
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus Oxycoccus of the genus Vaccinium. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species Vaccinium oxycoccos, while in North America, cranberry may refer to Vaccinium macrocarpon. Vaccinium oxycoccos is cultivated in central and northern Europe, while Vaccinium macrocarpon is cultivated throughout the northern United States, Canada and Chile. In some methods of classification, Oxycoccus is regarded as a genus in its own right. They can be found in acidic bogs throughout the cooler regions of the Northern Hemisphere.

Vaccinium is a common and widespread genus of shrubs or dwarf shrubs in the heath family (Ericaceae). The fruits of many species are eaten by humans and some are of commercial importance, including the cranberry, blueberry, bilberry (whortleberry), lingonberry (cowberry), and huckleberry. Like many other ericaceous plants, they are generally restricted to acidic soils.

Vaccinium vitis-idaea is a short evergreen shrub in the heath family that bears edible fruit, native to boreal forest and Arctic tundra throughout the Northern Hemisphere from Eurasia to North America. Lingonberries are picked in the wild and used to accompany a variety of dishes in Northern Baltoscandia, Russia, Canada and Alaska. Commercial cultivation is undertaken in the U.S. Pacific Northwest and in many other regions of the world.

Bilberries, or occasionally European blueberries, are a primarily Eurasian species of low-growing shrubs in the genus Vaccinium, bearing edible, dark blue berries. The species most often referred to is Vaccinium myrtillus L., but there are several other closely related species.
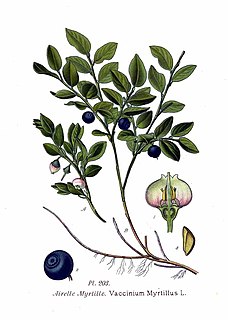
Vaccinium myrtillus is a species of shrub with edible fruit of blue color, commonly called "bilberry", "wimberry", "whortleberry", or European blueberry. It has much in common with the American blueberry. It is more precisely called common bilberry or blue whortleberry, to distinguish it from other Vaccinium relatives. Regional names include blaeberry, urts (Cornwall), hurtleberry, huckleberry, wimberry, whinberry, winberry, blueberry, and fraughan.

Vaccinium corymbosum, the northern highbush blueberry, is a North American species of blueberry which has become a food crop of significant economic importance. It is native to eastern Canada and the eastern and southern United States, from Ontario east to Nova Scotia and south as far as Florida and eastern Texas. It is also naturalized in other places: Europe, Japan, New Zealand, the Pacific Northwest of North America, etc. Other common names include blue huckleberry, tall huckleberry, swamp huckleberry, high blueberry, and swamp blueberry.

Vaccinium parvifolium, the red huckleberry, is a species of Vaccinium native to western North America, where it is common in forests from southeastern Alaska and British Columbia south through western Washington and Oregon to central California.

Vaccinium uliginosum is a Eurasian and North American flowering plant in the genus Vaccinium within the heath family.

Blueberries are perennial flowering plants with blue or purple–colored berries. They are classified in the section Cyanococcus within the genus Vaccinium.Vaccinium also includes cranberries, bilberries, huckleberries and Madeira blueberries. Commercial "blueberries" – including both wild ('lowbush') and cultivated ('highbush') blueberries – are all native to North America. The highbush blueberry varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s.

Huckleberry is a name used in North America for several plants in the family Ericaceae, in two closely related genera: Vaccinium and Gaylussacia. The huckleberry is the state fruit of Idaho.
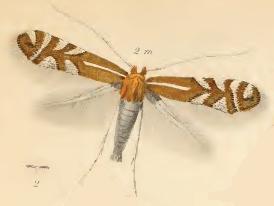
Phyllonorycter junoniella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from all of Europe, except Ireland, the Iberian Peninsula and the Balkan Peninsula.
Caloptilia geminata is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Japan (Honshū).

Cameraria nemoris is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from California and Maine in the United States.
Phyllonorycter diversella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Nova Scotia in Canada and Connecticut, Ohio, Kentucky, Maine and Vermont in the United States.
Parornix preciosella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Québec, Canada, and Connecticut, Pennsylvania and Vermont in the United States.
Parornix arbitrella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Pennsylvania and Maine in the United States.
Caloptilia anthobaphes is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Canada and the United States.

Caloptilia belfragella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Quebec and the United States.
Caloptilia burgessiella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Canada (Québec) and the United States.

Vaccinium oxycoccos is a species of flowering plant in the heath family. It is known as small cranberry, bog cranberry, swamp cranberry, or, particularly in Britain, just cranberry. It is widespread throughout the cool temperate northern hemisphere, including northern Europe, northern Asia and northern North America.











