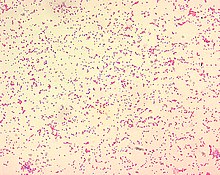
Brucellosis is a zoonosis caused by ingestion of unpasteurized milk from infected animals, or close contact with their secretions. It is also known as undulant fever, Malta fever, and Mediterranean fever.

A biovar is a variant prokaryotic strain that differs physiologically or biochemically from other strains in a particular species. Morphovars are those strains that differ morphologically. Serovars are those strains that have antigenic properties that differ from other strains.

Brucella is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, named after David Bruce (1855–1931). They are small, non-encapsulated, non-motile, facultatively intracellular coccobacilli.

Brucella melitensis is a Gram-negative coccobacillus bacterium from the Brucellaceae family. The bacterium causes ovine brucellosis, along with Brucella ovis. Humans can become infected if they have contact with an infected animal or its byproducts. Animals acquire B. melitensis by venereal transmission. The organism is found in blood, urine, milk, and semen. It is zoonotic, unlike B. ovis, causing Malta fever or localized brucellosis in humans.

Brucella suis is a bacterium that causes swine brucellosis, a zoonosis that affects pigs. The disease typically causes chronic inflammatory lesions in the reproductive organs of susceptible animals or orchitis, and may even affect joints and other organs. The most common symptom is abortion in pregnant susceptible sows at any stage of gestation. Other manifestations are temporary or permanent sterility, lameness, posterior paralysis, spondylitis, and abscess formation. It is transmitted mainly by ingestion of infected tissues or fluids, semen during breeding, and suckling infected animals.
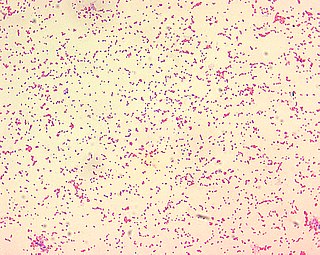
Brucella abortus is a Gram-negative bacterium in the family Brucellaceae and is one of the causative agents of brucellosis. The rod-shaped pathogen is classified under the domain Bacteria. The prokaryotic B. abortus is non-spore-forming, non-motile and aerobic.
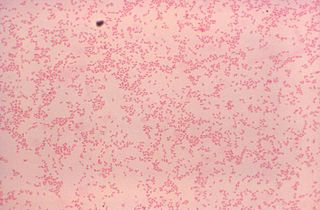
Brucella canis is a Gram-negative bacterium in the family Brucellaceae that causes brucellosis in dogs and other canids. It is a non-motile short-rod or coccus-shaped organism, and is oxidase, catalase, and urease positive. B. canis causes infertility in both male and female dogs. It can also cause inflammation in the eyes. The hosts of B. canis ranges from domestic animals to foxes and coyotes. It is passed from species to species via genital fluids. Treatments such as spaying, neutering, and long-term antibiotics have been used to combat B. canis. The species was first described in the United States in 1966 where mass abortions of beagles were documented. Brucella canis can be found in both pets and wild animals and lasts the lifespan of the animal it has affected. B. canis has two distinct circular chromosomes that can attribute to horizontal gene transfer.
The California Red is a breed of domestic sheep developed in the United States.
Actinobacillosis is a zoonotic disease caused by Actinobacillus. It is more commonly associated with animals than with humans.
Infectious pancreatic necrosis (IPN) is a severe viral disease of salmonid fish. It is caused by infectious pancreatic necrosis virus, which is a member of the Birnaviridae family. This disease mainly affects young salmonids such as trout or salmon of less than six months, although adult fish may carry the virus without showing symptoms. Resistance to infection develops more rapidly in warmer water. It is highly contagious and found worldwide, but some regions have managed to eradicate or greatly reduce the incidence of disease. The disease is normally spread horizontally via infected water, but spread also occurs vertically. It is unable to infect mammals.
Bovine gammaherpesvirus 4 (BoHV-4) is a member of the Herpesviridae family. It is part of the subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae and genus Rhadinovirus. Infection is normally sub-clinical but can cause reproductive disease in cattle such as endometritis, vulvovaginitis and mastitis. Transmission is both vertical and horizontal. It can also be indirectly spread by fomites. Distribution is worldwide and the virus infects a range of ruminants, including bison, buffalo, sheep and goats.
Ungulate bocaparvovirus 1, formerly Bovine parvovirus (BPV), also known as Haemadsorbing enteric Virus, is a member of the parvovirus group, with three significant sub-species: BPV1, 2 and 3. BPV most commonly causes diarrhea in neonatal calves and respiratory and reproductive disease in adult cattle. The distribution of the virus is worldwide. Transmission is both vertical and horizontal. The virus is very resistant to chemical and physical challenges.
Bovine campylobacteriosis is caused by Campylobacter jejuni or Campylobacter coli. Although it is a commensal in the gastrointestinal tract of many species, it can cause diarrhea - mainly in young animals. It is most commonly seen in cattle, but may also infect many other species, including humans. Campylobacter is spread horizontally via the fecal-oral route.
Edwardsiella ictaluri is a member of the family Hafniaceae. The bacterium is a short, gram negative, pleomorphic rod with flagella. It causes the disease enteric septicaemia of catfish (ESC), which infects a variety of fish species. The bacteria can cause either acute septicaemia or chronic encephalitis in infected fish. Outbreaks normally occur in spring and autumn.

Cardiovirus A is a member of the Picornaviridae family. Infection with the virus causes encephalomyocarditis and reproductive disease in pigs. Although a variety of mammals may host the virus, pigs are classed as the domestic host as they are most easily infected. It is thought to be spread by rodents.

Epizootic ulcerative syndrome (EUS), also known as mycotic granulomatosis (MG) or red spot disease (RSD), is a disease caused by the water mould Aphanomyces invadans. It infects many freshwater and brackish fish species in the Asia-Pacific region and Australia. The disease is most commonly seen when there are low temperature and heavy rainfall in tropical and sub-tropical waters.
Mycoplasma synoviae is a species of bacterium in the genus Mycoplasma. It causes disease in the joints, bones and respiratory system of birds. It is found throughout the world and infection may be referred to as infectious synovitis, avian mycoplasmosis, infectious sinusitis, or mycoplasma arthritis. It is of economic importance because infection can cause a drop in egg production. The disease is most commonly seen in chickens, and transmission occurs both vertically and horizontally.
Riemerella anatipestifer is a member of the Flavobacteriaceae family. It is a Gram-negative bacterium that causes septicaemia and death in young ducks and geese throughout the world. There are 21 known serotypes and infection is spread horizontally between birds. Infection may be referred to as duck septicaemia, goose flu, riemerellosis, new duck disease and polyserositis.
αr7 is a family of bacterial small non-coding RNAs with representatives in a broad group of Alphaproteobacterial species from the order Hyphomicrobiales. The first member of this family was found in a Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 locus located in the chromosome (C). Further homology and structure conservation analysis identified full-length homologs in several nitrogen-fixing symbiotic rhizobia, in the plant pathogens belonging to Agrobacterium species as well as in a broad spectrum of Brucella species. αr7 RNA species are 134-159 nucleotides (nt) long and share a well defined common secondary structure. αr7 transcripts can be catalogued as trans-acting sRNAs expressed from well-defined promoter regions of independent transcription units within intergenic regions (IGRs) of the Alphaproteobacterial genomes.
Brucella pinnipedialis is a species of bacteria. It causes infections and related diseases primarily in pinnipeds and cetaceans.