
Tuxtla Gutiérrez is the capital and the largest city of the Mexican southeastern state of Chiapas. It is the seat of the municipality of the same name, the most developed and populated in the state. A busy government, commercial and services-oriented city, Tuxtla had one of the fastest-growing rates in Mexico in the last 40 years. Unlike many other areas in Chiapas, it is not a major tourist attraction, but a transportation hub for tourists coming into the state, with a large airport and a bus terminal.

The Arizona bark scorpion is a small light brown scorpion common to the Sonoran Desert in the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. An adult male can reach 8 cm in length (3.14 inches), while a female is slightly smaller, with a maximum length of 7 cm (2.75 inches).

The Buthidae are the largest family of scorpions, containing about 80 genera and over 800 species as of mid-2008. Its members are known as, for example, fat-tailed scorpions and bark scorpions. A few very large genera are known, but a high number of species-poor or monotypic ones also exist. New taxa are being described at a rate of several to several dozen new species per year. They occur in the warmer parts of every major landmass on Earth, except on New Zealand. Together with four other families the Buthidae make up the superfamily Buthoidea. The family was established by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1837.

Centruroides is a genus of scorpions of the family Buthidae. Several North American species are known by the common vernacular name bark scorpion. Numerous species are extensively found throughout the southern United States, Mexico, Central America, the Antilles and northern South America. Some are known for their interesting patterning or large size ; most if not all fluoresce strongly under ultraviolet illumination, except after moulting. They contain several highly venomous species, and fatalities are known to occur. The venom of the Mexican scorpion Centruroides limpidus limpidus contains the neurotoxins Cll1 and Cll2.
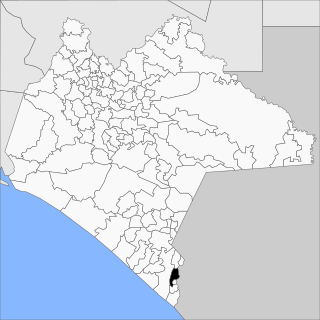
Tuxtla Chico is a town and one of the 119 municipalities of Chiapas, in southern Mexico.

Santiago Tuxtla is a small city and municipality in the Los Tuxtlas region of southern Veracruz, Mexico. The area was originally part of lands granted to Hernán Cortés by the Spanish Crown in 1531. The city was founded in 1525, but it did not gain municipal status until 1932. Today, the municipality is poor and agricultural, but is home to several unique traditions such as the Santiago Tuxtla Fair and the Acarreo de Niño Dios, when images of the Child Jesus are carried in procession several times during the Christmas season. It is also home to the Museo Regional Tuxteco which houses much of the area's Olmec artifacts, including a number of colossal heads and other monumental stone works. The city's main plaza hosts the largest Olmec colossal head in Mexico, thus making it famous.

San Andrés Tuxtla is a city and municipality in the south of the Mexican state of Veracruz. The city is the largest in the Los Tuxtlas region. It was founded after an eruption of the San Martín Volcano pushed people into this valley during the early colonial period. Since the 19th century, the area has been the center of Mexico's production of fine tobacco, mostly used in the making of cigars. The best known cigar producer here, Te Amo, is considered to be one of the best brands in the world.

Chiapas Fútbol Club, commonly known as Jaguares de Chiapas, was a football club based in Tuxtla Gutiérrez, Mexico, that played in the Mexican football league system Liga MX. The team played their home matches at the Estadio Víctor Manuel Reyna.
Centruroides farri is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae.
Centruroides jaragua is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae.
Centruroides marcanoi is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae.
Centruroides sissomi is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae.
Centruroides barbudensis is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae.
Centruroides flavopictus is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. It is native to Mexico.
Centruroides fulvipes is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. It is native to Mexico.

Centruroides ochraceus is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. It is native to Mexico.
Centruroides baergi is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae.
Centruroides chamulaensis is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. It is native to Mexico.
Centruroides tecomanus is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae. It is native to Mexico.
Ergtoxin is a family of toxins that can be isolated from the venom of several members of the Mexican scorpion genus of Centruroides. These toxins target hERG potassium channels.








