Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CITED2 gene. [5] [6] [7]
Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CITED2 gene. [5] [6] [7]
CITED2 has been shown to interact with EP300, [8] [9] [10] [11] LHX2, [11] TFAP2A, [9] [10] and WT1. [12]
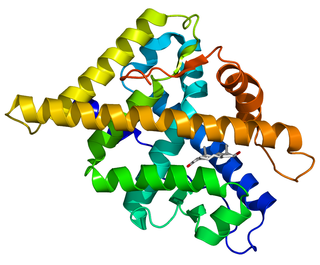
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4, is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor.

Histone acetyltransferase p300 also known as p300 HAT or E1A-associated protein p300 also known as EP300 or p300 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the EP300 gene. It functions as histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription of genes via chromatin remodeling by allowing histone proteins to wrap DNA less tightly. This enzyme plays an essential role in regulating cell growth and division, prompting cells to mature and assume specialized functions (differentiate), and preventing the growth of cancerous tumors. The p300 protein appears to be critical for normal development before and after birth.
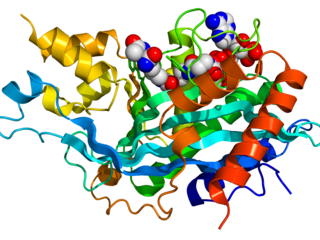
The p300-CBP coactivator family in humans is composed of two closely related transcriptional co-activating proteins :

P300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF), also known as K(lysine) acetyltransferase 2B (KAT2B), is a human gene and transcriptional coactivator associated with p53.

CREB-binding protein, also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, is a coactivator encoded by the CREBBP gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both transcription factors as well as histone lysines, the latter of which has been shown to alter chromatin structure making genes more accessible for transcription. This relatively unique acetyltransferase activity is also seen in another transcription enzyme, EP300 (p300). Together, they are known as the p300-CBP coactivator family and are known to associate with more than 16,000 genes in humans; however, while these proteins share many structural features, emerging evidence suggests that these two co-activators may promote transcription of genes with different biological functions.

Transcription factor p65 also known as nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p65 subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RELA gene.
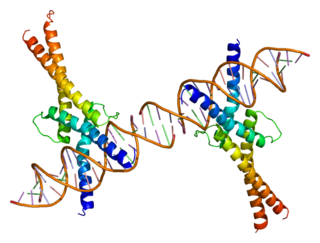
Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1 (SREBF1) also known as sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SREBF1 gene.

Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP-2) also known as sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 2 (SREBF2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SREBF2 gene.

Myb-related protein B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYBL2 gene.

Activating transcription factor 4 , also known as ATF4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATF4 gene.

Homeobox protein MSX-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MSX1 gene. MSX1 transcripts are not only found in thyrotrope-derived TSH cells, but also in the TtT97 thyrotropic tumor, which is a well differentiated hyperplastic tissue that produces both TSHß- and a-subunits and is responsive to thyroid hormone. MSX1 is also expressed in highly differentiated pituitary cells which until recently was thought to be expressed exclusively during embryogenesis. There is a highly conserved structural organization of the members of the MSX family of genes and their abundant expression at sites of inductive cell–cell interactions in the embryo suggest that they have a pivotal role during early development.

Interferon regulatory factor 7, also known as IRF7, is a member of the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors.
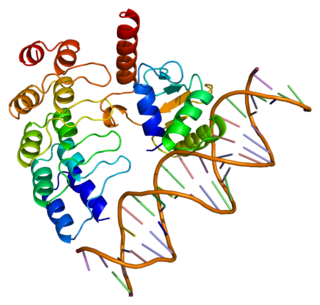
GA-binding protein alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABPA gene.
Protein SET, also known as Protein SET 1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SET gene.

Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CITED1 gene.

Transcription factor AP-2 alpha, also known as TFAP2A, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TFAP2A gene.

LIM/homeobox protein Lhx2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LHX2 gene.

In molecular biology, TAZ zinc finger domains are zinc-containing domains found in the homologous transcriptional co-activators CREB-binding protein (CBP) and the P300. CBP and P300 are histone acetyltransferases that catalyse the reversible acetylation of all four histones in nucleosomes, acting to regulate transcription via chromatin remodelling. These large nuclear proteins interact with numerous transcription factors and viral oncoproteins, including p53 tumour suppressor protein, E1A oncoprotein, MyoD, and GATA-1, and are involved in cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis. Both CBP and P300 have two copies of the TAZ domain, one in the N-terminal region, the other in the C-terminal region. The TAZ1 domain of CBP and P300 forms a complex with CITED2, inhibiting the activity of the hypoxia inducible factor (HIF-1alpha) and thereby attenuating the cellular response to low tissue oxygen concentration. Adaptation to hypoxia is mediated by transactivation of hypoxia-responsive genes by hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) in complex with the CBP and p300 transcriptional coactivators.

In biochemistry, the KIX domain (kinase-inducible domain (KID) interacting domain) or CREB binding domain is a protein domain of the eukaryotic transcriptional coactivators CBP and P300. It serves as a docking site for the formation of heterodimers between the coactivator and specific transcription factors. Structurally, the KIX domain is a globular domain consisting of three α-helices and two short 310-helices.
The transactivation domain or trans-activating domain (TAD) is a transcription factor scaffold domain which contains binding sites for other proteins such as transcription coregulators. These binding sites are frequently referred to as activation functions (AFs). TADs are named after their amino acid composition. These amino acids are either essential for the activity or simply the most abundant in the TAD. Transactivation by the Gal4 transcription factor is mediated by acidic amino acids, whereas hydrophobic residues in Gcn4 play a similar role. Hence, the TADs in Gal4 and Gcn4 are referred to as acidic or hydrophobic, respectively.