| Charisma arenacea | |
|---|---|
 | |
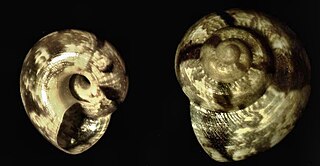
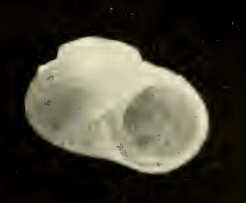
| Original image of a shell of Charisma arenacea | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| Clade: | Vetigastropoda |
| Superfamily: | Trochoidea |
| Family: | Trochidae |
| Genus: | Charisma |
| Species: | C. arenacea |
| Binomial name | |
| Charisma arenacea (Pritchard & Gatliff, 1902) | |
| Synonyms | |
Leptothyra arenaceaPritchard & Gatliff, 1902 | |
Charisma arenacea, common name the sandy charisma, is a species of extremely small sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails. [1]
In biology, a species ( ) is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. While these definitions may seem adequate, when looked at more closely they represent problematic species concepts. For example, the boundaries between closely related species become unclear with hybridisation, in a species complex of hundreds of similar microspecies, and in a ring species. Also, among organisms that reproduce only asexually, the concept of a reproductive species breaks down, and each clone is potentially a microspecies.

Sea snail is a common name for snails that normally live in salt water, in other words marine gastropods. The taxonomic class Gastropoda also includes snails that live in other habitats, such as land snails and freshwater snails. Many species of sea snails are edible and exploited as food sources by humans.
Family is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy; it is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as being the "walnut family".