Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually defined as consisting of seven countries: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama. Within Central America is the Mesoamerican biodiversity hotspot, which extends from southern Mexico to southeastern Panama. Due to the presence of several active geologic faults and the Central America Volcanic Arc, there is a high amount of seismic activity in the region, such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes, which has resulted in death, injury, and property damage.

Central America is commonly said to include Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama. This definition matches modern political borders. Central America begins geographically in Mexico, at the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, Mexico's narrowest point, and the former country of Yucatán (1841–1848) was part of Central America. At the other end, before its independence in 1903 Panama was part of South America, as it was a Department of Colombia. At times Belize, a British colony until 1981, where English instead of Spanish is spoken, and where the population is primarily of African origin, has been considered not part of (Spanish-speaking) Central America.

The Federal Republic of Central America, initially known as the United Provinces of Central America, was a sovereign state in Central America that existed between 1823 and 1839/1841. The republic was composed of five states, and a Federal District from 1835 to 1839. Guatemala City was its capital city until 1834, when the seat of government was relocated to San Salvador. The Federal Republic of Central America was bordered on the north by Mexico, on the south by Gran Colombia and on its eastern coastline by the Mosquito Coast and British Honduras, both claimed by the federal republic.

The Dominican Republic–Central America–United States Free Trade Agreement is a free trade agreement. Originally, the agreement encompassed the United States and the Central American countries of Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua, and was called CAFTA. In 2004, the Dominican Republic joined the negotiations, and the agreement was renamed CAFTA-DR.

The Greater Republic of Central America, later the United States of Central America, originally planned to be known as the Republic of Central America, was a short-lived political union between El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua, lasting from 1896 to 1898. It was an attempt to revive the failed Federal Republic of Central America that existed earlier in the century.
Operation Charly, was allegedly the code-name given to a program during the 1970s and 1980s undertaken by the junta in Argentina with the objective of providing military and counterinsurgency assistance to right-wing dictatorships and insurgents in Central America. According to Noam Chomsky, the operation was either headed by the Argentine military with the agreement of the United States Department of Defense, or was led by the US and used the Argentinians as a proxy.

Salvadoran passports are issued to citizens of El Salvador to travel outside the country.

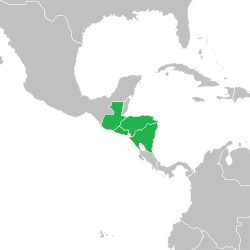
The Central American Integration System has been the economic and political organization of Central American states since 1 February 1993. On 13 December 1991, the ODECA countries signed the Protocol of Tegucigalpa, extending earlier cooperation for regional peace, political freedom, democracy and economic development. SICA's General Secretariat is in El Salvador.

This is an index of Central America-related articles. This index defines Central America as the seven nations of Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama.

Authoritarian General Tiburcio Carías Andino controlled Honduras during the Great Depression, until 1948. In 1955—after two authoritarian administrations and a general strike initiated by banana workers—young military reformists staged a coup that installed a provisional junta and paved the way for constituent assembly elections in 1957. This assembly appointed Ramón Villeda Morales as president and transformed itself into a national legislature with a 6-year term.
The modern history of Honduras is replete with large-scale disappearances of left-leaning union members, students and others. The legislature approved a new constitution in 1982, and the Liberal Party government of President Roberto Suazo Córdova took office. Suazo relied on United States support — including controversial social and economic development projects sponsored by the United States Agency for International Development — during a severe economic recession. According to the US State Department, "Honduras became host to the largest Peace Corps mission in the world, and non-governmental and international voluntary agencies proliferated."

Visitors to Montenegro must obtain a visa from one of the Montenegrin diplomatic missions unless they are citizens of one of the visa-exempt countries. Visa policy is regulated by Regulation on Visa Regime Act. Where there are no diplomatic or consular representations of Montenegro, visa requiring foreigners may obtain them from diplomatic or consular representations of Serbia, Bulgaria and Croatia.

Visitors to Venezuela must obtain a visa from one of the Venezuelan diplomatic missions, unless they come from one of the visa exempt countries.
Visitors are required to hold proof of sufficient funds to cover their stay and documents required for their next destination.
Visitors not holding return / onward tickets could be refused entry. Naturalized Venezuelan citizens, must hold in addition to their passport and National Identity Card, the original of the official decree of their naturalization issued by the Venezuelan government.
All visitors must hold a passport valid for 6 months.
The Central America-4 passport is a common-design passport issued by the Central America-4 Border Control Agreement member states. Although the design had been in use by Nicaragua and El Salvador since the mid-1990s, it became the norm for the CA-4 in January 2006. The main features are the navy blue cover with the words "Centroamérica" and a map of Central America, with the territory of the issuing country highlighted in gold. Costa Rica, not a C-4 Agreement member, also uses a passport with the inscription "América Central", retained from the Federal Republic of Central America and included in its coat of arms. Despite their similar appearances, passports from each of the C-4 member countries do not have equal mobility rankings. El Salvador's passport ranks 36th on the Henley visa restrictions index and allows visa free or visa on entry access to 136 countries and territories, while Nicaragua's passport ranks 42nd and allows access to 128.

Visitors to El Salvador must obtain a visa from one of the Salvadoran diplomatic missions, unless they come from one of the visa exempt countries. All visitors must hold a passport valid for 6 months.
Visitors to Guatemala must obtain a visa from one of the Guatemalan diplomatic missions, unless they come from one of the visa exempt countries.

Visitors to Honduras must obtain a visa from one of the Honduran diplomatic missions unless they come from one of the visa-exempt countries. All visitors must hold a passport valid for three months.

Visitors to Nicaragua must obtain a visa from one of the Nicaraguan diplomatic missions, unless they come from one of the visa exempt countries or countries that can obtain a visa on arrival. All visitors must hold a passport valid for 6 months.

The following lists events that happened during 2020 in Central America: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama.
The 1923 Central American Treaty of Peace and Amity, officially known as the General Treaty of Peace and Amity, 1923, was a treaty signed by the five nations of Central America in 1923 which established that all nations would denounce and not recognize any government which arose in any of the five signatory nations through illegal means. The treaty remained effective from its signing on 7 February 1923 until it was denounced by the Central American Court of Justice in 1934.