
The Bristol Scout was a single-seat rotary-engined biplane originally designed as a racing aircraft. Like similar fast, light aircraft of the period it was used by the RNAS and the RFC as a "scout", or fast reconnaissance type. It was one of the first single-seaters to be used as a fighter aircraft, although it was not possible to fit it with an effective forward-firing armament until the first British-designed gun synchronizers became available later in 1916, by which time the Scout was obsolescent. Single-seat fighters continued to be called "scouts" in British usage into the early 1920s.
Fabre Hydravion is the name used in English-language sources for an originally unnamed experimental floatplane designed by Henri Fabre. The aircraft is notable as the first to take off from water under its own power.

The Voisin Canard was an aircraft developed by Voisin brothers during 1910 and first flown early in 1911. It was named the Canard because of the resemblance of its forward fuselage to that of a duck's long neck while in flight. It was originally flown as a landplane: with the addition of floats it became one of the first seaplanes used by the French Navy.

The Bristol T.B.8, or Bristol-Coanda T.B.8 was an early British biplane built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company and designed by the Romanian Henri Coandă. Fifty four Bristol T.B.8s were built, being mainly used as a trainer. A small number of Bristol T.B.8s were briefly used as bombers at the start of the World War I by the Royal Naval Air Service.

The Morane-Borel monoplane was an early French single-engine, single-seat aircraft. It was flown in several European air races.

The Bristol Gordon England biplanes were a series of early British military biplane aircraft designed by Eric Gordon England for the Bristol Aeroplane Company that first flew in 1912. Designed for easy ground transport, the aircraft could be quickly disassembled.

The Morane-Saulnier G was a two-seat sport and racing monoplane produced in France before the First World War. It was a development of the racing monoplanes designed by Léon Morane and Raymond Saulnier after leaving Borel and, like its predecessors, was a wire-braced, shoulder-wing monoplane. Construction was of fabric-covered wood throughout, except for the undercarriage struts which were of steel tube.

The Blackburn Type L was a single-engine, two-seat biplane built for the 1914 Daily Mail Circuit of Britain seaplane race of 1914.

The Blackburn Type I was a single-engine civil two-seat monoplane built in the United Kingdom in 1913 by the Blackburn Aeroplane Company. Three were produced and used for flying demonstrations and training including seaplane pilotage.
The Hydro no.120 was a Romanian-designed two-seat, single-engine biplane configured as a single-float seaplane. Built by Bristol in 1913, it was lost on its first flight.

The Short S.41 was a British single-engined biplane built for the Royal Navy in 1912. Capable of being operated either on wheels or floats, it was successful enough for a further two similar aircraft to be built, with the type remaining in use until the early years of the First World War.
The Latécoère 550 was a four-engined French seaplane, designed in the early 1930s as a bomber/torpedo bomber. Though initial handling problems were partly resolved, the aircraft was deemed too slow and did not go into production.

The Dyott monoplane was a single-engined, single-seat mid-wing monoplane designed by George Miller Dyott for his own use as a sports and touring aircraft. It proved successful, making a six-month tour of the United States soon after its first flight in 1913.

The ASL Viking was a single-engined two seater biplane aircraft designed and built by Horatio Barber's Aeronautical Syndicate Ltd. at Hendon. It was first flown in January 1912.

The Short S.36 was a British two-seat tractor biplane, built by Short Brothers for Francis McClean in 1911. It was later developed into the Short S.41 and Short S.45, which were the first of a long series of similar aircraft built for the RNAS and RFC.

The Gabardini monoplane was a successful early monoplane constructed in Italy which made several notable flights, often carrying passengers, just before World War I. During the war, a number of lower-powered Gabardini monoplanes served as a training aircraft for the military.

The Ponnier D.III was a French monoplane racing aircraft, designed to compete in the 1913 Gordon Bennett Trophy race. It finished a close second.
The Caudron Type H was a collective name for three different Caudron designs of 1912-3. One of these was an amphibious three seat biplane built for the French military. Two were completed, one appearing at the Paris Aero Salon in November 1912.

The Caudron Type L was a two-seat French pusher configuration amphibious biplane, flown around 1913 and intended for naval use.
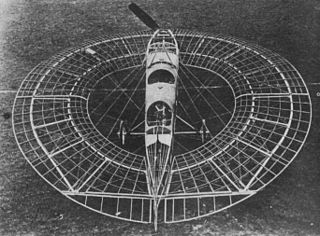
During the pioneer years before the First World War, Cedric Lee and G. Tilghman Richards in the UK built and flew a series of aircraft having a novel flat ring-shaped or annular wing. They built both biplane and monoplane types, and in 1913 their first monoplane proved to be an early example of a statically stable aircraft.
















