
The Chicago River is a system of rivers and canals with a combined length of 156 miles (251 km) that runs through the city of Chicago, including its center. Though not especially long, the river is notable because it is one of the reasons for Chicago's geographic importance: the related Chicago Portage is a link between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River Basin, and ultimately the Gulf of Mexico.

The Illinois and Michigan Canal connected the Great Lakes to the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico. In Illinois, it ran 96 miles (154 km) from the Chicago River in Bridgeport, Chicago to the Illinois River at LaSalle-Peru. The canal crossed the Chicago Portage, and helped establish Chicago as the transportation hub of the United States, before the railroad era. It was opened in 1848. Its function was partially replaced by the wider and deeper Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal in 1900, and it ceased transportation operations with the completion of the Illinois Waterway in 1933.

The Calumet River is a system of heavily industrialized rivers and canals in the region between the south side of Chicago, Illinois, and the city of Gary, Indiana. Historically, the Little Calumet River and the Grand Calumet River were one, the former flowing west from Indiana into Illinois, then turning back east to its mouth at Lake Michigan at Marquette Park in Gary. Now the system is part of the Chicago Area Waterway System and through the use of locks flows away from Lake Michigan to the Cal-Sag Channel.

The Indiana Harbor and Ship Canal is an artificial waterway on the southwest shore of Lake Michigan, in East Chicago, Indiana, which connects the Grand Calumet River to Lake Michigan. It consists of two branch canals, the 1.25 miles (2.01 km) Lake George Branch and the 2 miles (3.2 km) long Grand Calumet River Branch which join to form the main Indiana Harbor Canal.

The Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal, historically known as the Chicago Drainage Canal, is a 28-mile-long (45 km) canal system that connects the Chicago River to the Des Plaines River. It reverses the direction of the Main Stem and the South Branch of the Chicago River, which now flows out of Lake Michigan rather than into it. The related Calumet-Saganashkee Channel does the same for the Calumet River a short distance to the south, joining the Chicago canal about halfway along its route to the Des Plaines. The two provide the only navigation for ships between the Great Lakes Waterway and the Mississippi River system.

Jones Island is an industrialized peninsula in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. It began as a marsh island between the Milwaukee and Kinnickinnic rivers, and now forms the city's inner harbor design.

Northern Indiana is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the northern third of the U.S. state of Indiana and borders the states of Illinois to the west, Michigan to the north, and Ohio to the east. Spanning the state's northernmost 26 counties, its main population centers include Northwest Indiana, Michiana, and the Fort Wayne metropolitan area.

Ports of Indiana-Burns Harbor is an active maritime port owned by the State of Indiana. The state legislature created the Indiana Port Commission in 1961 to research and act upon opening maritime ports on Indiana's Lake Michigan shoreline as well as the Ohio River.
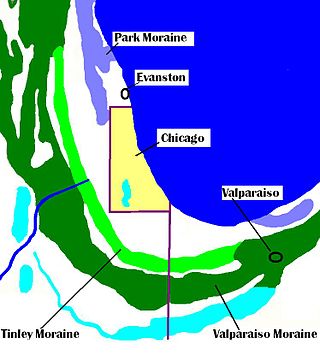
The Tinley Moraine is a moraine around the Lake Michigan basin in North America. It was formed during the Wisconsin Glaciation and is younger than the higher and wider terminal moraine called the Valparaiso Moraine, which is located farther from the lake than the Tinley Moraine. Compared to the Valparaiso Moraine, the Tinley Moraine is much narrower and occupies a similar swath, about 6 miles (10 km) closer to Lake Michigan, and passes through the communities of Flossmoor, Western Springs, and Arlington Heights. The moraine was named after the village of Tinley Park, a village southwest of Chicago that lies on the moraine.

The Indiana Harbor East Breakwater Light is an active aid to navigation that marks the end of a breakwater on the east side of the Indiana Harbor and Ship Canal where it enters Lake Michigan.

The Chicago Yacht Club is located in Chicago, Illinois. "CYC" is well known as being the Organizing Authority for the Chicago Yacht Club Race to Mackinac held each July. CYC also organizes dozens of other sailboat races and regattas throughout the boating season, which is usually considered May 1 to October 31 in the Chicago area. CYC has two club houses or stations, one at Monroe Harbor and one at Belmont Harbor.

The Chicago Lakefront Trail (LFT) is a 18.5-mile-long (29.8 km) partial shared-use path for walking, jogging, skateboarding, and cycling, located along the western shore of Lake Michigan in Chicago, Illinois. The trail passes through and connects Chicago's four major lakefront parks along with various beaches and recreational amenities. It also serves as a route for bicycle, skateboard and personal transporter commuters. On busy summer days 70,000 people use the trail.
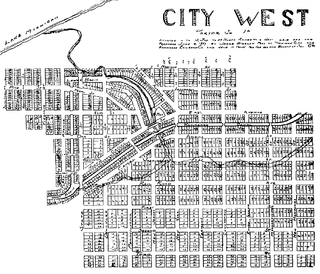
City West was a village in Porter County, Indiana, US, located on the shore of Lake Michigan approximately 10 miles west of Michigan City, Indiana. It was situated near the mouth of Fort Creek, now known as Dunes Creek, which empties into Lake Michigan near the Indiana Dunes State Park swimming beach. It was located near the former site of Petit Fort.
Indiana City was a notional community in northern Lake County, Indiana, at the mouth of the Grand Calumet River. It was located in present-day Marquette Park in Miller Beach, near the southern tip of Lake Michigan. Indiana City was one of a handful of early contenders to be a port city on southern Lake Michigan, alongside Chicago, City West, and Michigan City.

The Chicago Area Waterway System (CAWS) is a complex of natural and artificial waterways extending through much of the Chicago metropolitan area, covering approximately 87 miles altogether. It straddles the Chicago Portage and is the sole navigable inland link between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River and makes up the northern end of the Illinois Waterway.

The Grand Calumet River is a 13.0-mile-long (20.9 km) river that flows primarily into Lake Michigan. Originating in Miller Beach in Gary, it flows through the cities of Gary, East Chicago and Hammond, as well as Calumet City and Burnham on the Illinois side. The majority of the river's flow drains into Lake Michigan via the Indiana Harbor and Ship Canal, sending about 1,500 cubic feet (42 m3) per second of water into the lake. A smaller part of the flow, at the river's western end, enters the Calumet River, and through the Illinois ultimately drains into the Mississippi River.
The Chicago Maritime Museum is a maritime society and museum dedicated to the study and memorialization of Chicago's maritime traditions. The museum's webpage asserts that Lake Michigan and the Chicago River were key factors in Chicago's growth toward status as a world-class city, and pays tribute to Congress for granting lake frontage in 1818 to the infant state of Illinois. The museum opened in June 2016.
The Ogden Slip is a canal and harbor in Chicago, Illinois.















