
Anthozoa is a class of marine invertebrates which includes the sea anemones, stony corals and soft corals. Adult anthozoans are almost all attached to the seabed, while their larvae can disperse as part of the plankton. The basic unit of the adult is the polyp; this consists of a cylindrical column topped by a disc with a central mouth surrounded by tentacles. Sea anemones are mostly solitary, but the majority of corals are colonial, being formed by the budding of new polyps from an original, founding individual. Colonies are strengthened by calcium carbonate and other materials and take various massive, plate-like, bushy or leafy forms.

The Beryciformes are a poorly-understood order of carnivorous ray-finned fishes consisting of 7 families, 30 genera, and 161 species. They feed on small fish and invertebrates. Beyond this, little is known about the biology of most member species because of their nocturnal habits and deepwater habitats. All beryciform species are marine and most live in tropical to temperate, deepwater environments. Most live on the continental shelf and continental slope, with some species being found as deep as 2,000 m (6,600 ft). Some species move closer to the surface at night, while others live entirely in shallow water and are nocturnal, hiding in rock crevices and caves during the day. Several species are mesopelagic and bathypelagic. Beryciformes' bodies are deep and mildly compressed, typically with large eyes that help them see in darker waters. Colors range from red to yellow and brown to black, and sizes range from 8–61 cm (3.1–24.0 in). Member genera include the alfonsinos, squirrelfishes, flashlight fishes, fangtooth fishes, spinyfins, pineconefishes, redfishes, roughies, and slimeheads. A number of member species are caught commercially, including the alfonsino, the splendid alfonsino, and the orange roughy, the latter being much more economically important. Some species have bioluminescent bacteria contained in pockets of skin or in light organs near the eyes, including the anomalopids and monocentrids.

Antipatharians, also known as black corals or thorn corals, are an order of soft deep-water corals. These corals can be recognized by their jet-black or dark brown chitin skeletons, which are surrounded by their colored polyps. Antipatharians are a cosmopolitan order, existing in nearly every oceanic location and depth, with the sole exception of brackish waters. However, they are most frequently found on continental slopes under 50 m (164 ft) deep. A black coral reproduces both sexually and asexually throughout its lifetime. Many black corals provide housing, shelter, food, and protection for other animals.

Zoanthids are an order of cnidarians commonly found in coral reefs, the deep sea and many other marine environments around the world. These animals come in a variety of different colonizing formations and in numerous different colors. They can be found as individual polyps, attached by a fleshy stolon or a mat that can be created from small pieces of sediment, sand and rock. The term "zoanthid" refers to all animals within this order Zoantharia, and should not be confused with "Zoanthus", which is one genus within Zoantharia.

Hexacorallia is a class of Anthozoa comprising approximately 4,300 species of aquatic organisms formed of polyps, generally with 6-fold symmetry. It includes all of the stony corals, most of which are colonial and reef-forming, as well as all sea anemones, and zoanthids, arranged within five extant orders. The hexacorallia are distinguished from another class of Anthozoa, Octocorallia, in having six or fewer axes of symmetry in their body structure; the tentacles are simple and unbranched and normally number more than eight. These organisms are formed of individual soft polyps which in some species live in colonies and can secrete a calcite skeleton. As with all Cnidarians, these organisms have a complex life cycle including a motile planktonic phase and a later characteristic sessile phase. Hexacorallia also include the significant extinct order of rugose corals.

Umimayanthus parasiticus, commonly known as the sponge zoanthid, is a species of coral in the order Zoantharia which grows symbiotically on several species of sponge. It is found in shallow waters in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico.

Hawaiian gold coral is a rare, extremely long-lived deep-sea coral found on seamounts near Hawaii. It is the only member of the monotypic genus Kulamanamana. One colony has been dated as 2,740 years old, while others are considered 5,000 years old. Although it has been harvested commercially for use in jewellery for a long time, it was not formally described by taxonomists until 2012 when it was found to be related to both the genus Savalia and the octocoral-associated zoanthid, Corallizoanthus tsukaharai.

Palythoa is a genus of anthozoans in the order Zoantharia.

Isozoanthus sulcatus is a species of zoanthid in the family Parazoanthidae.
Palythoa toxica, also referred to by its Hawaiian common name, limu-make-o-Hana, is a species of zoanthid native to Hawaii. It is notable as the species in which palytoxin was discovered and from which it was first isolated.
Zoanthus gigantus is a zoanthid first described from southern Japan.

Zoanthus kuroshio is a species of zoanthid first described from southern Japan.
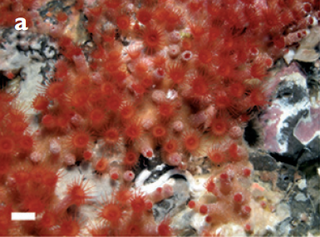
Terrazoanthus onoi is a species of uncertain validity of macrocnemic zoanthid first found in the Galapagos. It is potentially a junior synonym of Terrazoanthus patagonichus. It can be distinguished by its bright red oral disk colour, having about 32–40 tentacles, and having only basitrichs and mastigophores present in its pharynx.

Terrazoanthus sinnigeri is a species of uncertain validity of macrocnemic zoanthid first found in the Galapagos. It is potentially a junior synonym of Terrazoanthus patagonichus. It can be distinguished by commonly occurring on rubble and rocks on sandy bottoms, having about 30–36 tentacles, and numerous nematocysts in its pharynx.

Antipathozoanthus hickmani is a species of macrocnemic zoanthid first found in the Galapagos. It can be distinguished by its exclusive association with Antipathes galapagensis, and having about 40 tentacles.

Parazoanthus darwini is a species of macrocnemic zoanthid first found in the Galapagos. It can be distinguished by its association with sponges, by having about 24–30 tentacles and polyps embedded in a well-developed coenenchyme.

Oxypora glabra is a species of large polyp stony coral in the family Lobophylliidae. It is a colonial coral with thin encrusting laminae. It is native to the central Indo-Pacific.

Ricordea yuma is a species of coral in the family Ricordeidae, order Corallimorpharia; This order of corals do not produce the distinctive calcification of the closely related Scleractinian, or reef building corals. Ricordea yuma are found on the sea floor in relatively shallow, tropical or subtropical ocean environments. Distinctive features include a large mouth disk that takes up most of the organism, and brightly colored tentacles. Ricordea yuma can reproduce both sexually, and asexually by budding a new coral with replicated elements from the mother coral. This may be one mechanism of how they are able to spread and overtake areas rapidly; They have been observed being competitively successful at monopolizing areas by excluding reef-building coral species, after a disturbance in the substrate.

Zoanthus sansibaricus is a species of zoanthid generally found in the Indo-pacific but also off the western coast of South America. The range of habitation has been noted in intertidal zones along with areas below 7 m, but shows phenotypical and morphological differences based on depth and shading. Shaded individuals contain larger polyps compared to unshaded. It can be divided into three reproductive categories, male, female and asexual. Spawning has been observed within the middle of July, using lunar phases as an indicator. Various subclades are theorized to appear based on the time of year.
Palythoa heliodiscus, the sunray zoanthid, is a species of cnidarian in the family Sphenopidae.

















