Death domain-containing protein CRADD is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRADD gene. [5] [6] [7]
Death domain-containing protein CRADD is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRADD gene. [5] [6] [7]
The protein encoded by this gene is a death domain (CARD/DD)-containing protein and has been shown to induce cell apoptosis. Through its CARD domain, this protein interacts with, and thus recruits, caspase 2/ICH1 to the cell death signal transduction complex that includes tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1A), RIPK1/RIP kinase, and numbers of other CARD domain-containing proteins. [7]
CRADD has been shown to interact with RIPK1 [5] [6] and Caspase 2. [5] [8] [9]

Caspase recruitment domains, or caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARDs), are interaction motifs found in a wide array of proteins, typically those involved in processes relating to inflammation and apoptosis. These domains mediate the formation of larger protein complexes via direct interactions between individual CARDs. CARDs are found on a strikingly wide range of proteins, including helicases, kinases, mitochondrial proteins, caspases, and other cytoplasmic factors.

The BH3 interacting-domain death agonist, or BID, gene is a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 protein family. Bcl-2 family members share one or more of the four characteristic domains of homology entitled the Bcl-2 homology (BH) domains, and can form hetero- or homodimers. Bcl-2 proteins act as anti- or pro-apoptotic regulators that are involved in a wide variety of cellular activities.
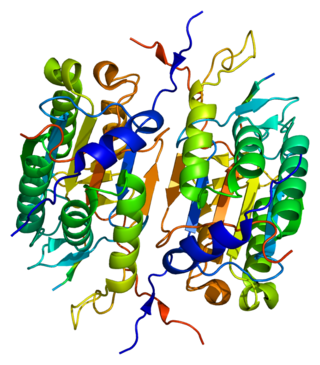
Caspase 2 also known as CASP2 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the CASP2 gene. CASP2 orthologs have been identified in nearly all mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs are also present in birds, lizards, lissamphibians, and teleosts.

Caspase-7, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase, also known as CASP7, is a human protein encoded by the CASP7 gene. CASP7 orthologs have been identified in nearly all mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs are also present in birds, lizards, lissamphibians, and teleosts.

Caspase-6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CASP6 gene. CASP6 orthologs have been identified in numerous mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs are also present in birds, lizards, lissamphibians, and teleosts. Caspase-6 has known functions in apoptosis, early immune response and neurodegeneration in Huntington's and Alzheimer's disease.

Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BIRC3 gene.

Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BIRC2 gene.

Caspase-10 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the CASP10 gene.

Diablo homolog (DIABLO) is a mitochondrial protein that in humans is encoded by the DIABLO gene on chromosome 12. DIABLO is also referred to as second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases or SMAC. This protein binds inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs), thus freeing caspases to activate apoptosis. Due to its proapoptotic function, SMAC is implicated in a broad spectrum of tumors, and small molecule SMAC mimetics have been developed to enhance current cancer treatments.

Apoptotic protease activating factor 1, also known as APAF1, is a human homolog of C. elegans CED-4 gene.

B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL10 gene. Like BCL2, BCL3, BCL5, BCL6, BCL7A, and BCL9, it has clinical significance in lymphoma.

Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) functions in a variety of cellular pathways related to both cell survival and death. In terms of cell death, RIPK1 plays a role in apoptosis and necroptosis. Some of the cell survival pathways RIPK1 participates in include NF-κB, Akt, and JNK.
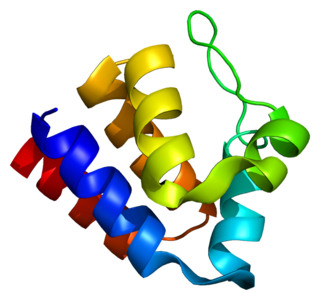
PYCARD, often referred to as ASC, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PYCARD gene. It is localized mainly in the nucleus of monocytes and macrophages. In case of pathogen infection, however, it relocalizes rapidly to the cytoplasm, perinuclear space, endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria and it is a key adaptor protein in activation of the inflammasome.

Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RIPK2 gene.

Serine protease HTRA2, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HTRA2 gene. This protein is involved in caspase-dependent apoptosis and in Parkinson's disease.

Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 11 also known as CARD-containing MAGUK protein 1 is a protein in the CARD-CC protein family that in humans is encoded by the CARD11 gene. CARD 11 is a membrane associated protein that is found in various human tissues, including the thymus, spleen, liver, and peripheral blood leukocytes. Similarly, CARD 11 is also found in abundance in various lines of cancer cells.

NLR family CARD domain-containing protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NLRC4 gene.

Leucine-rich repeats and death domain containing, also known as LRDD or p53-induced protein with a death domain (PIDD), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the LRDD gene.

For the membrane coated vesicle used in transport, see here.

Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 9 is an adaptor protein of the CARD-CC protein family, which in humans is encoded by the CARD9 gene. It mediates signals from pattern recognition receptors to activate pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, regulating inflammation. Homozygous mutations in CARD9 are associated with defective innate immunity against yeasts, like Candida and dermatophytes.