The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to strike the retina. It appears black because light rays entering the pupil are either absorbed by the tissues inside the eye directly, or absorbed after diffuse reflections within the eye that mostly miss exiting the narrow pupil. The size of the pupil is controlled by the iris, and varies depending on many factors, the most significant being the amount of light in the environment. The term "pupil" was coined by Gerard of Cremona.
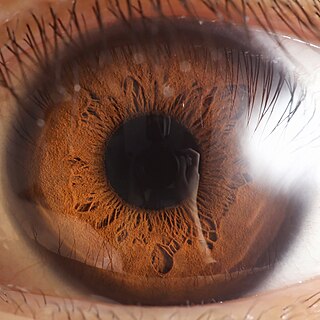
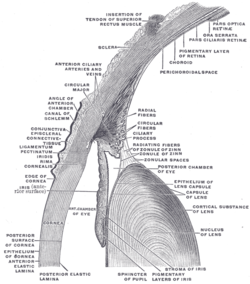
The iris is a thin, annular structure in the eye in most mammals and birds, responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupil, and thus the amount of light reaching the retina. In optical terms, the pupil is the eye's aperture, while the iris is the diaphragm. Eye color is defined by the iris.

Mydriasis is the dilation of the pupil, usually having a non-physiological cause, or sometimes a physiological pupillary response. Non-physiological causes of mydriasis include disease, trauma, or the use of certain types of drug. It may also be of unknown cause.
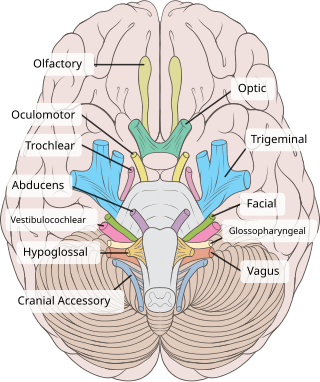
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements of the eye and that raise the eyelid. The nerve also contains fibers that innervate the intrinsic eye muscles that enable pupillary constriction and accommodation. The oculomotor nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic midbrain. Cranial nerves IV and VI also participate in control of eye movement.
The iris pigment epithelium (IPE) is a one cell thick layer of cuboidal cells lying behind the iris. The epithelial cells are highly pigmented due to the numerous large melanosomes which pack the cytoplasm of each cell. Towards the central axis, the IPE terminates at the pupillary margin. Peripherally, the IPE is continuous with the inner, non-pigmented layer of the ciliary epithelium. The iris dilator muscle is strictly attached to the anterior side of the iris pigmented epithelium and represents the anterior continuation of the pigmented ciliary epithelium. The ciliary epithelia represent the anterior continuation of the multilayered retina, whose retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) corresponds to the pigmented ciliary epithelium, while the multilayered sensory retina fades into the non-pigmented ciliary epithelium. Despite their very different functions and histological appearances, these regions have a common origin from the two layers of the embryological optic cup. The melanosomes of the IPE are distinctive, being larger, blacker and rounder than those in the ciliary epithelium or RPE.

The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary body. The ciliary body is part of the uvea, the layer of tissue that delivers oxygen and nutrients to the eye tissues. The ciliary body joins the ora serrata of the choroid to the root of the iris.

The human eye is a sensory organ in the visual system that reacts to visible light allowing eyesight. Other functions include maintaining the circadian rhythm, and keeping balance.

Horner's syndrome, also known as oculosympathetic paresis, is a combination of symptoms that arises when a group of nerves known as the sympathetic trunk is damaged. The signs and symptoms occur on the same side (ipsilateral) as it is a lesion of the sympathetic trunk. It is characterized by miosis, partial ptosis, apparent anhidrosis, with apparent enophthalmos.

The ciliary muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the eye formed as a ring of smooth muscle in the eye's middle layer, the uvea. It controls accommodation for viewing objects at varying distances and regulates the flow of aqueous humor into Schlemm's canal. It also changes the shape of the lens within the eye but not the size of the pupil which is carried out by the sphincter pupillae muscle and dilator pupillae.

The ciliary ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion located just behind the eye in the posterior orbit. It is 1–2 mm in diameter and in humans contains approximately 2,500 neurons. The ganglion contains postganglionic parasympathetic neurons. These neurons supply the pupillary sphincter muscle, which constricts the pupil, and the ciliary muscle which contracts to make the lens more convex. Both of these muscles are involuntary since they are controlled by the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.

The iris dilator muscle, is a smooth muscle of the eye, running radially in the iris and therefore fit as a dilator. The pupillary dilator consists of a spokelike arrangement of modified contractile cells called myoepithelial cells. These cells are stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system. When stimulated, the cells contract, widening the pupil and allowing more light to enter the eye.

The iris sphincter muscle is a muscle in the part of the eye called the iris. It encircles the pupil of the iris, appropriate to its function as a constrictor of the pupil.

The zonule of Zinn is a ring of fibrous strands forming a zonule that connects the ciliary body with the crystalline lens of the eye. These fibers are sometimes collectively referred to as the suspensory ligaments of the lens, as they act like suspensory ligaments.
Iris cysts are hollow cavities in the eye filled with secretion. They come in various sizes, numbers, shapes, pigments and can be free-floating, attached to the pupillary margin or within the posterior chamber. Most frequently iris cysts don't cause any issues, but they can cause problems like: "fly biting" behavior, corneal endothelial pigment, lens capsular pigmentation, altered iris movement, decreased aqueous outflow with subsequent glaucoma or block the vision when grown too big. They can be acquired or innate. Possible causes are inflammation, drug-induced, uveitis, a trauma, tumor-induced, parasitic or implantation. Most frequently iris cysts are benign and need no treatment. Sometimes iris cysts are causing problems and need to be deflated. Iris cysts can be treated with trans corneal diode laser treatment, fine-needle aspiration or surgical excision. For the treatment of iris cysts is a conservative approach favored.

The long ciliary nerves are 2-3 nerves that arise from the nasociliary nerve (itself a branch of the ophthalmic branch (CN V1) of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). They enter the eyeball to provide sensory innervation to parts of the eye, and sympathetic visceral motor innervation to the dilator pupillae muscle.
Polycoria is a pathological condition of the eye characterized by more than one pupillary opening in the iris. It may be congenital or result from a disease affecting the iris. It results in decreased function of the iris and pupil, affecting the physical eye and visualization.
The eye is made up of the sclera, the iris, and the pupil, a black hole located at the center of the eye with the main function of allowing light to pass to the retina. Due to certain muscle spasms in the eye, the pupil can resemble a tadpole, which consists of a circular body, no arms or legs, and a tail.

The eagle eye is among the sharpest in the animal kingdom, with an eyesight estimated at 4 to 8 times stronger than that of the average human. Although an eagle may only weigh 4.5 kilograms (10 lb), its eyes are roughly the same size as those of a human. Eagle weight varies: a small eagle could weigh 700 grams (1.5 lb), while a larger one could weigh 6.5 kilograms (14 lb); an eagle of about 4.5 kilograms (9.9 lb) weight could have eyes as big as that of a human who weighs 91 kilograms (200 lb). Although the size of the eagle eye is about the same as that of a human being, the back side shape of the eagle eye is flatter. Their eyes are stated to be larger in size than their brain, by weight. Color vision with resolution and clarity are the most prominent features of eagles' eyes, hence sharp-sighted people are sometimes referred to as "eagle-eyed". Eagles can identify five distinctly colored squirrels and locate their prey even if hidden.

The ciliary ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion located just behind the eye in the posterior orbit. Three types of axons enter the ciliary ganglion but only the preganglionic parasympathetic axons synapse there. The entering axons are arranged into three roots of the ciliary ganglion, which join enter the posterior surface of the ganglion.
Intrinsic ocular muscles or intraocular muscles are muscles of the inside of the eye structure.