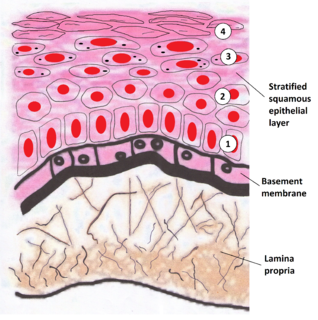
The lamina propria is a thin layer of connective tissue that forms part of the moist linings known as mucous membranes or mucosa, which line various tubes in the body, such as the respiratory tract, the gastrointestinal tract, and the urogenital tract.
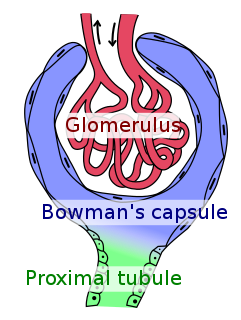
Bowman's capsule is a cup-like sac at the beginning of the tubular component of a nephron in the mammalian kidney that performs the first step in the filtration of blood to form urine. A glomerulus is enclosed in the sac. Fluids from blood in the glomerulus are collected in the Bowman's capsule.
The basal lamina is a layer of extracellular matrix secreted by the epithelial cells, on which the epithelium sits. It is often incorrectly referred to as the basement membrane, though it does constitute a portion of the basement membrane. The basal lamina is visible only with the electron microscope, where it appears as an electron-dense layer that is 20–100 nm thick.

The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and endothelium, and the underlying connective tissue.

Nepenthes izumiae is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Sumatra, where it grows in montane forest at 1700–1900 m above sea level. It appears to be most closely related to N. lingulata and N. singalana.
Mickelia nicotianifolia is a species of fern in the family Dryopteridaceae, subfamily Elaphoglossoideae. It has a widespread distribution in Central America and northern South America.

Bolbitis is a genus of ferns in the family Dryopteridaceae, subfamily Elaphoglossoideae, in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016.

Bolbitis heudelotii, also known as the African water fern, creeping fern, and Congo fern, is native to subtropical and tropical Africa, from Ethiopia west to Senegal; and down to northern South Africa.

Nepenthes peltata is a tropical pitcher plant known only from the upper slopes of Mount Hamiguitan on the island of Mindanao in the Philippines. It is characterised by a peltate tendril attachment and conspicuous indumentum. The species typically produces ovoid pitchers with a prominent basal crest and large nectar glands on the lower surface of the lid.

Oraniopsis is a monotypic genus of flowering plant in the palm family from Queensland, Australia, where the only known species, Oraniopsis appendiculata, grows in mountainous rain forest. Dioecious and extremely slow growing, the name means "similar to Orania" and the Latin epithet translates to "appendaged".

Nephrotoma appendiculata, the spotted crane fly, is a species of crane fly.

Bolbitis heteroclita is an aquatic fern species of Bolbitis, native to the Indochina region of tropical Southeast Asia.

Francoa appendiculata is a species of the Francoaceae family which consists of herbs endemic to Chile.
Salvia appendiculata is a perennial plant that is native to Guangdong province in China, growing in forests, open streamsides, and thickets. S. appendiculata grows on erect stems to a height of 17 to 55 cm. Inflorescences are 4-6 flowered widely spaced verticillasters in racemes or panicles, with an 8 to 10 mm purple or dark red corolla.
Nepenthes appendiculata is a tropical pitcher plant known only from the Hose Mountains of central Sarawak, Borneo, where it grows at elevations of 1450–1700 m above sea level. The species is characterised by an enlarged glandular appendage on the lower lid surface, for which it is named.

The 'Langra' mango, also known as Banarasi Langra, is a mango cultivar primarily grown in Bangladesh,Varanasi, or Banaras, Northern India. In some part of northern India and in Bihar 'Langra' mango is also known as 'Malda' Mango, referring to the town of Malda in West Bengal.

Dahalokely is an extinct genus of carnivorous abelisauroid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Turonian) of Madagascar.

The baju lamina is a mail and plate armor from the Nusantara archipelago.

Salix appendiculata is a plant from the willow genus (Salix). They can be found in France, Italy, Central and Eastern Europe, and on the Balkan Peninsula.














