
Deinotherium was a large prehistoric relative of modern-day elephants that appeared in the Middle Miocene and survived until the Early Pleistocene. During that time, it changed very little. In life, it probably resembled modern elephants, except it had downward-curving tusks attached to the lower jaw.

Deinotheriidae is a family of prehistoric elephant-like proboscideans that lived during the Cenozoic era, first appearing in Africa, then spreading across southern Asia (Indo-Pakistan) and Europe. During that time, they changed very little, apart from growing much larger in size; by the late Miocene, they had become the largest land animals of their time. Their most distinctive features were the downward-curving tusks on the lower jaw.

Chalicotherium is a genus of extinct odd-toed ungulates of the order Perissodactyla and family Chalicotheriidae, found in Europe, Africa, Asia, and North America from the Late Oligocene to Early Pliocene, 28.4–3.6 million years ago, existing for approximately 24.8 million years .
Adelphailurus is an extinct genus of saber-toothed cats of the family Felidae and tribe Metailurini which inhabited western North America during the Miocene, living from 10.3—5.33 Ma and existing for approximately 4.97 million years .
Herbstosaurus is the name given to a genus of pterosaurs that lived during the Late Jurassic period, in what is now Argentina. In 1969 Argentine paleobotanist Rafael Herbst in the province Neuquén at Picun Leufú dug up a piece of sandstone holding a number of disarticulated bones of a small reptile. At the time it was assumed the rock dated to the Middle Jurassic (Callovian), about 163 million years ago.

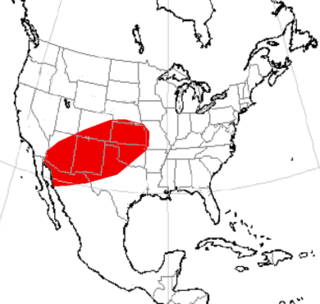
Ancylotherium is an extinct genus of the family Chalicotheriidae, subfamily Schizotheriinae, endemic to Europe, Asia, and Africa during the Late Miocene-Early Pleistocene, existing for approximately 7.2 million years .

Dissopsalis is a genus of extinct predatory mammals of the family Hyaenodontidae. The older species, D. pyroclasticus, lived in Kenya during the middle Miocene, while the type species, D. carnifex, ranged from, Pakistan, India to China during the middle to late Miocene.

Cormohipparion is an extinct genus of horse belonging to the tribe Hipparionini that lived in North America during the late Miocene to Pliocene.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1981.

Diplocynodon is an extinct genus of alligatoroid that lived during the Paleocene to middle Miocene in Europe. It looked very similar to the modern caiman in that it was small and had bony armour scutes covering its neck, back, belly, and tail. The longest Diplocynodon recovered was 4 feet in length and probably fed on small fish, frogs, and took insects when young.

Diceratherium is an extinct genus of rhinoceros endemic to North America, Europe, and Asia during the Oligocene through Miocene living from 33.9—11.6 mya, existing for approximately 22.3 million years . Mass estimates for the type species, D. armatum average around 1 t (2,200 lb)
Archaeohippus is an extinct three toed member of the family Equidae known from fossils of early Oligocene to middle Miocene age. The genus is noted for several distinct skeletal features. The skull possesses deeply pocketed fossa in a notably long preorbital region. The genus is considered an example of phyletic dwarfism with adults estimated at being on average 20kg in weight. This is in contrast to the most common equid of the period, Miohippus. Characters of the teeth show a mix of both primitive and advanced traits. The advanced traits are very similar to those shown in the genus Parahippus. The noted similarities of Archaeohippus and Parahippus show them to be descended from a common ancestor and are considered sister species.
Acherontemys is an extinct genus of turtle from Miocene of United States.
Chelydrops is an extinct genus of Chelydridae from Miocene of North America. Only one species is described, Chelydrops stricta.
Balanerodus is an extinct genus of alligatorid crocodylian. Fossils have been found from the Fitzcarrald Arch in the Peruvian Amazon and the La Victoria Formation of the Honda Group in Colombia and date back to the Friasian and Laventan regional South American land mammal ages of the Middle Miocene.
Charactosuchus is an extinct genus of crocodilian. It was assigned to the family Crocodylidae in 1988. Specimens have been found in Colombia, Brazil, Jamaica, and possibly Florida and South Carolina. It was gharial-like in appearance with its long narrow snout but bore no relation to them, being more closely related to modern crocodiles than to gharials.
Crenilepis is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived in the seas of present-day Europe during the Anisian stage of the Middle Triassic epoch.

Paracamelus is an extinct genus of camel in the family Camelidae. It originated in North America during the Middle Miocene but crossed the Beringian land bridge into Eurasia during the Late Miocene, approximately 7.5–6.5 Ma; its later range spanned from Spain and Italy to Chad and Shanxi Province, China. It is ancestral to living camels of the genus Camelus. A population remained in northern North America, which became the high Arctic camel, which survived until the Middle Pleistocene approximately 1 Ma.

Palaeomeryx is an extinct genus of Artiodactyla, of the family Palaeomerycidae, endemic to Europe and Asia from the Miocene epoch, 16.9 – 7.25 Ma, existing for approximately 9.65 million years .

Pliogonodon is an extinct genus of crocodylomorph. The type species, P. priscus, was named by Joseph Leidy in 1856. The holotype, known as USNM 7448, is a worn and broken tooth found from Phoebus Landing on the Cape Fear River in North Carolina. Although the age of the strata in which the tooth was found was not recorded, it is thought to have come from Miocene-age beds. The holotype and another tooth found at the same location are all that is known from the genus. The genus is considered a nomen dubium because of the lack of diagnostic features possessed by the teeth, and has been suggested to be synonymous with the alligatoroid Deinosuchus. Although Carroll (1988) assigned the genus to the basal neosuchian family Goniopholididae, current consensus is that Pligonodon is a Deinosuchus specimen.











