Cadherin-23 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDH23 gene. [5] [6] [7]
Cadherin-23 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDH23 gene. [5] [6] [7]
This gene is a member of the cadherin superfamily, genes encoding calcium dependent cell-cell adhesion glycoproteins. The protein encoded by this gene is a large, single-pass transmembrane protein composed of an extracellular domain containing 27 repeats that show significant homology to the cadherin ectodomain. Expressed in the neurosensory epithelium, the protein is thought to be involved in stereocilia organization and hair bundle formation. Specifically, it is thought to interact with protocadherin 15 to form tip-link filaments. [8]
The gene is located in a region containing the human deafness loci DFNB12 and USH1D. Usher syndrome 1D and nonsyndromic autosomal recessive deafness DFNB12 are caused by allelic mutations of this novel cadherin-like gene. [7] [9] The gene is associated with kidney function decline. [10]

Usher syndrome, also known as Hallgren syndrome, Usher–Hallgren syndrome, retinitis pigmentosa–dysacusis syndrome or dystrophia retinae dysacusis syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder caused by a mutation in any one of at least 11 genes resulting in a combination of hearing loss and visual impairment. It is the most common cause of deafblindness and is at present incurable.

Collagen alpha-2(XI) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL11A2 gene.

Myosin VIIA is protein that in humans is encoded by the MYO7A gene. Myosin VIIA is a member of the unconventional myosin superfamily of proteins. Myosins are actin binding molecular motors that use the enzymatic conversion of ATP - ADP + inorganic phosphate (Pi) to provide the energy for movement.

Gap junction beta-2 protein (GJB2), also known as connexin 26 (Cx26) — is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GJB2 gene.

Usherin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the USH2A gene.

Harmonin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the USH1C gene. It is expressed in sensory cells of the inner ear and retina, where it plays a role in hearing, balance, and vision. Mutations at the USH1C locus cause Usher syndrome type 1c and nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness.

Protocadherin-15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PCDH15 gene.

Usher syndrome type-1G protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the USH1G gene.
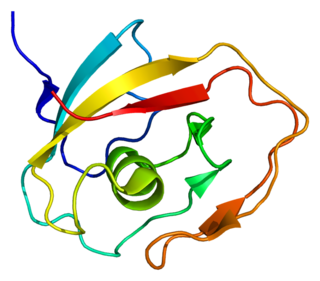
Cochlin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COCH gene. It is an extracellular matrix (ECM) protein highly abundant in the cochlea and vestibule of the inner ear, constituting the major non-collagen component of the ECM of the inner ear. The protein is highly conserved in human, mouse, and chicken, showing 94% and 79% amino acid identity of human to mouse and chicken sequences, respectively.

TRIO and F-actin-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRIOBP gene.

Claudin-14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLDN14 gene. It belongs to a related family of proteins called claudins.

Alpha-tectorin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TECTA gene.

Protein SGT1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ECD gene.

Otoferlin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OTOF gene. It is involved in vesicle membrane fusion, and mutations in the OTOF gene are associated with a genetic form of deafness.

Transmembrane channel-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMC1 gene. TMC1 contains six transmembrane domains with both the C and N termini on the endoplasmic side of the membrane, as well as a large loop between domains 4 and 5. This topology is similar to that of transient receptor potential channels (TRPs), a family of proteins involved in the perception of senses such as temperature, taste, pressure, and vision. TMC1 has been located in the post-natal mouse cochlea, and knockouts for TMC1 and TMC2 result in both auditory and vestibular deficits indicating TMC1 is a molecular part of auditory transduction.

Stereocilin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STRC gene.

Unconventional myosin-XV is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYO15A gene.

Espin, also known as autosomal recessive deafness type 36 protein or ectoplasmic specialization protein, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ESPN gene. Espin is a microfilament binding protein.

Lipoxygenase homology domains 1 is a protein in humans that is encoded by the LOXHD1 gene.

Pejvakin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PJVK gene.