
Rickettsia is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci, bacilli, or threads. The genus was named after Howard Taylor Ricketts in honor of his pioneering work on tick-borne spotted fever.

Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by Borrelia bacteria, which are spread by ticks in the genus Ixodes. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migrans (EM), which appears at the site of the tick bite about a week afterwards. The rash is typically neither itchy nor painful. Approximately 70–80% of infected people develop a rash. Early diagnosis can be difficult. Other early symptoms may include fever, headaches and tiredness. If untreated, symptoms may include loss of the ability to move one or both sides of the face, joint pains, severe headaches with neck stiffness or heart palpitations. Months to years later, repeated episodes of joint pain and swelling may occur. Occasionally, shooting pains or tingling in the arms and legs may develop. Despite appropriate treatment, about 10 to 20% of those affected develop joint pains, memory problems, and tiredness for at least six months.

Borrelia burgdorferi is a bacterial species of the spirochete class in the genus Borrelia, and is one of the causative agents of Lyme disease in humans. Along with a few similar genospecies, some of which also cause Lyme disease, it makes up the species complex of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato. The complex currently comprises 20 accepted and 3 proposed genospecies. B. burgdorferi sensu stricto exists in North America and Eurasia and until 2016 was the only known cause of Lyme disease in North America. Borrelia species are Gram-negative.

The white-footed mouse is a rodent native to North America from Ontario, Quebec, Labrador, and the Maritime Provinces to the southwestern United States and Mexico. In the Maritimes, its only location is a disjunct population in southern Nova Scotia. It is also known as the woodmouse, particularly in Texas.
"Candidatus Midichloria" is a candidatus genus of Gram-negative, non-endospore-forming bacteria, with a bacillus shape around 0.45 µm in diameter and 1.2 µm in length. First described in 2004 with the temporary name IricES1, "Candidatus Midichloria" species are symbionts of several species of hard ticks. They live in the cells of the ovary of the females of this tick species. These bacteria have been observed in the mitochondria of the host cells, a trait that has never been described in any other symbiont of animals.
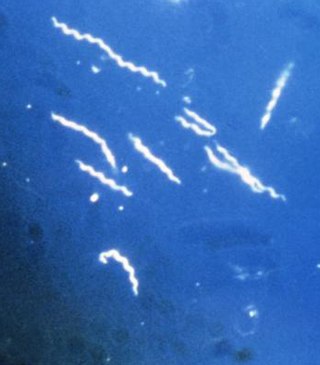
Lyme disease, or borreliosis, is caused by spirochetal bacteria from the genus Borrelia, which has 52 known species. Three main species are the main causative agents of the disease in humans, while a number of others have been implicated as possibly pathogenic. Borrelia species in the species complex known to cause Lyme disease are collectively called Borrelia burgdorferisensu lato (s.l.) not to be confused with the single species in that complex Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto which is responsible for nearly all cases of Lyme disease in North America.

Ixodes scapularis is commonly known as the deer tick or black-legged tick, and in some parts of the US as the bear tick. It was also named Ixodes dammini until it was shown to be the same species in 1993. It is a hard-bodied tick found in the eastern and northern Midwest of the United States as well as in southeastern Canada. It is a vector for several diseases of animals, including humans and is known as the deer tick owing to its habit of parasitizing the white-tailed deer. It is also known to parasitize mice, lizards, migratory birds, etc. especially while the tick is in the larval or nymphal stage.

Virulence-related outer membrane proteins, or outer surface proteins (Osp) in some contexts, are expressed in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria and are essential to bacterial survival within macrophages and for eukaryotic cell invasion.
Borrelia miyamotoi is a bacterium of the spirochete phylum in the genus Borrelia. A zoonotic organism, B. miyamotoi can infect humans through the bite of several species of hard-shell Ixodes ticks, the same kind of ticks that spread B. burgdorferi, the causative bacterium of Lyme disease. Ixodes ticks are also the primary vector in the spread of babesiosis and anaplasmosis.
Borrelia spielmanii is a spirochete bacterium; it routinely infects Ixodes ricinus, and subsequently humans, causing Lyme disease.
Borrelia japonica is a spirochete bacterium first isolated from Japanese mammals.
Borrelia lusitaniae is a bacterium of the spirochete class of the genus Borrelia, which has a diderm (double-membrane) envelope. It is a part of the Borrelia burgdorferisensu lato genospecies and is a Gram-negative bacterium. B. lusitaniae is tick-borne; he type strain is PotiB2. It can be pathogenic, being involved in cases of Lyme borreliosis. A species of tick, Ixodes ricinus, is the host of B. lusitaniae. It is thought to have originated from Portugal and has since spread to parts of Europe and North Africa. Lizards of the family Lacertidae are now believed to be important reservoir hosts of this bacterium.
Borrelia andersonii is a spirochete bacterium. It can be pathogenic, being involved in cases of Lyme borreliosis.
Borrelia turdi, formerly known as Borrelia turdae, is a spirochete bacterium first isolated from specimens of Ixodes tanuki. Its name refers to its reservoir, Turdus merula.
Rickettsia heilongjiangensis is a species of gram negative Alphaproteobacteria, within the spotted fever group, being carried by ticks. It is pathogenic.
Borrelia sinica is a spirochete bacterium. Its cells contain only four periplasmic flagella inserted at each end of the spirochaetes, differing from other Borrelia species. It is associated with Lyme disease. CMN3T is the type strain of this species.
Rickettsia asiatica is a tick-borne pathogenic species borne by Ixodes ovatus. The type strain of Rickettsia asiatica sp. nov. is IO-1T.
Borrelia coriaceae is a species of spirochete bacteria and member of the genus Borrelia. Strains of this species have been isolated from the soft tick Ornithodoros coriaceus and from mule deer.

Amblyomma testudinarium is a hard-bodied tick of the genus Amblyomma. It is found in Indonesia, India, Japan, Thailand, Sri Lanka and Vietnam. Adults parasitize various larger mammals such as buffalo and cattle, whereas nymphs and larvae use mostly larger and medium mammals.
Borrelia mayonii is a Gram-negative, host-associated spirochete that is capable of causing Lyme disease. This organism can infect various vertebrate hosts such as humans via the bite of a black legged tick.






