
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any species of the genus Candida. When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it may be referred to as a yeast infection or thrush. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Yeast infections of the penis are less common and typically present with an itchy rash. Very rarely, yeast infections may become invasive, spreading to other parts of the body. This may result in fevers along with other symptoms depending on the parts involved.

Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species.
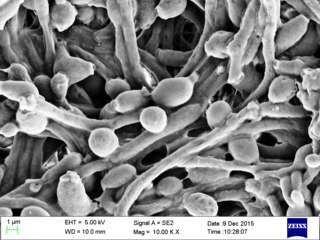
Candida albicans is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usually a commensal organism, but it can become pathogenic in immunocompromised individuals under a variety of conditions. It is one of the few species of the genus Candida that cause the human infection candidiasis, which results from an overgrowth of the fungus. Candidiasis is, for example, often observed in HIV-infected patients. C. albicans is the most common fungal species isolated from biofilms either formed on (permanent) implanted medical devices or on human tissue. C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis, and C. glabrata are together responsible for 50–90% of all cases of candidiasis in humans. A mortality rate of 40% has been reported for patients with systemic candidiasis due to C. albicans. By one estimate, invasive candidiasis contracted in a hospital causes 2,800 to 11,200 deaths yearly in the US. Nevertheless, these numbers may not truly reflect the true extent of damage this organism causes, given new studies indicating that C. albicans can cross the blood–brain barrier in mice.

Candida is a genus of yeasts. It is the most common cause of fungal infections worldwide and the largest genus of medically important yeast.

Dimorphic fungi are fungi that can exist in the form of both mold and yeast. This is usually brought about by change in temperature and the fungi are also described as thermally dimorphic fungi. An example is Talaromyces marneffei, a human pathogen that grows as a mold at room temperature, and as a yeast at human body temperature.
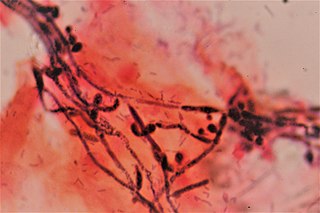
Vaginal yeast infection, also known as candidal vulvovaginitis and vaginal thrush, is excessive growth of yeast in the vagina that results in irritation. The most common symptom is vaginal itching, which may be severe. Other symptoms include burning with urination, a thick, white vaginal discharge that typically does not smell bad, pain during sex, and redness around the vagina. Symptoms often worsen just before a woman's period.
Candida blankii is a species of budding yeast (Saccharomycotina) in the family Saccharomycetaceae. The yeast may be a dangerous pathogen and resistant to treatment in human hosts. Research on the fungi has therapeutic, medical and industrial implications.
Candida theae is a species of yeast in the genus Candida. The species name means "tea". It was first isolated from Indonesian tea drinks and in Quito from clay pots that contained chicha dating from 680 CE.

The Kriegeriales are an order of fungi in the subdivision Pucciniomycotina. Most species are known only from their yeast states and can be found in a variety of habitats, ranging from arctic waters to tropical ferns. Hyphal states produce auricularioid basidia.
Candida keroseneae is a species of yeast in the genus Candida, family Saccharomycetaceae. Described as new to science in 2011, it was isolated from aviation fuel.
Candida tolerans is an ascomycetous yeast species first isolated from Australian Hibiscus flowers. It is small and a pseudomycelium is formed. The carbon and nitrogen assimilation pattern is similar to that of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii. Its type strain is UWO (PS) 98-115.5.
Candida bromeliacearum is a yeast species. Its type strain is UNESP 00-103T.
Candida zemplinina is a yeast species that is osmotolerant, psychrotolerant and ferments sweet botrytized wines. Its type strain is 10-372T.
Nakaseomyces bracarensis is an anamorphic yeast species with type strain 153MT.
Hanseniaspora clermontiae is a species of yeast in the family Saccharomycetaceae. It was first isolated from stem rot occurring in a lobelioid plant in Hawaii, and may be endemic to the Hawaiian Islands.
Hanseniaspora lachancei is a species of yeast in the family Saccharomycetaceae. It is associated with fermenting agave juice and a tequila production facility in Mexico.
Hanseniaspora meyeri is a species of yeast in the family Saccharomycetaceae. Samples of the species have been obtained worldwide from flowers, fruit flies, stem rot, and spoiled grape punch.






