Calcium silicate is the chemical compound Ca2SiO4, also known as calcium orthosilicate and is sometimes formulated as 2CaO·SiO2. It is also referred to by the shortened trade name Cal-Sil or Calsil. It occurs naturally as the mineral larnite.

Wollastonite is a calcium inosilicate mineral (CaSiO3) that may contain small amounts of iron, magnesium, and manganese substituting for calcium. It is usually white. It forms when impure limestone or dolomite is subjected to high temperature and pressure, which sometimes occurs in the presence of silica-bearing fluids as in skarns or in contact with metamorphic rocks. Associated minerals include garnets, vesuvianite, diopside, tremolite, epidote, plagioclase feldspar, pyroxene and calcite. It is named after the English chemist and mineralogist William Hyde Wollaston (1766–1828).

Dickite is a phyllosilicate clay mineral named after the metallurgical chemist Allan Brugh Dick, who first described it. It is chemically composed of 20.90% aluminium, 21.76% silicon, 1.56% hydrogen and 55.78% oxygen. It has the same composition as kaolinite, nacrite, and halloysite, but with a different crystal structure (polymorph). Dickite sometimes contains impurities such as titanium, iron, magnesium, calcium, sodium and potassium.

Afwillite is a calcium hydroxide nesosilicate mineral with formula Ca3(SiO3OH)2·2H2O. It occurs as glassy, colorless to white prismatic monoclinic crystals. Its Mohs scale hardness is between 3 and 4. It occurs as an alteration mineral in contact metamorphism of limestone. It occurs in association with apophyllite, natrolite, thaumasite, merwinite, spurrite, gehlenite, ettringite, portlandite, hillebrandite, foshagite, brucite and calcite.

Xonotlite, or eakleite, is a mineral of general formula Ca6Si6O17(OH)2 named by the German mineralogist Karl Friedrich August Rammelsberg in 1866. The name originates from its discovery locality, Tetela de Xonotla, Puebla, Mexico. Although it was discovered in 1866, it was first described in 1959. It is approved by the IMA, but it is a grandfathered species, meaning the name supposedly represents a valid species til this day.

Bentorite is a mineral with the chemical formula Ca6(Cr,Al)2(SO4)3(OH)12·26H2O. It is colored violet to light violet. Its crystals are hexagonal to dihexagonal dipyramidal. It is transparent and has vitreous luster. It has perfect cleavage. It is not radioactive. Bentorite is rated 2 on the Mohs scale.

Ettringite is a hydrous calcium aluminium sulfate mineral with formula: Ca6Al2(SO4)3(OH)12·26H2O. It is a colorless to yellow mineral crystallizing in the trigonal system. The prismatic crystals are typically colorless, turning white on partial dehydration. It is part of the ettringite-group which includes other sulfates such as thaumasite and bentorite.

Ye'elimite is the naturally occurring form of anhydrous calcium sulfoaluminate, Ca
4(AlO
2)
6SO
4. It gets its name from Har Ye'elim in Israel in the Hatrurim Basin west of the Dead Sea where it was first found in nature by Shulamit Gross, an Israeli mineralogist and geologist who studied the Hatrurim Formation.

Calcium aluminates are a range of materials obtained by heating calcium oxide and aluminium oxide together at high temperatures. They are encountered in the manufacture of refractories and cements.
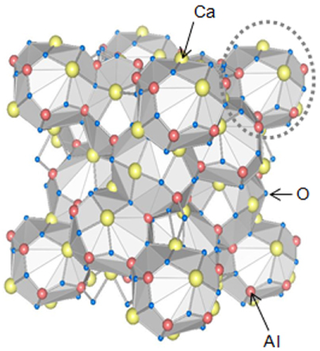
Dodecacalcium hepta-aluminate (12CaO·7Al2O3, Ca12Al14O33 or C12A7) is an inorganic solid that occurs rarely in nature as the mineral mayenite. It is an important phase in calcium aluminate cements and is an intermediate in the manufacture of Portland cement. Its composition and properties have been the subject of much debate, because of variations in composition that can arise during its high-temperature formation.

Portlandite is a hydroxide-bearing mineral typically included in the oxide mineral class. It is the naturally occurring form of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) and the calcium analogue of brucite (Mg(OH)2).

Thaumasite is a calcium silicate mineral, containing Si atoms in unusual octahedral configuration, with chemical formula Ca3Si(OH)6(CO3)(SO4)·12H2O, also sometimes more simply written as CaSiO3·CaCO3·CaSO4·15H2O.

Jennite is a calcium silicate hydrate mineral of general chemical formula: Ca9Si6O18(OH)6·8H2O.

Chlormayenite (after Mayen, Germany), Ca12Al14O32[☐4Cl2], is a rare calcium aluminium oxide mineral of cubic symmetry.

Tobermorite is a calcium silicate hydrate mineral with chemical formula: Ca5Si6O16(OH)2·4H2O or Ca5Si6(O,OH)18·5H2O.

Grossite is a calcium aluminium oxide mineral with formula CaAl4O7. It is a colorless to white vitreous mineral which crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system.
The Hatrurim Formation or Mottled Zone is a geologic formation with outcrops all around the Dead Sea Basin: in the Negev Desert in Israel, in the Judaean Desert on the West Bank, and in western Jordan. It includes late Cretaceous to Eocene aged impure limestone along with coal bearing chalk and marl. The rocks have been subjected to pyrometamorphism resulting from combustion of contained or underlying coal or hydrocarbon deposits. The formation is named for exposures in the Hatrurim Basin which lies west of the Dead Sea.
Larnite is a calcium silicate mineral with the formula Ca2SiO4. It is the calcium member of the olivine group of minerals.

Shulamit Gross was an Israeli mineralogist and geologist who studied the Hatrurim Formation.

Tacharanite is a calcium aluminium silicate hydrate (C-A-S-H) mineral of general chemical formula Ca12Al2Si18O33(OH)36 with some resemblance to the calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) mineral tobermorite. It is often found in mineral assemblage with zeolites and other hydrated calcium silicates.
















