
Transport in Papua New Guinea is mainly based around roads and air travel. It is in many cases heavily limited by the mountainous terrain and copious amount of rainfall and frequent severe weather occurring in many locations, such as Lae. The capital, Port Moresby, is not linked by road to any of the other major towns and many highland villages can only be reached by light aircraft or on foot.
Lae (German: Preußen-Reede, later Lehe) is the capital of Morobe Province and is the second-largest city in Papua New Guinea. It is located near the delta of the Markham River and at the start of the Highlands Highway, which is the main land transport corridor between the Highlands Region and the coast. Lae is the largest cargo port of the country and is the industrial hub of Papua New Guinea. The city is known as the Garden City and home of the University of Technology.

Kaiser-Wilhelmsland formed part of German New Guinea, the South Pacific protectorate of the German Empire. Named in honour of Wilhelm I, who reigned as German Emperor from 1871 to 1888, it included the northern part of present-day Papua New Guinea. From 1884 until 1920 the territory was a protectorate of the German Empire. Kaiser-Wilhelmsland, the Bismarck Archipelago, the northern Solomon Islands, the Caroline Islands, Palau, Nauru, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the Marshall Islands comprised German New Guinea.

Madang is the capital of Madang Province and is a town with a population of 27,420 on the north coast of Papua New Guinea. It was first settled by the Germans in the 19th century.

Morobe Province is a province on the northern coast of Papua New Guinea. The provincial capital and largest city is Lae. The province covers 33,705 km2, with a population of 674,810, and since the division of Southern Highlands Province in May 2012 it is the most populous province. It includes the Huon Peninsula, the Markham River, and delta, and coastal territories along the Huon Gulf. The province has nine administrative districts. At least 101 languages are spoken, including Kâte and Yabem language. English and Tok Pisin are common languages in the urban areas, and in some areas pidgin forms of German are mixed with the native language.
The Catholic Church in Papua New Guinea is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope in Rome. Papua New Guinea has approximately two million Catholic adherents, approximately 27% of the country's total population.
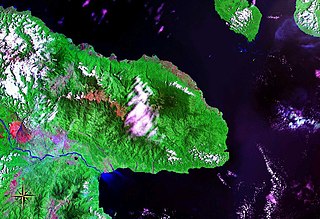
Huon Peninsula is a large rugged peninsula on the island of New Guinea in Morobe Province, eastern Papua New Guinea. It is named after French explorer Jean-Michel Huon de Kermadec. The peninsula is dominated by the steep Saruwaged and Finisterre and Cromwell Mountains. The nearest large town is the Morobe provincial capital Lae to the south, while settlements on the north coast include the former German town of Finschhafen, the district capital of Wasu, Malalamai and Saidor with its World War II era Saidor Airport.

The Huon Peninsula campaign was a series of battles fought in north-eastern Papua New Guinea in 1943–1944 during the Second World War. The campaign formed the initial part of an offensive that the Allies launched in the Pacific in late 1943 and resulted in the Japanese being pushed north from Lae to Sio on the northern coast of New Guinea over the course of a four-month period. For the Australians, a significant advantage was gained through the technological edge that Allied industry had achieved over the Japanese by this phase of the war, while the Japanese were hampered by a lack of supplies and reinforcements due to Allied interdiction efforts at sea and in the air.

The Salamaua–Lae campaign was a series of actions in the New Guinea campaign of World War II. Australian and United States forces sought to capture two major Japanese bases, one in the town of Lae, and another one at Salamaua. The campaign to take the Salamaua and Lae area began after the successful defence of Wau in late January, which was followed up by an Australian advance towards Mubo as the Japanese troops that had attacked Wau withdrew to positions around Mubo. A series of actions followed over the course of several months as the Australian 3rd Division advanced north-east towards Salamaua. After an amphibious landing at Nassau Bay, the Australians were reinforced by a US regimental combat team, which subsequently advanced north up the coast.

The Papuan Infantry Battalion (PIB) was a unit of the Australian Army raised in the Territory of Papua for service during the Second World War. Formed in early 1940 in Port Moresby to help defend the territory in the event of a Japanese invasion, its soldiers were primarily Papuan natives led by Australian officers and non-commissioned officers. Following the outbreak of the Pacific War, the PIB served in many of the Allied campaigns in New Guinea; however, due to the nature of its role its sub-units mainly operated separately, attached to larger Australian and US Army units and formations. Slow in forming, the first members of the PIB were not officially posted in until March 1941. By 1942 it consisted of only three companies, all of which were under-strength and poorly equipped. It was subsequently employed on scouting, reconnaissance and surveillance patrols against the Japanese, where the natural bushcraft of its native soldiers could be used to their advantage. The PIB was sent forward in June 1942 to patrol the northern coast of Papua and was dispersed over a wide area. These small parties were the first to make contact with the Imperial Japanese forces upon their landing in Papua, before participating in the Kokoda Track campaign. As part of Maroubra Force, the PIB fought alongside the Australian 39th Battalion at Kokoda, Deniki, and Isurava as the Japanese forced them back along the Kokoda track, but was withdrawn before the campaign finally turned in favour of the Australians.

The Landing at Lae was an amphibious landing to the east of Lae and then the subsequent advance on the town during the Salamaua–Lae campaign of World War II. Part of Operation Postern, which was undertaken to capture the Japanese base at Lae, the landing was undertaken between 4 and 6 September 1943 by Australian troops from the 9th Division, supported by US naval forces from the VII Amphibious Force. The first major amphibious operation undertaken by the Australian Army since the failed Gallipoli Campaign, the Australians invested a significant amount of effort into planning the operation.

Malahang is a suburb of Lae, Morobe Province in Papua New Guinea.

The 51st Division was an infantry division of the Imperial Japanese Army. Its call sign was the Base Division. It was formed on 10 July 1940 at Utsunomiya, Tochigi, simultaneously with 52nd, 54th, 55th, 56th, and 57th divisions. The 51st Division was initially assigned to the Eastern District Army and placed under command of Lieutenant General Kenichiro Ueno.

The Malahang Mission Station is a Lutheran filial station situated in Malahang, Morobe Province in Papua New Guinea now under the auspices of the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Papua New Guinea. The Mission station is located on Busu Road, Malahang opposite the Malahang Industrial Area.
Taraka is a suburb of Lae in the Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea. The main campus for the Papua New Guinea University of Technology is located in Taraka.
Tent City (Tent siti) is a suburb of Lae in the Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea. The main campus for the Papua New Guinea University of Technology is located 1 kilometre to the South of Tent City.
Bumayong is an outer suburb of Lae in the Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea.
Voco Point is a suburb of Lae in the Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea. Voco Point is one of the busiest coastal trading points in the country and coastal vessels from throughout the country, from Alotau to Manus, from Lihir to Vanimo line up at the wharves. The passenger boats ferry people to Finschhafen, the Siassi islands, Kimbe, Rabaul, New Ireland, Oro Bay, Alotau, Madang, and Wewak. The local Lae villages call the area around Voco Point Asiawi, which according to mythology, used to be a long point that went out much further but was eaten by the evil spirit Yaayaa.

As the township of Lae, in Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea is a relatively new entity, the history of the Lae environs is much older.
















