Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to damage of the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of sight" because the loss of vision usually occurs slowly over a long period of time. A major risk factor for glaucoma is increased pressure within the eye, known as intraocular pressure (IOP). It is associated with old age, a family history of glaucoma, and certain medical conditions or the use of some medications. The word glaucoma comes from the Ancient Greek word γλαυκός, meaning 'gleaming, blue-green, gray'.
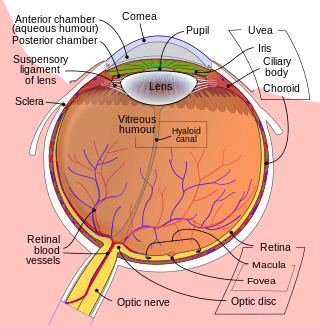
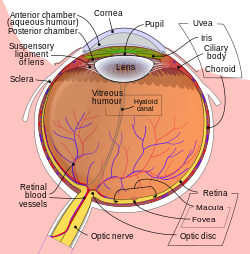
The aqueous humour is a transparent water-like fluid similar to blood plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the ciliary body, a structure supporting the lens of the eyeball. It fills both the anterior and the posterior chambers of the eye, and is not to be confused with the vitreous humour, which is located in the space between the lens and the retina, also known as the posterior cavity or vitreous chamber. Blood cannot normally enter the eyeball.

A phakic intraocular lens (PIOL) is an intraocular lens that is implanted surgically into the eye to correct refractive errors without removing the natural lens. Intraocular lenses that are implanted into eyes after the eye's natural lens has been removed during cataract surgery are known as pseudophakic.

The trabecular meshwork is an area of tissue in the eye located around the base of the cornea, near the ciliary body, and is responsible for draining the aqueous humor from the eye via the anterior chamber.

Hyphema is the medical condition of bleeding in the anterior chamber of the eye between the iris and the cornea. People usually first notice a loss or decrease in vision. The eye may also appear to have a reddish tinge, or it may appear as a small pool of blood at the bottom of the iris in the cornea. A traumatic hyphema is caused by a blow to the eye. A hyphema can also occur spontaneously.

Schlemm's canal, also known as the canal of Schlemm, and as the scleral venous sinus, is a circular lymphatic-like vessel in the eye. It collects aqueous humor from the anterior chamber and delivers it into the episcleral blood vessels. Canaloplasty may be used to widen it.

In ophthalmology, gonioscopy is a routine procedure that measures the angle between the iris and the cornea, using a goniolens together with a slit lamp or operating microscope. Its use is important in diagnosing and monitoring various eye conditions associated with glaucoma.

The posterior chamber is a narrow space behind the peripheral part of the iris, and in front of the suspensory ligament of the lens and the ciliary processes. The posterior chamber consists of small space directly posterior to the iris but anterior to the lens. The posterior chamber is part of the anterior segment and should not be confused with the vitreous chamber.

Glaucoma is a group of diseases affecting the optic nerve that results in vision loss and is frequently characterized by raised intraocular pressure (IOP). There are many glaucoma surgeries, and variations or combinations of those surgeries, that facilitate the escape of excess aqueous humor from the eye to lower intraocular pressure, and a few that lower IOP by decreasing the production of aqueous humor.

The scleral spur in the visual system is a protrusion of the sclera into the anterior chamber. The spur is an annular structure composed of collagen in the human eye.
Fuchs heterochromic iridocyclitis (FHI) is a chronic unilateral uveitis appearing with the triad of heterochromia, predisposition to cataract and glaucoma, and keratitic precipitates on the posterior corneal surface. Patients are often asymptomatic and the disease is often discovered through investigation of the cause of the heterochromia or cataract. Neovascularisation is possible and any eye surgery, such as cataract surgery, can cause bleeding from the fragile vessels in the atrophic iris causing accumulation of blood in the anterior chamber of the eye, also known as hyphema.
The Trabectome is a surgical device that can be used for ab interno trabeculotomy, a minimally invasive glaucoma surgery for the surgical management of adult, juvenile, and infantile glaucoma. The trabecular meshwork is a major site of resistance to aqueous humor outflow. As angle surgeries such as Trabectome follow the physiologic outflow pathway, the risk of complications is significantly lower than filtering surgeries. Hypotony with damage to the macula, can occur with pressures below 5 mmHg, for instance, after traditional trabeculectomy, because of the episcleral venous pressure limit. The Trabectome handpiece is inserted into the anterior chamber, its tip positioned into Schlemm's canal, and advanced to the left and to the right. Different from cautery, the tip generates plasma to molecularize the trabecular meshwork and remove it drag-free and with minimal thermal effect. Active irrigation of the trabectome surgery system helps to keep the anterior chamber formed during the procedure and precludes the need for ophthalmic viscoelastic devices. Viscoelastic devices tend to trap debris or gas bubbles and diminish visualization. The Trabectome decreases the intra-ocular pressure typically to a mid-teen range and reduces the patient's requirement to take glaucoma eye drops and glaucoma medications. The theoretically lowest pressure that can be achieved is equal to 8 mmHg in the episcleral veins. This procedure is performed through a small incision and can be done on an outpatient basis.
Micro-invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS) is the latest advance in surgical treatment for glaucoma, which aims to reduce intraocular pressure by either increasing outflow of aqueous humor or reducing its production. MIGS comprises a group of surgical procedures which share common features. MIGS procedures involve a minimally invasive approach, often with small cuts or micro-incisions through the cornea that causes the least amount of trauma to surrounding scleral and conjunctival tissues. The techniques minimize tissue scarring, allowing for the possibility of traditional glaucoma procedures such as trabeculectomy or glaucoma valve implantation to be performed in the future if needed.
The Van Herick technique is an eye examination method used to determine the size of the anterior chamber angle of the eye.
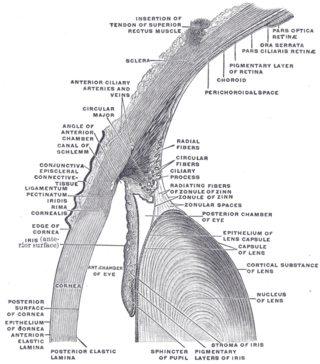
The anterior chamber angle is a part of the eye located between the cornea and iris which contains the trabecular meshwork. The size of this angle is an important determinant of the rate aqueous humour flows out of the eye, and thus, the intraocular pressure. The anterior chamber angle is the structure which determines the anterior chamber depth. An extremely narrow anterior chamber angle is a feature of angle closure glaucoma.

Secondary glaucoma is a collection of progressive optic nerve disorders associated with a rise in intraocular pressure (IOP) which results in the loss of vision. In clinical settings, it is defined as the occurrence of IOP above 21 mmHg requiring the prescription of IOP-managing drugs. It can be broadly divided into two subtypes: secondary open-angle glaucoma and secondary angle-closure glaucoma, depending on the closure of the angle between the cornea and the iris. Principal causes of secondary glaucoma include optic nerve trauma or damage, eye disease, surgery, neovascularization, tumours and use of steroid and sulfa drugs. Risk factors for secondary glaucoma include uveitis, cataract surgery and also intraocular tumours. Common treatments are designed according to the type and the underlying causative condition, in addition to the consequent rise in IOP. These include drug therapy, the use of miotics, surgery or laser therapy.
Uveitis–glaucoma–hyphaema (UGH) syndrome, also known as Ellingson syndrome, is a complication of cataract surgery, caused by intraocular lens subluxation or dislocation. The chafing of mispositioned intraocular lens over iris, ciliary body or iridocorneal angle cause elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) anterior uveitis and hyphema. It is most commonly caused by anterior chamber IOLs and sulcus IOLs but, the condition can be seen with any type of IOL, including posterior chamber lenses and cosmetic iris implants.
Ghost cell glaucoma (GCG) is a type of secondary glaucoma occurs due to long standing vitreous hemorrhage. The rigid and less pliable degenerated red blood cells block the trabecular meshwork and increase the pressure inside eyes.

Uveitic glaucoma is most commonly a progression stage of noninfectious anterior uveitis or iritis.
Manual small incision cataract surgery (MSICS) is an evolution of extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE); the lens is removed from the eye through a self-sealing scleral tunnel wound. A well-constructed scleral tunnel is held closed by internal pressure, is watertight, and does not require suturing. The wound is relatively smaller than that in ECCE but is still markedly larger than a phacoemulsification wound. Comparative trials of MSICS against phaco in dense cataracts have found no statistically significant difference in outcomes but MSICS had shorter operating times and significantly lower costs. MSICS has become the method of choice in the developing world because it provides high-quality outcomes with less surgically induced astigmatism than ECCE, no suture-related problems, quick rehabilitation, and fewer post-operative visits. MSICS is easy and fast to learn for the surgeon, cost effective, simple, and applicable to almost all types of cataract.