
The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of unicellular algae found in freshwater and moist terrestrial environments, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. The stated number of species in the group varies from about 14 to 26. Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants, they form the Archaeplastida.

Charales is an order of freshwater green algae in the division Charophyta, class Charophyceae, commonly known as stoneworts. Depending on the treatment of the genus Nitellopsis, living (extant) species are placed into either one family (Characeae) or two. Further families are used for fossil members of the order. Linnaeus established the genus Chara in 1753.

The Trebouxiophyceae are a class of green algae, in the division Chlorophyta. Their circumscription within the green algae is not well established due to the need for more genetic studies at higher levels within the group.

Bryopsidales is an order of green algae, in the class Ulvophyceae.

Hormotila is a genus of green algae in the family Chaetophoraceae.

Staurodesmus is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Desmidiaceae.
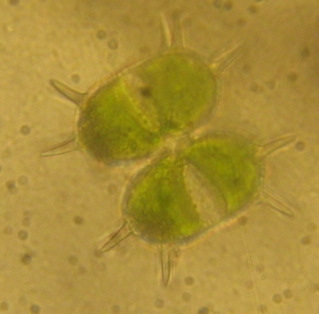
Xanthidium is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Desmidiaceae.

Sykidion is a genus of green algae. Pseudoneochloris is a synonym of this genus. As of March 2022, Sykidion was the only genus in the family Sykidiacaeae, which was the only family in the order Sykidiales.

Chlorokybus is a multicellular (sarcinoid) genus of basal green algae or charophyte. It has been classified as the sole member of the family Chlorokybaceae, which is the sole member of the order Chlorokybales, in turn the sole member of the class Chlorokybophyceae. It grows on soil and rock surfaces, and is rare.
Mesostigma is a genus of unicellular biflagellate freshwater green algae, with a single species Mesostigma viride, covered by an outer layer of basket‐like scales instead of a cell wall. AlgaeBase classifies it as the only genus in the family Mesostigmataceae, the only family in the order Mesostigmatales, the only order in the class Mesostigmatophyceae. It is now considered to be one of the earliest diverging members of green plants/algae (Viridiplantae).
Pyrenomonas is a genus of cryptomonad.
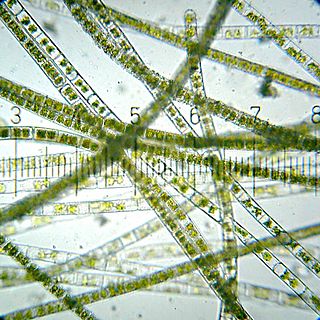
Zygnema is a genus of freshwater filamentous thalloid alga comprising about 100 species. A terrestrial species, Z. terrestre, is known from India. Zygnema grows as a free-floating mass of filaments, although young plants may be found anchored to streambeds with a holdfast. The filaments form a yellow-green to bright green colored tangled mat, and are composed of elongate barrel-shaped cells, each with two star-shaped (stellate) chloroplasts arrayed along the axis of the cell.
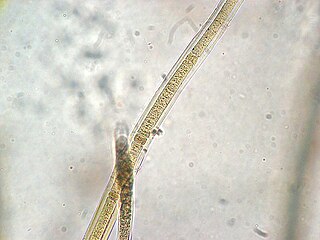
The Scytonemataceae are a family of filamentous, heterocystous cyanobacteria within the order Nostocales. The family is known from freshwater, marine, and terrestrial environments, where it grows in colonies attached to the substrate. Akinetes are not known, and the members of the family are known to reproduce with nonheterocystous hormogonia.

Abas is an extinct genus of diatoms consisting of only one known species: Abas wittii. Originally observed as a fossil genus classified with diatom spore forms under the name Syringidium. Abas was observed to be live from the Eocene to Oligocene epoch appearing in tropical sites.
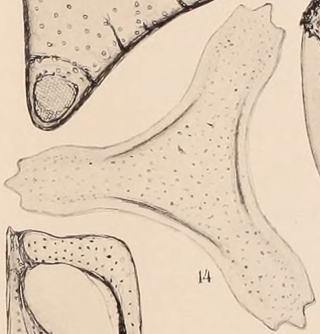
Trinacria is an extinct genus of diatoms present during the early Eocene, named for its triskelion shape.
Chrysomerophyceae is a monotypic class of photosynthetic heterokont eukaryotes.













