
Saint Paul is the capital of the U.S. state of Minnesota and the county seat of Ramsey County. Situated on high bluffs overlooking a bend in the Mississippi River, Saint Paul is a regional business hub and the center of Minnesota's government. The Minnesota State Capitol and the state government offices all sit on a hill close to the city's downtown district. One of the oldest cities in Minnesota, Saint Paul has several historic neighborhoods and landmarks, such as the Summit Avenue Neighborhood, the James J. Hill House, and the Cathedral of Saint Paul. Like the adjacent city of Minneapolis, Saint Paul is known for its cold, snowy winters and humid summers.

Bruce Frank Vento was an American politician, a Democratic-Farmer-Labor member of the United States House of Representatives from 1977 until his death in 2000, representing Minnesota's 4th congressional district.

Jonathan Carver was a captain in a Massachusetts colonial unit, explorer, and writer. After his exploration of the northern Mississippi valley and western Great Lakes region, he published an account of his expedition, Travels through America in the Years 1766, 1767, and 1768 (1778), that was widely read and raised interest in the territory.

Fort Snelling State Park is a state park of the U.S. state of Minnesota, at the confluence of the Mississippi and Minnesota rivers. For many centuries, the area of the modern park has been of importance to the Mdewakanton Dakota people who consider it the center of the Earth. The state park, which opened in 1962, is named for the historic Fort Snelling, which dates from 1820. The fort structure is maintained and operated by the Minnesota Historical Society. The bulk of the state park preserves the bottomland forest, rivers, and backwater lakes below the river bluffs. Both the state and historic fort structure are part of the Mississippi National River and Recreation Area, a National Park Service site.

The Mississippi National River and Recreation Area is a 72-mile (116 km) and 54,000-acre (22,000 ha) protected corridor along the Mississippi River through Minneapolis–Saint Paul in the U.S. state of Minnesota, from the cities of Dayton and Ramsey to just downstream of Hastings. This stretch of the upper Mississippi River includes natural, historical, recreational, cultural, scenic, scientific, and economic resources of national significance. This area is the only national park site dedicated exclusively to the Mississippi River. The Mississippi National River and Recreation Area is sometimes abbreviated as MNRRA or MISS, the four-letter code the National Park Service assigned to the area. The Mississippi National River and Recreation Area is classified as one of four national rivers in the United States, and despite its name is technically not one of the 40 national recreation areas.

Indian Mounds Regional Park is a public park in Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States, featuring six burial mounds overlooking the Mississippi River. The oldest mounds were constructed about 2,500 years ago by local Indigenous people linked to the Archaic period, who may have been inspired by the burial style known as the Hopewell Tradition. Mdewakanton Dakota people are also known to have interred their dead here well into that period. At least 31 mounds were destroyed by development in the late 19th century. This burial mound group includes the tallest mounds constructed by people Indigenous to Minnesota and Wisconsin. Indian Mounds Regional Park is a component of the Mississippi National River and Recreation Area, a unit of the National Park System. In 2014, the extant Mounds Group was listed in the National Register of Historic Places. The nomination document describes the archaeology and context. A Cultural Landscape Study provides more context about the cultural landscape.
The East Side Review was an American, English language newspaper headquartered in St. Paul, Minnesota, until publication ceased in September 2019. While it was published, it was the only neighborhood-focused, general-interest weekly newspaper in either Minneapolis or St. Paul.

Kaposia or Kapozha was a seasonal and migratory Dakota settlement, also known as "Little Crow's village," once located on the east side of the Mississippi River in present-day Saint Paul, Minnesota. The Kaposia band of Mdewakanton Dakota was established in the late 18th century and led by a succession of chiefs known as Little Crow or "Petit Corbeau." After a flood in 1826, the band moved to the west side of the river, about nine miles below Fort Snelling.

Coldwater Spring is a spring in the Fort Snelling unorganized territory of the U.S. state of Minnesota, that is considered a sacred site by the Dakota people, and was also the site of the U.S. Army's Camp Coldwater for troops that constructed Fort Snelling. Coldwater Spring is located on the west bluffs of the Mississippi River directly south of Minnehaha Park and adjacent to Fort Snelling State Park. Waters from the naturally occurring spring flow continuously year round and remain unfrozen in winter months. The spring and surrounding area is managed as a protected historic site and natural park by the National Park Service as part of the Mississippi National River and Recreation Area.

The Bruce Vento Regional Trail is a rail trail in the cities of Vadnais Heights, Gem Lake, Maplewood, and Saint Paul, Minnesota, USA.
Swede Hollow was a neighborhood of Saint Paul, Minnesota. It was one of a large group of neighborhoods collectively known as the East Side, lying just to the east of the near-downtown Railroad Island neighborhood, and at the northwestern base of Dayton's Bluff. It was capped in the north by the sprawling Hamm's Brewery, and in the south by the historic Seventh Street Improvement Arches. Although one of the oldest settlements in the city, it was also arguably the poorest as each wave of immigrants settled in the valley. Swedes, Poles, Italians and Mexicans all at one point called the valley home. A similar community just downstream called Connemara Patch also existed for Irish immigrants.
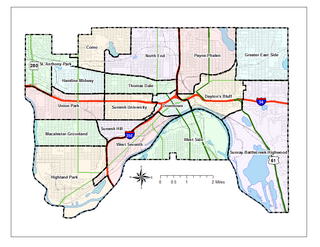
Saint Paul, Minnesota, consists of 17 officially defined city districts or neighborhoods.

Dayton's Bluff is a neighborhood located on the east side of the Mississippi River in the southeast part of the city of Saint Paul, Minnesota which has a large residential district on the plateau extending backward from its top. The name of the bluff commemorates Lyman Dayton, for whom a city in Hennepin County was also named. On the edge of the southern and highest part of Dayton's Bluff, in Indian Mounds Park, is a series of seven large aboriginal mounds, 4 to 18 feet high, that overlook the river and the central part of the city.
Edward Phelan, also Phalen or Felyn (c.1811–1850), was an early settler of Saint Paul, Minnesota. Phelan was born in approximately 1811 in Derry, Ireland and later became, along with John Hays and William Evans, one of the first settlers of Saint Paul. Phelan was later accused of Hays' murder, the first ever in Saint Paul, but was acquitted. He was indicted for perjury a year later but fled to California before he could be prosecuted. Phelan was killed by his companions in what they describe as self-defense before he could reach California. Many locations in Saint Paul, Minnesota are named after Phelan as a result of his early land claims. Phelan's name was spelled variously and as a result most locations are named Phalen and not Phelan

Saint Paul is the second largest city in the U.S. state of Minnesota, the county seat of Ramsey County, and the state capital of Minnesota. The origin and growth of the city were spurred by the proximity of Fort Snelling, the first major United States military installation in the area, as well as by the city's location on the northernmost navigable port of the Upper Mississippi River.

Lake Phalen is an urban lake located in Saint Paul, Minnesota and in its suburb of Maplewood. It is one of the largest lakes in Saint Paul and is the centerpiece of the Phalen Regional Park System. The lake drains into the Mississippi River after traveling through Phalen Creek. The lake and surrounding 494-acre (2.00 km2) park receive around 500,000 visitors each year.

Crosby Farm is a regional park in Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States, in the floodplain forests along the Mississippi River. It is named after a farmstead Thomas Crosby owned from 1858 to 1886. Crosby Farm Regional Park is maintained by the City of Saint Paul and is within the Mississippi National River and Recreation Area.

Mississippi Gorge Regional Park is a regional park along the east and west bluffs of the Mississippi River in the cities of Minneapolis and Saint Paul in the U.S. state of Minnesota. The two-city park area is between Mississippi river miles 848 and 852, from just south of Northern Pacific Bridge Number 9 to just north of Minnehaha Regional Park, and lies within the Mississippi National River and Recreation Area. The park area protects scenic and natural areas of the Mississippi River gorge, the only true gorge along the entire length of the 2,320-mile (3,730 km) river.

Bdóte is a significant Dakota sacred landscape where the Minnesota and Mississippi Rivers meet, encompassing Pike Island, Fort Snelling, Coldwater Spring, Indian Mounds Park, and surrounding areas in present-day Minneapolis and Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. In Dakota geographic memory, it is a single contiguous area not delineated by any contemporary areas' borders. According to Dakota oral tradition, it is the site of creation; the interconnectedness between the rivers, earth, and sky are important to the Dakota worldview and the site maintains its significance to the Dakota people.
















