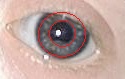
Brushfield spots are small, white or greyish/brown spots on the periphery of the iris in the human eye due to aggregation of connective tissue, a normal constituent of the iris stroma. The spots are named after the physician Thomas Brushfield, who first described them in his 1924 M.D. thesis. [1]
Brushfield spots are a characteristic feature of the chromosomal condition Down syndrome or trisomy 21. They occur in 35–78% of newborn infants with Down syndrome. [2] Brushfield spots tend to be obscured by pigmentation of the anterior border layer of the iris in patients with darker irides. Hence, they are much more likely to be observed in children with lightly pigmented eyes. Brushfield spots are more commonly found in people with Down syndrome of European descent than people with Down Syndrome of Asian heritage. [3]
Brushfield spots comprise focal areas of iris stromal hyperplasia, surrounded by relative hypoplasia.
Similar spots described by Krückmann [4] and Wolfflin [5] are found in individuals without Down syndrome. Termed Krückmann-Wolfflin bodies, these spots typically are less well defined, fewer in number and more peripherally located than the Brushfield spots of trisomy 21. [6]