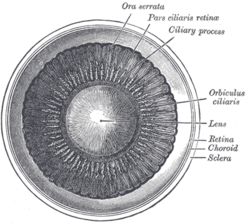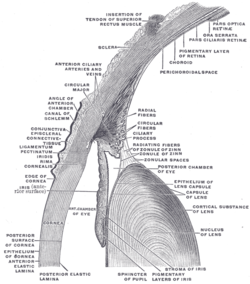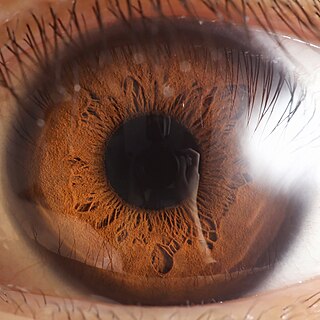
The iris is a thin, annular structure in the eye in most mammals and birds, responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupil, and thus the amount of light reaching the retina. In optical terms, the pupil is the eye's aperture, while the iris is the diaphragm. Eye color is defined by the iris.

The lens, or crystalline lens, is a transparent biconvex structure in most land vertebrate eyes. Relatively long, thin fiber cells make up the majority of the lens. These cells vary in architecture and are arranged in concentric layers. New layers of cells are recruited from a thin epithelium at the front of the lens, just below the basement membrane surrounding the lens. As a result the vertebrate lens grows throughout life. The surrounding lens membrane referred to as the lens capsule also grows in a systematic way ensuring the lens maintains an optically suitable shape in concert with the underlying fiber cells. Thousands of suspensory ligaments are embedded into the capsule at its largest diameter which suspend the lens within the eye. Most of these lens structures are derived from the epithelium of the embryo during before birth.

The choroid, also known as the choroidea or choroid coat, is a part of the uvea, the vascular layer of the eye. It contains connective tissues, and lies between the retina and the sclera. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear of the eye, while in the outlying areas it narrows to 0.1 mm. The choroid provides oxygen and nourishment to the outer layers of the retina. Along with the ciliary body and iris, the choroid forms the uveal tract.

The ora serrata is the serrated junction between the choroid and the ciliary body. This junction marks the transition from the simple, non-photosensitive area of the ciliary body to the complex, multi-layered, photosensitive region of the retina. The pigmented layer is continuous over choroid, ciliary body and iris while the nervous layer terminates just before the ciliary body. This point is the ora serrata. In this region the pigmented epithelium of the retina transitions into the outer pigmented epithelium of the ciliary body and the inner portion of the retina transitions into the non-pigmented epithelium of the cilia. In animals in which the region does not have a serrated appearance, it is called the ora ciliaris retinae.

The uvea, also called the uveal layer, uveal coat, uveal tract, vascular tunic or vascular layer, is the pigmented middle layer of the three concentric layers that make up an eye, precisely between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea.

The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary body. The ciliary body is part of the uvea, the layer of tissue that delivers oxygen and nutrients to the eye tissues. The ciliary body joins the ora serrata of the choroid to the root of the iris.

The human eye is an organ of the sensory nervous system that reacts to visible light and allows the use of visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm.

The accommodation reflex is a reflex action of the eye, in response to focusing on a near object, then looking at a distant object, comprising coordinated changes in vergence, lens shape (accommodation) and pupil size. It is dependent on cranial nerve II, superior centers (interneuron) and cranial nerve III. The change in the shape of the lens is controlled by ciliary muscles inside the eye. Changes in contraction of the ciliary muscles alter the focal distance of the eye, causing nearer or farther images to come into focus on the retina; this process is known as accommodation. The reflex, controlled by the parasympathetic nervous system, involves three responses: pupil constriction, lens accommodation, and convergence.
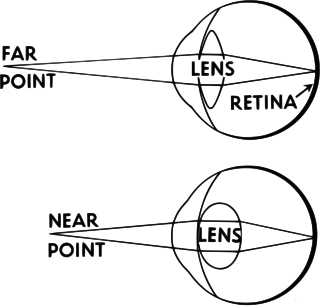
Accommodation is the process by which the vertebrate eye changes optical power to maintain a clear image or focus on an object as its distance varies. In this, distances vary for individuals from the far point—the maximum distance from the eye for which a clear image of an object can be seen, to the near point—the minimum distance for a clear image. Accommodation usually acts like a reflex, including part of the accommodation-convergence reflex, but it can also be consciously controlled.

The ciliary muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the eye formed as a ring of smooth muscle in the eye's middle layer, uvea. It controls accommodation for viewing objects at varying distances and regulates the flow of aqueous humor into Schlemm's canal. It also changes the shape of the lens within the eye but not the size of the pupil which is carried out by the sphincter pupillae muscle and dilator pupillae.

The iris sphincter muscle is a muscle in the part of the eye called the iris. It encircles the pupil of the iris, appropriate to its function as a constrictor of the pupil.

The zonule of Zinn is a ring of fibrous strands forming a zonule that connects the ciliary body with the crystalline lens of the eye. These fibers are sometimes collectively referred to as the suspensory ligaments of the lens, as they act like suspensory ligaments.

The suspensory ligament of the ovary, also infundibulopelvic ligament, is a fold of peritoneum that extends out from the ovary to the wall of the pelvis.

The posterior chamber is a narrow space behind the peripheral part of the iris, and in front of the suspensory ligament of the lens and the ciliary processes. The posterior chamber consists of small space directly posterior to the iris but anterior to the lens. The posterior chamber is part of the anterior segment and should not be confused with the vitreous chamber.

The long posterior ciliary arteries are arteries of the orbit. There are long posterior ciliary arteries two on each side of the body. They are branches of the ophthalmic artery. They pass forward within the eye to reach the ciliary body where they ramify and anastomose with the anterior ciliary arteries, thus forming the major arterial circle of the iris.The long posterior ciliary arteries contribute arterial supply to the choroid, ciliary body, and iris.
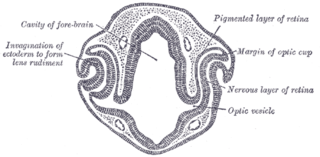
Eye formation in the human embryo begins at approximately three weeks into embryonic development and continues through the tenth week. Cells from both the mesodermal and the ectodermal tissues contribute to the formation of the eye. Specifically, the eye is derived from the neuroepithelium, surface ectoderm, and the extracellular mesenchyme which consists of both the neural crest and mesoderm.

The equine eye is one of the largest of any land mammal. Its visual abilities are directly related to the animal's behavior; for example, it is active during both day and night, and it is a prey animal. Both the strengths and weaknesses of the horse's visual abilities should be taken into consideration when training the animal, as an understanding of the horse's eye can help to discover why the animal behaves the way it does in various situations.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
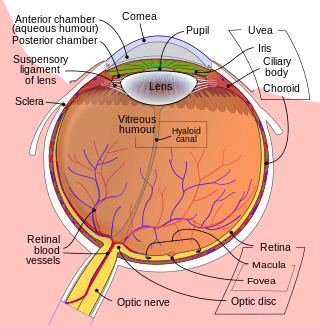
Mammals normally have a pair of eyes. Although mammalian vision is not so excellent as bird vision, it is at least dichromatic for most of mammalian species, with certain families possessing a trichromatic color perception.
Major arterial circle of the iris" is a circular artery of the eye formed by anastomoses of the anterior ciliary arteries and long posterior ciliary arteries at the ciliary body. It supplies arterial blood to the iris, ciliary processes of the ciliary body, and anterior choroid.