years distant from the Sun.
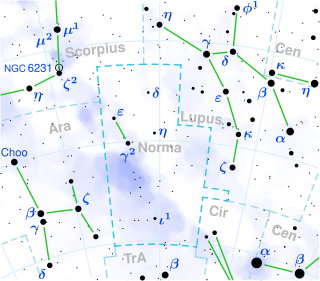
S Normae is a yellow supergiant variable star in the constellation Norma. It is the brightest member of the open cluster NGC 6087.

DV Aquarii is a binary star system in the zodiac constellation of Aquarius, near the border with Capricornus. It has a peak apparent visual magnitude of 5.89, which is bright enough to be visible to the naked eye. The distance can be estimated from its annual parallax shift of 11.2 mas, yielding a separation of 291 light years.

HD 150136 is a multiple star system in the southern constellation of Ara, around 4,300 light years away. It is the brightest member of the faint open cluster NGC 6193, part of the Ara OB1 association.

NGC 6025 is an open cluster of stars in the southern constellation of Triangulum Australe, near the northern constellation border with Norma. It was discovered by Abbe Lacaille in 1751 during his expedition to the Cape of Good Hope. The cluster is in the Caldwell catalogue as entry number 95, and is located at a mean distance of 2,410 ly from the Sun. NGC 6025 can be spotted with the naked eye, but is better viewed with a set of large binoculars. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.1 and spans an angular size of 15′.

S Monocerotis, also known as 15 Monocerotis, is a massive multiple and variable star system located in the constellation Monoceros. It is the brightest star in the Christmas Tree open cluster in the area catalogued as NGC 2264.
Lambda Cygni is a class B5V star in the constellation Cygnus. Its apparent magnitude is 4.54 and it is approximately 770 light years away based on parallax.

HD 21278 is a binary star system in the constellation Perseus, located within the 60±7 million year old Alpha Persei Cluster. It has a blue-white hue and is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.99. The system is located at a distance of approximately 580 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +1.20 km/s.
Zeta Horologii, Latinized from ζ Horologii, is a yellow-white-hued binary star system in the southern constellation of Horologium. It is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.20. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 20.37 mas as seen from Earth, it is located around 160 light-years from the Sun.

Phi1 Orionis is a binary star system in the constellation Orion, positioned less than a degree to the south of Meissa. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.42. The distance to this system, based upon an annual parallax shift of 3.0 mas, is around 1,090 light-years.

U Lacertae is a spectroscopic binary star in the constellation Lacerta.

BU Crucis is a variable star in the open cluster NGC 4755, which is also known as the Kappa Crucis Cluster or Jewel Box Cluster.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Moraux, E.; et al. (August 2007), "The lower mass function of the young open cluster Blanco 1: from 30 MJup to 3 M⊙", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 471 (2): 499–513, arXiv: 0706.2102 , Bibcode:2007A&A...471..499M, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20066308, S2CID 14759280.
- ↑ Blanco, Victor M. (August 1949), "A New Galactic Star Cluster in Sculptor", Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 61 (361): 183, Bibcode:1949PASP...61..183B, doi: 10.1086/126171 , S2CID 121905502.
- ↑ Bagnall, Philip M. (2012), The Star Atlas Companion: What You Need to Know about the Constellations, Springer, p. 409, ISBN 978-1461408307.
- ↑ Stauffer, John R.; et al. (August 1949), "Debris Disks of Members of the Blanco 1 Open Cluster", The Astrophysical Journal, 719 (2): 1859–1871, arXiv: 1007.0239 , Bibcode:2010ApJ...719.1859S, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/719/2/1859, S2CID 30296284.
- ↑ González, J. F.; Levato, H. (November 2009), "Spectroscopic study of the open cluster Blanco 1", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 507 (1): 541–547, Bibcode:2009A&A...507..541G, doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/200912772 .
- ↑ Smith, Gareth D.; Gillen, Edward; Queloz, Didier; Hillenbrand, Lynne A.; Acton, Jack S.; Alves, Douglas R.; Anderson, David R.; Bayliss, Daniel; Briegal, Joshua T.; Burleigh, Matthew R.; Casewell, Sarah L.; Delrez, Laetitia; Dransfield, Georgina; Ducrot, Elsa; Gill, Samuel; Gillon, Michaël; Goad, Michael R.; Günther, Maximilian N.; Henderson, Beth A.; Jenkins, James S.; Jehin, Emmanuël; Moyano, Maximiliano; Murray, Catriona A.; Pedersen, Peter P.; Sebastian, Daniel; Thompson, Samantha; Tilbrook, Rosanna H.; Triaud, Amaury H M J.; Vines, Jose I.; Wheatley, Peter J. (2021). "NGTS clusters survey – III. A low-mass eclipsing binary in the Blanco 1 open cluster spanning the fully convective boundary". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 507 (4): 5991–6011. arXiv: 2109.00836 . doi: 10.1093/mnras/stab2374 .