Additional images



| External limiting membrane | |
|---|---|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | membrana limitans externa |
| TA98 | A15.2.04.011 |
| FMA | 58683 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The external limiting membrane (or outer limiting membrane) is one of the ten distinct layers of the retina of the eye. It has a network-like structure and is situated at the bases of the rods and cones.




The retina is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera.
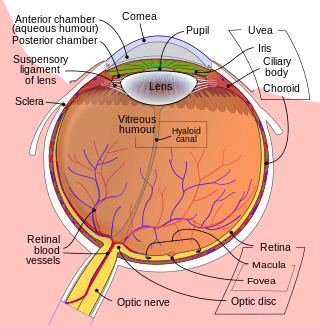
The vitreous body is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball in humans and other vertebrates. It is often referred to as the vitreous humor or simply "the vitreous". Vitreous fluid or "liquid vitreous" is the liquid component of the vitreous gel, found after a vitreous detachment. It is not to be confused with the aqueous humor, the other fluid in the eye that is found between the cornea and lens.

The choroid, also known as the choroidea or choroid coat, is a part of the uvea, the vascular layer of the eye. It contains connective tissues, and lies between the retina and the sclera. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear of the eye, while in the outlying areas it narrows to 0.1 mm. The choroid provides oxygen and nourishment to the outer layers of the retina. Along with the ciliary body and iris, the choroid forms the uveal tract.

The fastigial nucleus is located in the cerebellum. It is one of the four deep cerebellar nuclei, and is grey matter embedded in the white matter of the cerebellum.

In embryogenesis, Rathke's pouch is an evagination at the roof of the developing mouth in front of the buccopharyngeal membrane. It gives rise to the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis), a part of the endocrine system.

Descemet's membrane is the basement membrane that lies between the corneal proper substance, also called stroma, and the endothelial layer of the cornea. It is composed of different kinds of collagen than the stroma. The endothelial layer is located at the posterior of the cornea. Descemet's membrane, as the basement membrane for the endothelial layer, is secreted by the single layer of squamous epithelial cells that compose the endothelial layer of the cornea.
The capillary lamina of choroid or choriocapillaris is a part of the choroid of the eye. It is a layer of capillaries immediately adjacent to Bruch's membrane of the choroid. The choriocapillaris consists of a dense network of freely anastomosing highly permeable fenestrated large-calibre capillaries. It nourishes the outer avascular layers of the retina.

The ampullary cupula, or cupula, is a structure in the vestibular system, providing the sense of spatial orientation.

The facial colliculus is an elevated area located in the pontine tegmentum, within the floor of the fourth ventricle. It is formed by fibres from the facial motor nucleus looping over the abducens nucleus. The facial colliculus is an essential landmark of the rhomboid fossa.

In the anatomy of the eye, the ciliary processes are formed by the inward folding of the various layers of the choroid, viz. the choroid proper and the lamina basalis, and are received between corresponding foldings of the suspensory ligament of the lens.

The elements composing the layer of rods and cones in the retina of the eye are of two kinds, rod cells and cone cells, the former being much more numerous than the latter except in the macula lutea.

The pigmented layer of retina or retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is the pigmented cell layer just outside the neurosensory retina that nourishes retinal visual cells, and is firmly attached to the underlying choroid and overlying retinal visual cells.

Neuroectoderm consists of cells derived from the ectoderm. Formation of the neuroectoderm is the first step in the development of the nervous system. The neuroectoderm receives bone morphogenetic protein-inhibiting signals from proteins such as noggin, which leads to the development of the nervous system from this tissue. Histologically, these cells are classified as pseudostratified columnar cells.

The internal limiting membrane, or inner limiting membrane, is the boundary between the retina and the vitreous body, formed by astrocytes and the end feet of Müller cells. It is separated from the vitreous body by a basal lamina.

The crista ampullaris is the sensory organ of rotation. They are found in the ampullae of each of the semicircular canals of the inner ear, meaning that there are three pairs in total. The function of the crista ampullaris is to sense angular acceleration and deceleration.

The vitreous membrane is a layer of collagen separating the vitreous humour from the rest of the eye. At least two parts have been identified anatomically. The posterior hyaloid membrane separates the rear of the vitreous from the retina. It is a false anatomical membrane. The anterior hyaloid membrane separates the front of the vitreous from the lens. Bernal et al. describe it "as a delicate structure in the form of a thin layer that runs from the pars plana to the posterior lens, where it shares its attachment with the posterior zonule via Weigert's ligament, also known as Egger's line".
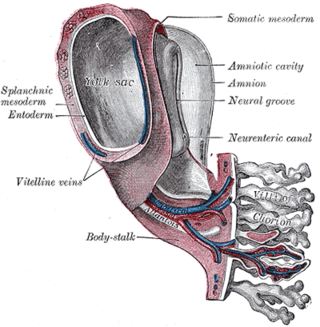
The vitelline arteries are the arterial counterpart to the vitelline veins. Like the veins, they play an important role in the vitelline circulation of blood to and from the yolk sac of a fetus. They are a branch of the dorsal aorta.

The mantle zone of a lymphatic nodule is an outer ring of small lymphocytes surrounding a germinal center.

Diktyoma, or ciliary body medulloepithelioma, or teratoneuroma, is a rare tumor arising from primitive medullary epithelium in the ciliary body of the eye. Almost all diktyomas arise in the ciliary body, although, rarely, they may arise from the optic nerve head or retina.

Atul Kumar is an Indian ophthalmologist who is currently the Chief & Professor of Ophthalmology at Dr. Rajendra Prasad Centre for Ophthalmic Sciences (RPC-AIIMS), the national apex ophthalmic centre at All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi. He was awarded the Padma Shri award in January 2007 for his services to the medical field. He specializes in vitreoretinal surgery and also heads the Vitreo-Retinal, Uvea and ROP services at RPC-AIIMS.