A pterygium is a pinkish, triangular tissue growth on the cornea of the eye. It typically starts on the cornea near the nose. It may slowly grow but rarely grows so large that the pupil is covered. Often both eyes are involved.

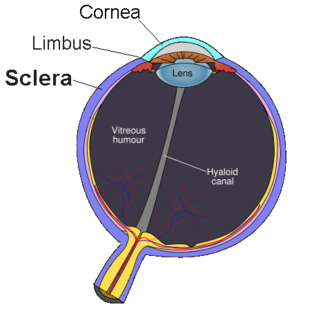
The uvea (/ˈjuːvɪə/), also called the uveal layer, uveal coat, uveal tract, vascular tunic or vascular layer is the pigmented middle of the three concentric layers that make up an eye. The name is possibly a reference to its reddish-blue or almost black colour, wrinkled appearance and grape-like size and shape when stripped intact from a cadaveric eye. Its use as a technical term in anatomy and ophthalmology is relatively modern.

Subconjunctival bleeding, also known as subconjunctival hemorrhage, is bleeding underneath the conjunctiva. The conjunctiva contains many small, fragile blood vessels that are easily ruptured or broken. When this happens, blood leaks into the space between the conjunctiva and sclera.

A red eye is an eye that appears red due to illness or injury. It is usually injection and prominence of the superficial blood vessels of the conjunctiva, which may be caused by disorders of these or adjacent structures. Conjunctivitis and subconjunctival hemorrhage are two of the less serious but more common causes.
Enucleation is the removal of the eye that leaves the eye muscles and remaining orbital contents intact. This type of ocular surgery is indicated for a number of ocular tumors, in eyes that have suffered severe trauma, and in eyes that are otherwise blind and painful.

Scleritis is a serious inflammatory disease that affects the white outer coating of the eye, known as the sclera. The disease is often contracted through association with other diseases of the body, such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis or rheumatoid arthritis. There are three types of scleritis: diffuse scleritis, nodular scleritis, and necrotizing scleritis. Scleritis may be the first symptom of onset of connective tissue disease.

The anterior ciliary arteries are seven small arteries in each eye-socket that supply the conjunctiva, sclera and the rectus muscles. They are derived from the muscular branches of the ophthalmic artery.
Trabeculectomy is a surgical procedure used in the treatment of glaucoma to relieve intraocular pressure by removing part of the eye's trabecular meshwork and adjacent structures. It is the most common glaucoma surgery performed and allows drainage of aqueous humor from within the eye to underneath the conjunctiva where it is absorbed. This outpatient procedure was most commonly performed under monitored anesthesia care using a retrobulbar block or peribulbar block or a combination of topical and subtenon anesthesia. Due to the higher risks associated with bulbar blocks, topical analgesia with mild sedation is becoming more common. Rarely general anesthesia will be used, in patients with an inability to cooperate during surgery.

Eye neoplasms can affect all parts of the eye, and can be a benign tumor or a malignant tumor (cancer). Eye cancers can be primary or metastatic cancer. The two most common cancers that spread to the eye from another organ are breast cancer and lung cancer. Other less common sites of origin include the prostate, kidney, thyroid, skin, colon and blood or bone marrow.
Ciliary Body Melanoma is a type of cancer arising from the coloured part (uvea) of the eye.
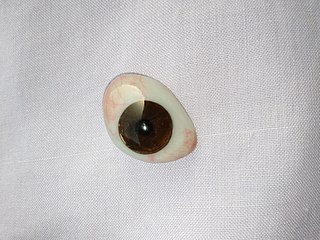
An ocular prosthesis, artificial eye or glass eye is a type of craniofacial prosthesis that replaces an absent natural eye following an enucleation, evisceration, or orbital exenteration. The prosthesis fits over an orbital implant and under the eyelids. Though often referred to as a glass eye, the ocular prosthesis roughly takes the shape of a convex shell and is made of medical grade plastic acrylic. A few ocular prostheses today are made of cryolite glass. A variant of the ocular prosthesis is a very thin hard shell known as a scleral shell which can be worn over a damaged or eviscerated eye. Makers of ocular prosthetics are known as ocularists. An ocular prosthesis does not provide vision; this would be a visual prosthesis. Someone with an ocular prosthesis is totally blind on the affected side and has monocular vision.

The periscleral lymph space or episcleral space of the eye is the space between the outer surface of the sclera and the inner surface of the capsule of Ténon. It is continuous with the subdural and subarachnoid spaces, and is traversed by fine bands of connective tissue.

The ocular immune system protects the eye from infection and regulates healing processes following injuries. The interior of the eye lacks lymph vessels but is highly vascularized, and many immune cells reside in the uvea, including mostly macrophages, dendritic cells, and mast cells. These cells fight off intraocular infections, and intraocular inflammation can manifest as uveitis or retinitis. The cornea of the eye is immunologically a very special tissue. Its constant exposure to the exterior world means that it is vulnerable to a wide range of microorganisms while its moist mucosal surface makes the cornea particularly susceptible to attack. At the same time, its lack of vasculature and relative immune separation from the rest of the body makes immune defense difficult. Lastly, the cornea is a multifunctional tissue. It provides a large part of the eye’s refractive power, meaning it has to maintain remarkable transparency, but must also serve as a barrier to keep pathogens from reaching the rest of the eye, similar to function of the dermis and epidermis in keeping underlying tissues protected. Immune reactions within the cornea come from surrounding vascularized tissues as well as innate immune responsive cells that reside within the cornea.

Scleral reinforcement is a surgical procedure used to reduce or stop further macular damage caused by high myopia, which can be degenerative.

Conjunctivochalasis is a common eye surface condition characterized by the presence of excess folds of the conjunctiva located between the globe of the eye and the eyelid margin.
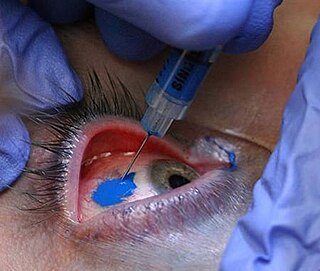
Scleral tattooing is the practice of tattooing the sclera, or white part of the human eye. The dye is not injected into the tissue, but between two layers of the eye, where it spreads out over a large area. The process is not common. Some procedures have caused loss of vision, severe permanent pain, and loss of the eye.