
Celtis is a genus of about 60–70 species of deciduous trees, commonly known as hackberries or nettle trees, in the hemp family Cannabaceae. It has a cosmopolitan distribution.
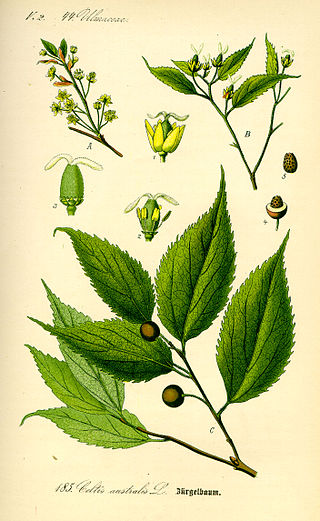
Celtis australis, the European nettle tree, Mediterranean hackberry, lote tree, or honeyberry, is a deciduous tree native to Southern Europe, North Africa, and Asia Minor. The tree was introduced to England in 1796.

Celtis occidentalis, commonly known as the common hackberry, is a large deciduous tree native to North America. It is also known as the nettletree, beaverwood, northern hackberry, and American hackberry. It is a moderately long-lived hardwood with a light-colored wood, yellowish gray to light brown with yellow streaks.

Pterocarpus angolensis is a species of Pterocarpus native to southern Africa, in Angola, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Eswatini, Tanzania, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zimbabwe, and Zambia. It is a protected tree in South Africa. The name Kiaat, although Afrikaans, is sometimes used outside South Africa as well. In Zimbabwe, depending on what region you are in, it is known as Mukwa( which it is also called in Zambia) or Mubvamaropa.

Adenium obesum, more commonly known as a desert rose, is a poisonous species of flowering plant belonging to the tribe Nerieae of the subfamily Apocynoideae of the dogbane family, Apocynaceae. It is native to the Sahel regions south of the Sahara, tropical and subtropical eastern and southern Africa, as well as the Arabian Peninsula. Other names for the flower include Sabi star, kudu, mock azalea, and impala lily. Adenium obesum is a popular houseplant and bonsai in temperate regions.

Tipuana tipu, also known as tipa, rosewood and pride of Bolivia, is a South American tree.

Tecoma stans is a species of flowering perennial shrub in the trumpet vine family, Bignoniaceae, that is native to the Americas. Common names include yellow trumpetbush, yellow bells, yellow elder, ginger Thomas. Tecoma stans is the official flower of the United States Virgin Islands and the floral emblem of The Bahamas.

Dichrostachys cinerea, known as sicklebush, Bell mimosa, Chinese lantern tree or Kalahari Christmas tree, is a legume of the genus Dichrostachys in the family Fabaceae.

Celtis sinensis is a species of flowering plant in the hemp family, Cannabaceae, that is native to slopes in East Asia.

Celtis mildbraedii is a species of forest tree in the family Cannabaceae. It was previously assigned to the family Ulmaceae. These trees grow in limited areas of South Africa, Mozambique and Zimbabwe. They are also found in forested areas from West Africa to Sudan, DRC, Angola and Tanzania. Common names include natal white stinkwood, red-fruited white-stinkwood and natal elm. This species is more common in Tropical Africa than in Southern Africa.

Celtis africana, the white stinkwood, is a deciduous tree in the family Cannabaceae. Its habit ranges from a tall tree in forest to a medium-sized tree in bushveld and open country, and a shrub on rocky soil. It occurs in Yemen and Somaliland and over large parts of Africa south of the Sahara. It is a common tree in the south and east of southern Africa, where the odour given off by freshly-cut green timber is similar to that of Ocotea bullata or black stinkwood.
Hypodaphnis is a monotypic genus of flowering plants of the family Lauraceae. Its only extant species, Hypodaphnis zenkeri, is native to Gabon. Although only one living species is known, fossils of some species of this genus are present in North America, especially in Northern Mexico. In most phylogenetic analysis, Hypodaphnis appears as the basal branch, the sister group of the rest of the family Lauraceae.
Celtis madagascariensis is a species of flowering plant endemic to Madagascar.

Trema lamarckianum, Lamarck's trema, West Indian nettle tree, or pain-in-the-back is a plant species in the genus Trema of the family Cannabaceae. It is a small evergreen shrub that is native of Florida and the West Indies. It has several common names such as pain-in-back, cabrilla and Lamarck trema. It is 6 m tall growing all year.

Celtis tournefortii, commonly known as the oriental hackberry is a deciduous tree in the genus Celtis.

Celtis ehrenbergiana, called the desert hackberry or spiny hackberry, is a plant species that has long been called C. pallida by many authors, including in the "Flora of North America" database. It is native to Arizona, Florida, New Mexico and Texas, and to Latin America as far south as central Argentina. It grows in dry locations such as deserts, brushlands, canyons, mesas and grasslands.

Celtis glabrata is a deciduous tree in the genus Celtis, native to parts of eastern Europe and western Asia. Its Turkish common name is dahum.

The Victoria Basin forest–grassland mosaic is an ecoregion that lies mostly in Uganda and extends into neighboring countries. The ecoregion is centered north and west of Lake Victoria, with an outlier on the border of Ethiopia and South Sudan.
Croton macrostachyus is a species of flowering plant native to the mountains of Sub-Saharan Africa.

Celtis gomphophylla is a species of flowering plant native to sub-Saharan Africa, Madagascar, and the Comoros.

















