The Andean passport is a passport for South American countries that are members of the Andean Community of Nations (ACN).
The Andean passport was created in June 2001 pursuant to ACN Decisión 504. This passport is based on a standard model containing harmonised features of nomenclature and security based on the recommendations of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). The member states of the ACN agreed to phase in new Andean passports bearing the official name of the regional body in Spanish by January 2005, although previously issued national passports will be valid until their expiry date.
The passport is effective in Bolivia, Ecuador, Peru and formerly, in Venezuela. Because Venezuela left the ACN in 2006, the country no longer issues Andean passports, and it is most likely to start issuing a new MERCOSUR-style passport as the country became a full member of that organization. Venezuelan ACN passports issued are valid until its expiration date. The last Venezuelan ACN passports were more likely to expire between 2011 and 2012.
The Andean passport features:

A passport is an official travel document issued by a government that contains a person's identity. A person with a passport can travel to and from foreign countries more easily and access consular assistance. A passport certifies the personal identity and nationality of its holder. It is typical for passports to contain the full name, photograph, place and date of birth, signature, and the expiration date of the passport. While passports are typically issued by national governments, certain subnational governments are authorised to issue passports to citizens residing within their borders.

The Andean Community is a free trade area with the objective of creating a customs union comprising the South American countries of Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. The trade bloc was called the Andean Pact until 1996 and came into existence when the Cartagena Agreement was signed in 1969. Its headquarters are in Lima, Peru.

A biometric passport is a traditional passport that has an embedded electronic microprocessor chip which contains biometric information that can be used to authenticate the identity of the passport holder. It uses contactless smart card technology, including a microprocessor chip and antenna embedded in the front or back cover, or centre page, of the passport. The passport's critical information is printed on the data page of the passport, repeated on the machine readable lines and stored in the chip. Public key infrastructure (PKI) is used to authenticate the data stored electronically in the passport chip, supposedly making it expensive and difficult to forge when all security mechanisms are fully and correctly implemented.

The Czech passport is an international travel document issued to nationals of the Czech Republic, and may also serve as proof of Czech citizenship. Besides enabling the bearer to travel internationally and serving as indication of Czech citizenship, the passport facilitates the process of securing assistance from Czech consular officials abroad or other European Union member states in case a Czech consular is absent, if needed.

A South African passport is a travel document issued to citizens of South Africa for the purpose of international travel. It allows the bearer to travel in foreign countries in accordance with visa requirements, and facilitates the process of securing assistance from South African consular officials abroad, if necessary. A South African passport is a valid proof of citizenship document according to South African nationality law. As of 2018, citizens of South Africa enjoyed visa-free access to 100 countries, of which some may require pre-travel registration according to the Visa Restrictions Index.

A Philippine passport is both a travel document and a primary national identity document issued to citizens of the Philippines. It is issued by the Department of Foreign Affairs (DFA) and Philippine diplomatic missions abroad, with certain exceptions.

Greek passports are issued to Greek citizens for the purpose of international travel. Biometric passports have been issued since 26 August 2006, with old-style passports being declared invalid as of 1 January 2007. Since June 2009, the passport's RFID chip includes two index fingerprints as well as a high-resolution JPEG image of the passport holder. Every Greek citizen is also a citizen of the European Union. The passport, along with the national identity card allows for free rights of movement and residence in any of the states of the European Union, European Economic Area, and Switzerland.

Mexican passport is the passport issued to Mexican citizens for the purpose of travelling abroad. The Mexican passport is also an official ID and proof of Mexican citizenship. According to the 2021 Henley Visa Restrictions Index, holders of a Mexican passport can visit 164 countries without a visa, placing Mexico in the 22nd rank in terms of global travel freedom.

Venezuelan passports are issued to citizens of Venezuela to travel outside the country. Biometric passports have been issued since July 2007, with a RFID chip containing a picture and fingerprints; passports issued earlier remained valid until they expired.

Japanese passports are issued to Japanese citizens to facilitate international travel. From 2018 to 2022, it was the world's most powerful passport. As of July 2023 however, it is ranked as the third most powerful passport, with holders able to travel visa-free to 189 countries and territories.

A Peruvian passport is a travel document issued to citizens of Peru with the purpose of identification and to travel outside the country. It is issued by the Superintendencia Nacional de Migraciones, the Peruvian immigration and naturalization authority, which is part of the Ministry of the Interior. The Peruvian passport has the benefit of "visa free" status for member nations of the Andean Community and Mercosur, as well as several Central American nations.

A Chilean passport is an identity document issued to citizens of Chile to facilitate international travel. Chilean passports are valid for worldwide travel and facilitate the access to consular services whilst abroad. They are issued by the Registro Civil e Identificación.

Vietnamese passports are issued to citizens of Vietnam to facilitate international travel. They enable the bearer to exit and re-enter Vietnam freely; to travel to and from other countries in accordance with visa requirements, and secure assistance from Vietnamese consular officials when abroad, if necessary.

The Brazilian passport is the official document for foreign travel issued by the federal government, through the Federal Police.

The Kenyan passport is issued to Kenyan citizens in accordance with the Constitution of Kenya, 2010 and as provided for in the Kenya Citizens and Immigration Act that commenced on 30 August 2011. In addition issuance process is regulated by Legal Notice No. 64. If eligible, an individual can apply for a New Passport, Renewal Passport and Replacement Passport. Passports are issued by the Department of Immigration. The department is under the Ministry of Interior and Coordination of National Government. Kenyan passports are usually used as a form of ID as well and would be rated as second to the Kenyan national ID card. Before Kenya got independence from Britain, British passports were used.

The Azerbaijani passport is issued by the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Azerbaijan to the citizens of Azerbaijan for international travel. Ordinary passports are valid for 10 years from the date of issue and contain 34 visa pages. Passport content is printed both in Azerbaijani and in English.

The passport of Bangladesh is an ICAO compliant, machine-readable and biometric e-passport issued for the purpose of travel to foreign countries by the passport holder. Bangladesh is the first country in South Asia to issue e-passports for all eligible citizens. The passport booklet is manufactured, printed and issued by the Department of Immigration & Passports of the Ministry of Home Affairs. This electronic microprocessor chip embedded e-passport has forty-one different security features, including holographic images embossed in thin-film laminate, which change colour under light and appear to move. Demographic and biometric information of the e-passport holder are stored on the chip inside the e-passport. This information includes the fingerprints of all ten fingers of the passport holder; the iris scan of both eyes; a color photograph of the face of the bearer; their digital signature; etc. Depending on the age of the applicant, the e-passport is valid for either five years or ten years and it is distributed by the Government of The People's Republic of Bangladesh, or by any of its overseas diplomatic missions, to eligible Bangladeshi nationals who are citizens by birth, by descent or through naturalization.
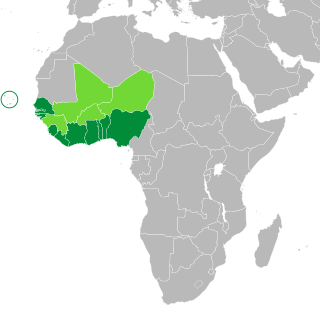
The ECOWAS passport is a common passport document for several countries in West Africa.

An Interpol Travel Document is a travel document issued to Interpol officers for travel to Interpol member countries. They are intended to reduce response times for personnel deployed to assist with transnational criminal investigations, major events or emergency situations by waiving normal visa requirements.

Passports of the EFTA member states are passports issued by the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) member states Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. EFTA is in this article used as a common name for these countries.