
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class, which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose, and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease.
An antipyretic is a substance that reduces fever. Antipyretics cause the hypothalamus to override a prostaglandin-induced increase in temperature. The body then works to lower the temperature, which results in a reduction in fever.

Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used for treating pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus arteriosus in a premature baby. It can be used by mouth or intravenously. It typically begins working within an hour.

Naproxen, sold under the brand name Aleve among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain, menstrual cramps, inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout and fever. It is taken orally. It is available in immediate and delayed release formulations. Onset of effects is within an hour and lasts for up to twelve hours.
Anti-inflammatory is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs remedy pain by reducing inflammation as opposed to opioids, which affect the central nervous system to block pain signaling to the brain.
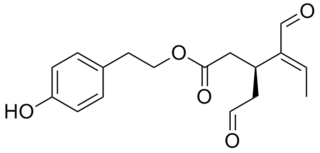
Oleocanthal is a phenylethanoid, or a type of natural phenolic compound found in extra-virgin olive oil. It appears to be responsible for the burning sensation that occurs in the back of the throat when consuming such oil. Oleocanthal is a tyrosol ester and its chemical structure is related to oleuropein, also found in olive oil.

Flurbiprofen is a member of the phenylalkanoic acid derivative family of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It is primarily indicated as a pre-operative anti-miotic as well as orally for arthritis or dental pain. Side effects are analogous to those of ibuprofen.

Curcuma amada, or mango ginger is a plant of the ginger family Zingiberaceae and is closely related to turmeric. The rhizomes are very similar to common ginger but lack its pungency, and instead have a raw mango flavour. They are used in making pickles in south India and chutneys in north India. It is served as chutney in community feasts in Nepal's southern plains. Mango ginger and elephant foot yam pickle is popular in Nepal's southern plains. The taxonomy of the species is a subject of some confusion as some authorities have considered the name C. mangga as identical while others describe it as a distinct species with C. mangga being found in southern India while C. amada is of east Indian origin. Mango-ginger is a popular spice and vegetable due to its rich flavor, which is described as sweet with subtle earthy floral and pepper overtones and similar to that of raw mango. It is a delicious addition to salads and stir fries. It is used in South Asian and Southeast Asian as well as Far East Asian cuisines.

Benzydamine, available as the hydrochloride salt, is a locally acting nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with local anaesthetic and analgesic properties for pain relief and anti-inflammatory treatment of inflammatory conditions of the mouth and throat. It falls under class of chemicals known as indazole.

Diproqualone is a quinazolinone class GABAergic and is an analogue of methaqualone developed in the late 1950s by a team at Nogentaise de Produits Chimique. It was marketed primarily in France and some other European countries. It has sedative, anxiolytic, antihistamine and analgesic properties, resulting from its agonist activity at the β subtype of the GABAa receptor, antagonist activity at all histamine receptors, inhibition of the cyclooxygenase-1 enzyme, and possibly its agonist activity at both the sigma-1 receptor and sigma-2 receptor. Diproqualone is used primarily for the treatment of inflammatory pain associated with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, and more rarely for treating insomnia, anxiety and neuralgia.
Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors are compounds that slow or stop the action of the arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase enzyme, which is responsible for the production of inflammatory leukotrienes. The overproduction of leukotrienes is a major cause of inflammation in asthma, allergic rhinitis, and osteoarthritis.
Nadifloxacin is a topical fluoroquinolone antibiotic for the treatment of acne vulgaris. It is also used to treat bacterial skin infections.

Selective glucocorticoid receptor modulators (SEGRMs) and selective glucocorticoid receptor agonists (SEGRAs) formerly known as dissociated glucocorticoid receptor agonists (DIGRAs) are a class of experimental drugs designed to share many of the desirable anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, or anticancer properties of classical glucocorticoid drugs but with fewer side effects such as skin atrophy. Although preclinical evidence on SEGRAMs’ anti-inflammatory effects are culminating, currently, the efficacy of these SEGRAMs on cancer are largely unknown.
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) is an endogenous fatty acid amide, and lipid modulator PEA has been studied in in vitro and in vivo systems using exogenously added or dosed compound; there is evidence that it binds to a nuclear receptor, through which it exerts a variety of biological effects, some related to chronic inflammation and pain.
Givinostat (INN) or gavinostat is a histone deacetylase inhibitor with potential anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic, and antineoplastic activities. It is a hydroxamate used in the form of its hydrochloride.
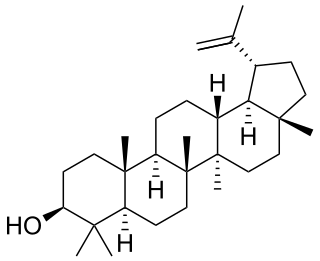
Lupeol is a pharmacologically active pentacyclic triterpenoid. It has several potential medicinal properties, like anticancer and anti-inflammatory activity.
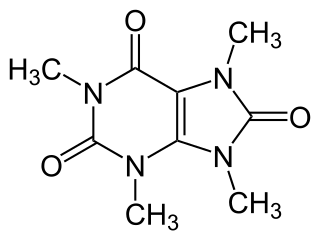
Theacrine, also known as 1,3,7,9-tetramethyluric acid, is a purine alkaloid found in Cupuaçu and in a Chinese tea known as kucha. It shows anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects and appears to affect adenosine signalling in a manner similar to caffeine. In kucha leaves, theacrine is synthesized from caffeine in what is thought to be a three-step pathway.
A drug class is a set of medications and other compounds that have a similar chemical structures, the same mechanism of action, a related mode of action, and/or are used to treat the same disease.

Epiestriol (INN), or epioestriol (BAN), also known as 16β-epiestriol or simply 16-epiestriol as well as 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol, is a minor and weak endogenous estrogen, and the 16β-epimer of estriol. Epiestriol is used clinically in the treatment of acne. In addition to its estrogenic actions, epiestriol has been found to possess significant anti-inflammatory properties without glycogenic activity or immunosuppressive effects, an interesting finding that is in contrast to conventional anti-inflammatory steroids like hydrocortisone.

Glucametacin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for the treatment of mild or moderate pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and other rheumatological disorders. It has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.














