
The Angara is a major river in Siberia, which traces a course through Russia's Irkutsk Oblast and Krasnoyarsk Krai. It drains out of Lake Baikal and is the headwater tributary of the Yenisey. It is 1,849 kilometres (1,149 mi) long, and has a drainage basin of 1,039,000 square kilometres (401,000 sq mi). It was formerly known as the Lower or Nizhnyaya Angara. Below its junction with the Ilim, it was formerly known as the Upper Tunguska and, with the names reversed, as the Lower Tunguska.

The Yenisey is the fifth-longest river system in the world, and the largest to drain into the Arctic Ocean.

The Lena is a river in the Russian Far East and is the easternmost river of the three, great rivers of Siberia, including the River Ob and the River Yenisey, which flow into the Arctic Ocean. The Lena river is 4,294 km (2,668 mi) long and has a capacious drainage basin of 2,490,000 km2 (960,000 sq mi); thus the Lena is the eleventh-longest river in the world and the longest river entirely within Russia. Geographically, permafrost is the type of soil that underlies most of the Lena river's catchment, twenty per cent (20%) of which is continuous.

The Nizhnyaya Tunguska is a river in Siberia, Russia, that flows through the Irkutsk Oblast and the Krasnoyarsk Krai. The river is a right tributary of the Yenisey joining it at Turukhansk. The ice-free period on the Nizhnyaya Tunguska starts in mid-June and ends in the first half of October. The river forms the western limit of the Lena Plateau.

The Turukhan is a river in northern Krasnoyarsk Krai in Russia. It is a southeast-flowing left tributary of the Yenisey. The river is 639 kilometres (397 mi) long. The area of its basin is 35,800 square kilometres (13,800 sq mi). The Turukhan freezes up in October and stays under the ice until late May or the first half of June. Its main tributaries are the Usomchik, Bolshaya Bludnaya, Verkhnyaya Baikha and Nizhnyaya Baikha from the right and Makovskaya from the left. Its mouth is 20 kilometres (12 mi) downstream from Turukhansk, where the Lower Tunguska joins the Yenisei. The river is navigable for about 288 kilometres (179 mi) from its mouth to the settlement of Yanov Stan. It was part of the canoe route from the Gulf of Ob – Taz – Turukhan – Yenisey – Nizhnyaya Tunguska – Yakutsk. The uncompleted Salekhard–Igarka Railway from the Ob to the Yenisey was planned to cross the Turukhan at Yanov Stan.

The Belaya in its upper course Yurumkuveyem is a south-flowing tributary of the Anadyr in the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug administrative region of Russia.

The Yenisey Gulf is a large and long estuary through which the lower Yenisey flows into the Kara Sea.

The Great Yenisey is a river in the Republic of Tuva, the right source of the Yenisey, at its confluence with the Little Yenisey.

The Konda is a river in the Khanty–Mansia region of Russia. The town of Uray and the Shaimskoye oil field are along the Konda.
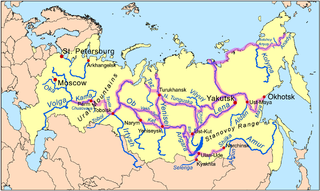
Siberian River Routes were the main ways of communication in Russian Siberia before the 1730s, when roads began to be built. The rivers were also of primary importance in the process of Russian conquest and exploration of vast Siberian territories eastwards. Since the three great Siberian rivers, the Ob, the Yenisey, and the Lena all flow into the Arctic Ocean, the aim was to find parts or branches of these rivers that flow approximately east-west and find short portages between them. Since Siberia is relatively flat, portages were usually short. Despite resistance from the Siberian tribes, Russian Cossacks were able to expand from the Urals to the Pacific in only 57 years (1582-1639). These river routes were crucial in the first years of the Siberian fur trade as the furs were easier to transport over water than land. The rivers connected the major fur gathering centers and provided for relatively quick transport between them.

The Sym is a left, western tributary of the Yenisey in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is 694 kilometres (431 mi) long, and has a drainage basin of 31,600 square kilometres (12,200 sq mi). It is navigable about 265 km (165 mi) upstream from its mouth.

The Tsipa is the largest tributary of the Vitim in Buryatia, Russia. It is 692 kilometres (430 mi) long, and has a drainage basin of 42,200 square kilometres (16,300 sq mi). Maksim Perfilyev was the first Russian to reach the Tsipa in 1640.
The Tanama is a river in northern Siberia, Russia. It is one of the main tributaries of the Yenisey.

The Yenisey Range is a range of mountains in Siberia. Administratively the range is part of the Krasnoyarsk Krai of the Russian Federation. The nearest town is Severo-Yeniseysk.

The Bakhta is a river in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is a right hand tributary of the Yenisey.

The Yeloguy is a river in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is one of the main tributaries of the Yenisey. Its basin marks the eastern limit of the Siberian Uvaly.

The Amalat is a river in Buryatia, Russia. It is the largest tributary of the Tsipa, of the Vitim basin. The river is 374 kilometres (232 mi) long, and has a drainage basin of 16,600 square kilometres (6,400 sq mi). The villages of Baysa, Mongoy and Rossoshino are the only inhabited places close to the banks of the river. There are jade deposits in the Amalat river basin, including the valuable white jade variety.

The Bolshoy Patom, "Big Patom", is a river in Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. It is the 11th longest tributary of the Lena with a length of 570 kilometres (350 mi) and a drainage basin area of 28,400 square kilometres (11,000 sq mi).

The Pilyuda is a river in Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. It is a tributary of the Lena with a length of 105 kilometres (65 mi) and a drainage basin area of 1,760 square kilometres (680 sq mi).

The Synya is a river in Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Russia. The river is 217 kilometres (135 mi) long —304 km (189 mi) from the source of the Mokraya Synya at its head— and has a catchment area of 13,500 square kilometres (5,200 sq mi).



















