
The Hexanchiformes are a primitive order of sharks, that numbering just seven extant species in two families. Fossil sharks that were apparently very similar to modern sevengill species are known from Jurassic specimens.

Marine reptiles are reptiles which have become secondarily adapted for an aquatic or semiaquatic life in a marine environment.

Cow sharks are a shark family, the Hexanchidae, characterized by an additional pair or pairs of gill slits. Its 37 species are placed within the 10 genera: Gladioserratus, Heptranchias, Hexanchus, Notidanodon, Notorynchus, Pachyhexanchus, Paraheptranchias, Pseudonotidanus, Welcommia, and Weltonia.

Mesosaurs were a group of small aquatic reptiles that lived during the early Permian period (Cisuralian), roughly 299 to 270 million years ago. Mesosaurs were the first known aquatic reptiles, having apparently returned to an aquatic lifestyle from more terrestrial ancestors. It is uncertain which and how many terrestrial traits these ancestors displayed; recent research cannot establish with confidence if the first amniotes were fully terrestrial, or only amphibious. Most authors consider mesosaurs to have been aquatic, although adult animals may have been amphibious, rather than completely aquatic, as indicated by their moderate skeletal adaptations to a semiaquatic lifestyle. Similarly, their affinities are uncertain; they may have been among the most basal sauropsids or among the most basal parareptiles.

Friedrich von Huene, born Friedrich Richard von Hoinigen, was a German paleontologist who renamed more dinosaurs in the early 20th century than anyone else in Europe. He also made key contributions about various Permo-Carboniferous limbed vertebrates.

Heptranchias is a genus of sharks in the family Hexanchidae.

Mesosaurus is an extinct genus of reptile from the Early Permian of southern Africa and South America. Along with it, the genera Brazilosaurus and Stereosternum, it is a member of the family Mesosauridae and the order Mesosauria. Mesosaurus was long thought to have been one of the first marine reptiles, although new data suggests that at least those of Uruguay inhabited a hypersaline water body, rather than a typical marine environment. In any case, it had many adaptations to a fully aquatic lifestyle. It is usually considered to have been anapsid, although Friedrich von Huene considered it to be a synapsid. Recent study of Mesosauridae phylogeny places the group as either the basal most clade within Parareptilia or the basal most clade within Sauropsida despite the skull of Mesosaurus possessing the "Synapsid condition" of one temporal fenestra.

Simaetha is a genus of Australasian jumping spiders that was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1881. They resemble members of Simaethula and Stertinius.

Vertiginidae, common name the whorl snails, is a family of minute, air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs or micromollusks in the superfamily Pupilloidea.

Stereosternum tumidum is an extinct genus of mesosaur marine reptile from the Early Permian of Brazil and also the Great Karoo Basin of South Africa. The taxon mesosaur is a monophyletic group containing Brazilosaurus sanpauloensis and Mesosaurus tenuidens.

Ichthyodectes is an extinct genus of ichthyodectid fish which lived during the Late Cretaceous. Fossils of the species included have been found from Canada to Texas.
Cerdodontenuidens is an extinct genus of gorgonopsian therapsids. However, some consider this genus to be a nomen dubium. The holotype skull is of a crushed skull of a small therocephalian.

Goniopora, often called flowerpot coral, is a genus of colonial stony coral found in lagoons and turbid water conditions. Goniopora have numerous daisy-like polyps that extend outward from the base, each tipped with 24 stinging tentacles which surrounds a mouth.
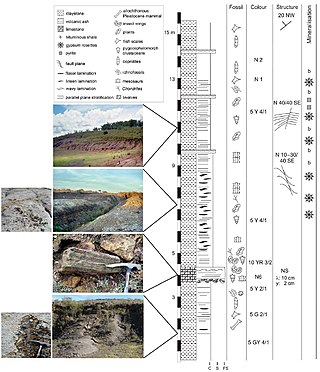
The Mangrullo Formation is an Early Permian (Artinskian) fossiliferous geological formation in northeastern Uruguay. Some authors alternatively group it together with the Paso Aguiar Formation and the Frayle Muerto Formation as the three subdivisions of the Melo Formation, in which case it is referred to as the Mangrullo Member. Like the correlated formations of Irati and Whitehill, it is known for its abundant mesosaur fossils. It also contains the oldest known Konservat-Lagerstätte in South America, as well as the oldest known fossils of amniote embryos.
Zimirina is a genus of long-spinneret ground spiders that was first described by R. de Dalmas in 1919. It was transferred to the ground spiders in 2018, but was returned to Prodidominae in 2022.
Cliona orientalis is a species of demosponge in the family Clionaidae. It occurs in the Indo-Pacific region and is a bioeroding species, with various specialisations for living on and inside calcareous substrates such as massive corals and molluscs.
Goniopora tenuidens is a species of colonial stony coral in the family Poritidae. It occurs in shallow water in the tropical Indo-Pacific region. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".

Carcharoides is an extinct genus of mackerel shark which lived during the Oligocene and Miocene epochs. It is a widespread genus, known from specimens in North and South America, Europe, Africa, and Australia. It is most common in the European portion of its range, being comparatively uncommon in other places. It is only known from isolated teeth, which are relatively delicate.
Bothriopupa is a genus of gastropods belonging to the family Vertiginidae.













