Related Research Articles

Madeira, officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira, is an autonomous region of Portugal. It is an archipelago situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, in the region of Macaronesia, just under 400 kilometres (250 mi) north of the Canary Islands, 520 kilometres (320 mi) west of the Kingdom of Morocco and 805 kilometres (500 mi) southwest of mainland Portugal. Madeira sits on the African Tectonic Plate, although it is culturally, politically and ethnically associated with Europe, with its population predominantly descended from Portuguese settlers. Its population was 251,060 in 2021. The capital of Madeira is Funchal, on the main island's south coast.

Artemia is a genus of aquatic crustaceans also known as brine shrimp, Aqua Dragons or sea monkeys. It is the only genus in the family Artemiidae. The first historical record of the existence of Artemia dates back to the first half of the 10th century AD from Lake Urmia, Iran, with an example called by an Iranian geographer an "aquatic dog", although the first unambiguous record is the report and drawings made by Schlösser in 1757 of animals from Lymington, England. Artemia populations are found worldwide, typically in inland saltwater lakes, but occasionally in oceans. Artemia are able to avoid cohabiting with most types of predators, such as fish, by their ability to live in waters of very high salinity.

The Decapoda or decapods are an order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, and includes crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, and prawns. Most decapods are scavengers. The order is estimated to contain nearly 15,000 extant species in around 2,700 genera, with around 3,300 fossil species. Nearly half of these species are crabs, with the shrimp and Anomura including hermit crabs, porcelain crabs, squat lobsters making up the bulk of the remainder. The earliest fossils of the group date to the Devonian.

The Stenopodidea or boxer shrimps are a small group of decapod crustaceans. Often confused with Caridea shrimp or Dendrobranchiata prawns, they are neither, belonging to their own group.

Axiidea is an infraorder of decapod crustaceans. They are colloquially known as mud shrimp, ghost shrimp, or burrowing shrimp; however, these decapods are only distantly related to true shrimp. Axiidea and Gebiidea are divergent infraoders of the former infraorder Thalassinidea. These infraorders have converged ecologically and morphologically as burrowing forms. Based on molecular evidence as of 2009, it is now widely believed that these two infraorders represent two distinct lineages separate from one another. Since this is a recent change, much of the literature and research surrounding these infraorders still refers to the Axiidea and Gebiidea in combination as "thalassinidean" for the sake of clarity and reference. This division based on molecular evidence is consistent with the groupings proposed by Robert Gurney in 1938 based on larval developmental stages.

Retroplumidae is a family of heterotrematan crabs, placed in their own (monotypic) superfamily, Retroplumoidea.

Upogebia is a genus of mud shrimp, in the family Upogebiidae, containing the following species:

Callianassidae is a family of ghost shrimp crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Axiidea, within the order Decapoda.

The Paguridae are a family of hermit crabs of the order Decapoda. The king crabs, Lithodidae, are now widely understood to be derived from deep within the Paguridae, with some authors placing their ancestors within the genus Pagurus.

Palaemonidae is a family of shrimp in the order Decapoda. Many species are carnivores that eat small invertebrates, and can be found in any aquatic habitat except the deep sea. One significant genus is Macrobrachium, which contains commercially fished species. Others inhabit coral reefs, where they associate with certain invertebrates, such as sponges, cnidarians, mollusks, and echinoderms, as cleaner shrimps, parasites, or commensals. They generally feed on detritus, though some are carnivores and hunt tiny animals.

Parartemia is a genus of brine shrimp endemic to Australia. One species, P. contracta is listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. Parartemia contains the following species:

Squilla mantis is a species of mantis shrimp found in shallow coastal areas of the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Atlantic Ocean: it is also known as "pacchero" or "canocchia". Its abundance has led to it being the only commercially fished mantis shrimp in the Mediterranean.

Thalassina is a genus of mud lobsters found in the mangrove swamps of the Indian Ocean and western Pacific Ocean. Its nocturnal burrowing is important for the recycling of nutrients in the mangrove ecosystem, although it is sometimes considered a pest of fish and prawn farms.
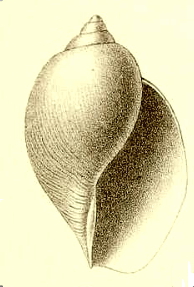
Harpovoluta charcoti is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Volutidae, the volutes.
Calliapagurops charcoti is a species of mud shrimp from Macaronesia. It is the only mud shrimp known from Madeira, and is the only species of mud shrimp thought to be a filter feeder.

Campylonotoidea is a superfamily of shrimp, containing the two families Campylonotidae and Bathypalaemonellidae. Fenner A. Chace considered it to be the sister group to the much larger superfamily Palaemonoidea, with which it shares the absence of endopods on the pereiopods, and the fact that the first pereiopod is thinner than the second. Using molecular phylogenetics, Bracken et al. proposed that Campylonotoidea may be closer to Atyoidea. There are sixteen described species in 3 genera; no fossils are known.

Spongicolidae is a family of glass sponge shrimp in the order Decapoda. There are about 8 genera and more than 40 described species in Spongicolidae. Apart from the shallows-dwelling genus Microprosthema, the family consists of glass sponge infauna, living within the body cavity of the sponge, presumably for life with a few other sponge shrimp. The sponge infaunal species most often inhabit Euplectella sponges, but can be found in Hyalonema sieboldii, Dactylocalyx pumiceus, Regradella phoenix, and R. okinosena.

Munididae is a family of squat lobsters, taxonomically separated from the family Galatheidae in 2010.

A shrimp (pl.: shrimp or shrimps is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – typically belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchiata of the order Decapoda, although some crustaceans outside of this order are also referred to as "shrimp".

Cinetorhynchus rigens is a species of shrimp in the family Rhynchocinetidae. Common names include mechanical shrimp, Atlantic dancing shrimp, red night shrimp and red coral shrimp. It occurs in shallow water in the tropical Atlantic Ocean.
References
- 1 2 Gary Poore & Michael Türkay (2010). "Calliapagurops de Saint Laurent, 1973". WoRMS. World Register of Marine Species . Retrieved December 9, 2011.
- ↑ Peter C. Dworschak & Peter Wirtz (2010). "Discovery of the rare burrowing shrimp Calliapagurops charcoti de Saint Laurent, 1973 (Decapoda: Axiidea: Callianassidae) in shallow water: first record of the infraorder for Madeira Island" (PDF). Zootaxa . 2691: 53–56.