Marriageable age, marriage age, or the age of marriage is the general age, a legal age or the minimum age marriage. Age and other prerequisites to marriage vary between jurisdictions, but in the vast majority of jurisdictions, the marriage age as a right is set at the age of majority. Nevertheless, most jurisdictions allow marriage at a younger age with parental or judicial approval, especially if the female is pregnant. Among most indigenous cultures, people marry at fifteen, the age of sexual maturity for both the male and the female. In industrialized cultures, the age of marriage is most commonly 18 years old, but there are variations, and the marriageable age should not be confused with the age of majority or the age of consent, though they may be the same.
Child marriage is a marriage or domestic partnership, formal or informal, between a child and an adult, or between a child and another child.

Forced marriage is a marriage in which one or more of the parties is married without their consent or against their will. A marriage can also become a forced marriage even if both parties enter with full consent if one or both are later forced to stay in the marriage against their will.

Women in the Democratic Republic of the Congo have not attained a position of full equality with men, with their struggle continuing to this day. Although the Mobutu regime paid lip service to the important role of women in society, and although women enjoy some legal rights, custom and legal constraints still limit their opportunities.

Teenage marriage is the union of two adolescents between the ages of 13 and 19. Many factors contribute to teenage marriage, such as love, teenage pregnancy, religion, security, wealth, family, peer pressure, arranged marriage, economic and/or political reasons, social advancement, and cultural reasons. Studies have shown that teenage married couples are often disadvantaged, may come from broken homes, may have little education, and work in low-status jobs and lead a poor economic life in comparison with those that marry after adolescence.
Women in Yemen suffer from gender-based discrimination due to the highly patriarchal character of Yemeni society. Although the government of Yemen has made efforts to improve the rights of women, many cultural and religious norms stand in the way of equal rights for women. Poor enforcement of the legislation by the Yemeni government exacerbates the problem.
According to UNICEF, child marriage is the "formal marriage or informal union before age 18", and it affects more girls than boys. In Afghanistan, up to 57% of girls are married before they are 19. The most common ages for girls to get married are 15 and 16. Factors such as gender dynamics, family structure, cultural, political, and economic perceptions/ideologies all play a role in determining if a girl is married at a young age.
Prostitution in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is legal but related activities are prohibited. The Congolese penal code punishes pimping, running a bawdy house or brothel, the exploitation of debauchery or prostitution, as well as forced prostitution. Activities that incite minors or promote the prostitution of others have been criminalised. The government does little to enforce the law. During the colonial era and the years that followed independence, the Ministry of Health issued calling cards identifying professional sex workers and provided them with medical health checks. However, this system was abandoned in the 1980s. Public order laws are sometimes used against sex workers. Street prostitutes report harassment, violence and extortion from the police. UNAIDS estimated there are 2.9 million sex workers in the country.

International Day of the Girl Child is an international observance day declared by the United Nations; it is also called the Day of Girls and the International Day of the Girl. October 11, 2012, was the first Day of the Girl Child. The observation supports more opportunity for girls and increases awareness of gender inequality faced by girls worldwide based upon their gender. This inequality includes areas such as access to education, nutrition, legal rights, medical care, and protection from discrimination, violence against women and forced child marriage. The celebration of the day also "reflects the successful emergence of girls and young women as a distinct cohort in development policy, programming, campaigning and research."

Women in South Sudan are women who live in and are from South Sudan. Since the Independence of South Sudan on 9 July 2011, these women have gained more power but still face issues of inequality. Many women in this area do not have adequate access to health resources and education. While these women often face inequality, there has been progress since South Sudan's official declaration of independence. In recent years, this inequality has gained national attention and people have become more interested in the issue of child marriage that this area faces. Along with this, there has started to be a focus on the very high level of maternal mortality in South Sudan. With a maternal mortality rate of 789 deaths per 100,000 live births, South Sudan has one of the highest rates in the world.

Women in Niger are women that are from or live in the West African country of Niger. These women belong to a population in which 98% are practitioners of Islam. Laws adopted by the government of Niger to protect the rights of Nigerien women are most often based on Muslim beliefs.

Child soldiers in Africa refers to the military use of children under the age of 18 by national armed forces or other armed groups in Africa. Typically, this classification includes children serving in non-combatant roles, as well as those serving in combatant roles. In 2008, it was estimated that 40 percent of child soldiers worldwide were in Africa, and the use of child soldiers in armed conflict was increasing faster than any other continent. Additionally, average age of children recruited as soldiers appears to be decreasing. As of 2017, the UN listed that seven out of fourteen countries recruiting and using child soldiers in state forces or armed groups were in Africa: Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Mali, Nigeria, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan.
The Islamic Republic of Iran signed the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) in 1991 and ratified it in 1994. Upon ratification, Iran made the following reservation: "If the text of the Convention is or becomes incompatible with the domestic laws and Islamic standards at any time or in any case, the Government of the Islamic Republic shall not abide by it."

There are over 57 million children in Bangladesh. Although Bangladesh has an increasingly stable and growing economy, half of these children continue to live below the international poverty line. Protection, health, education, nutrition, safe water and hygiene are considered basic rights for all children, yet children in Bangladesh face issues on all these fronts. 26 million children live below the national poverty line. Bangladesh has one of the highest rates of child-marriage in the world. 66% of women were married before they turned 18. 13% of children are involved in child labor. Child laborers are frequently denied an education and are vulnerable to violence and abuse. Less than 80% of students enrolled in grade one complete primary school. High drop-out rates and poor quality teaching and learning are serious problems for primary schools.

Child marriage is a marriage or union between a child under the age of 18 to another child or to an adult. Child marriage is common in a multitude of African countries. In South Sudan, child marriage is a growing epidemic. Child marriage in South Sudan is driven by socioeconomic factors such as poverty and gender inequality. Current figures state that South Sudan is one of the leading countries in the world when it comes to child marriage. Child marriage has negative consequences for children, including health problems and lower education rates for South Sudanese girls. Many initiatives have been taken to combat child marriage in South Sudan, but the presence of societal norms and instability continues to drive its presence in the nation.
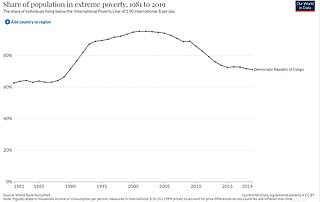
Poverty is widespread and unchecked across the 26 provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Despite being the second-largest country in Africa, with an approximate area of 2.3 million square kilometres (890,000 sq mi), and being endowed with rich natural resources, the DRC is the second-poorest country in the world. The average annual income is only $449 US dollars. In 2019, the United Nations (UN) Human Development Index (HDI) ranked the DRC as the 175th least-developed country out of 189 countries with an HDI of 0.480. In 2023, almost 75% of Congolese people live on less than $2.15 a day, defined as the threshold for extreme poverty.
Child marriage in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the eighteenth highest in the world. In a child marriage, one or both parties are under the age of eighteen years old. In the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), 37% of girls are married before they turn eighteen, and 10% of girls are married before age fifteen. Though significantly less than the rate of child marriage for girls, 6% of boys in the DRC are married before age eighteen.
In 2017 in Ethiopia, 40% of girls are married off before 18 years old. 14% are married before they turn 15. Ethiopia is the 16th highest nation in the world for child marriage.
Child Marriage in Mali is an ongoing practice. Mali has the 5th highest prevalence of female child marriages globally. A study conducted by the Institut National de la Statistique in 2018 found that 15% of 15-19 year old girls were married by the age of 15, a reduction compared to the 18% of women aged 20-49 who had been married by that age. The same study also shows that while 53% of women aged 20-49 were married before the age of 18, the same was true for only 3% of men, with no recorded marriages of boys aged 15 or younger.
UNICEF's Early Marriage: A Harmful Traditional Practice report characterizes child marriage as a harmful institution that often exposes young women in developing nations to damaging domestic, health, and sexual conditions. The report also highlights the practice as a human rights violation. In World Vision's "Before She's Ready: 15 Places Girls Marry by 15", the organization highlights the socioeconomic consequences of child marriage on girls, noting that many girls are forced to stop their schooling as a result of their marriages. With the denial of education, girl brides are often not able to make income as adults or become politically active citizens.










