A tokamak is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field generated by external magnets to confine plasma in the shape of an axially symmetrical torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. The tokamak concept is currently one of the leading candidates for a practical fusion reactor.
This timeline of nuclear fusion is an incomplete chronological summary of significant events in the study and use of nuclear fusion.

The Joint European Torus (JET) was a magnetically confined plasma physics experiment, located at Culham Centre for Fusion Energy in Oxfordshire, UK. Based on a tokamak design, the fusion research facility was a joint European project with the main purpose of opening the way to future nuclear fusion grid energy. At the time of its design JET was larger than any comparable machine.
ITER is an international nuclear fusion research and engineering megaproject aimed at creating energy through a fusion process similar to that of the Sun. It is being built next to the Cadarache facility in southern France. Upon completion of construction of the main reactor and first plasma, planned for 2033–2034, ITER will be the largest of more than 100 fusion reactors built since the 1950s, with six times the plasma volume of JT-60SA in Japan, the largest tokamak operating today.

The French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission, or CEA, is a French public government-funded research organisation in the areas of energy, defense and security, information technologies and health technologies. The CEA maintains a cross-disciplinary culture of engineers and researchers, building on the synergies between fundamental and technological research.

Rokkasho is a village in Aomori Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 March 2023, the village had an estimated population of 9,845 in 4988 households, and a population density of 40 persons per km². The total area of the village is 252.68 square kilometres (97.56 sq mi).

Magnetic confinement fusion (MCF) is an approach to generate thermonuclear fusion power that uses magnetic fields to confine fusion fuel in the form of a plasma. Magnetic confinement is one of two major branches of controlled fusion research, along with inertial confinement fusion.

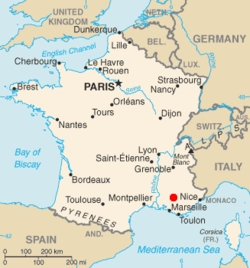
Saint-Paul-lès-Durance is a commune in the Bouches-du-Rhône department in Provence, southern France.

The Kurchatov Institute is Russia's leading research and development institution in the field of nuclear energy. It is named after Igor Kurchatov and is located at 1 Kurchatov Square, Moscow.

Marcoule Nuclear Site is a nuclear facility in the Chusclan and Codolet communes, near Bagnols-sur-Cèze in the Gard department of France, which is in the tourist, wine and agricultural Côtes-du-Rhône region. The plant is around 25 km north west of Avignon, on the banks of the Rhone.

The WEST, or Tungsten Environment in Steady-state Tokamak, is a French tokamak that originally began operating as Tore Supra after the discontinuation of TFR and of Petula. The original name came from the words torus and superconductor, as Tore Supra was for a long time the only tokamak of this size with superconducting toroidal magnets, allowing the creation of a strong permanent toroidal magnetic field. After a major upgrade to install tungsten walls and a divertor, the tokamak was renamed WEST.

Robert Aymar was a French physicist who was the Director General of CERN (2004–2008), serving a five-year term in that role.

The Saint-Laurent Nuclear Power Station is located in the commune of Saint-Laurent-Nouan in Loir-et-Cher on the Loire — 28 km (17 mi) upstream from Blois and 30 km (19 mi) downstream from Orléans.
The Tokamak de Fontenay-aux-Roses (TFR) was the first French tokamak, built in a research centre of the French Atomic Energy Commission (CEA) in Fontenay-aux-Roses, a commune in the southwestern suburbs of Paris. The project was spearheaded by Paul-Henri Rebut, and is sometimes jokingly referred to as the "Tokamak façon Rebut" – a pun on the name Rebut and the French word "rebut" meaning "rubbish".

Fusion for Energy(F4E) is a joint undertaking of the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom) that is responsible for the EU's contribution to the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), the world's largest scientific partnership aiming to demonstrate fusion as a viable and sustainable source of energy. The organisation is officially named European Joint Undertaking for ITER and the Development of Fusion Energy and was created under article 45 of the Treaty establishing the European Atomic Energy Community by the decision of the Council of the European Union on 27 March 2007 for a period of 35 years.

The Fort de Châtillon was a fortification located about 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) south of Paris in the communes of Châtillon-sous-Bagneux and Fontenay-aux-Roses. It was built in 1874 and was razed beginning in 1957, making way for expansion of the French nuclear research facility at Fontenay-aux-Roses.

The Culham Centre for Fusion Energy (CCFE) is the UK's national laboratory for fusion research. It is located at the Culham Science Centre, near Culham, Oxfordshire, and is the site of the Joint European Torus (JET), Mega Ampere Spherical Tokamak (MAST) and the now closed Small Tight Aspect Ratio Tokamak (START).

ASTRID was a proposal for a 600 MW sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor, proposed by the Commissariat à l'énergie atomique (CEA). It was to be built on the Marcoule Nuclear Site in France. It was the successor of the three French fast reactors Rapsodie, Phénix and Superphénix.
Robert Dautray was a French engineer, scientific director of the French Commissariat à l'Energie Atomique (CEA) and High Commissioner for Atomic Energy. He was a member of the French Academy of Sciences, section mechanical and computer sciences, and of the French Academy of Technology.
The history of France's civil nuclear program traces the evolution that led France to become the world's second largest producer of nuclear-generated electricity by the end of the 20th century, based on units deployed, installed capacity, and total production. Since the 1990s, nuclear energy has furnished three-fourths of France's electricity; by 2018, this portion had reached 71.7%.