
The spectral bat, also called the great false vampire bat or Linnaeus's false vampire bat, is a large, carnivorous leaf-nosed bat found in Mexico, Central America, and South America. It is the only member of the genus Vampyrum; its closest living relative is the big-eared woolly bat. It is the largest bat species in the New World, as well as the largest carnivorous bat: its wingspan is 0.7–1.0 m (2.3–3.3 ft). It has a robust skull and teeth, with which it delivers a powerful bite to kill its prey. Birds are frequent prey items, though it may also consume rodents, insects, and other bats.

The lesser horseshoe bat is a type of small European and North African insectivorous bat, related to its larger cousin, the greater horseshoe bat. As with all horseshoe bats, the species gets its name from its distinctive horseshoe-shaped noseleaf.

The family Natalidae, or funnel-eared bats, are found from Mexico to Brazil and the Caribbean islands. The family has three genera, Chilonatalus, Natalus and Nyctiellus. They are slender bats with unusually long tails and, as their name suggests, funnel-shaped ears. They are small, at only 3.5 to 5.5 cm in length, with brown, grey, or reddish fur. Like many other bats, they are insectivorous, and roost in caves.

The broad-eared bat or broad-tailed bat is a species of free-tailed bat from the Americas.

The tricolored big-eared bat is a bat species from South and Central America.

The yellow-throated big-eared bat or orange-throated bat(Lampronycteris brachyotis) is a species of bat from South and Central America, where it ranges from southern Mexico to Brazil. It is monotypic within the genus Lampronycteris. A frugivore and insectivore, it is found in lowland forest up to an elevation of 700 m. Its activity is greatest in the first two hours after sunset, and peaks again after midnight.

Hodgson's bat, also called the copper-winged bat or black-and-orange myotis, is a species of vesper bat in the genus Myotis, the mouse-eared bats. Favouring mountain forests, it is found throughout Central, Southeast, and East Asia, from Afghanistan to Taiwan. It is about 5 centimetres (2.0 in) long and is distinguished from most other species of bat in this range by its yellowish colouration.

The greater mouse-eared bat is a European species of bat in the family Vespertilionidae.

Rafinesque's big-eared bat, sometimes known as the southeastern big-eared bat, is a species of vesper bat native to the southeastern United States.

Nyctophilus arnhemensis, known as the northern or Arnhem long-eared bat, is a species of Chiroptera (bats) native to northern regions of Australia. The distribution range is from north-western Queensland to northern Western Australia.

The long-eared myotis is a species of vesper bat in the suborder Microchiroptera. It can be found in western Canada, the western United States, and Baja California in Mexico.

The eastern small-footed bat is a species of vesper bat. It can be found in southern Ontario and Quebec in Canada and in mountainous portions of the eastern United States from New England to northern Georgia, and westward to northern Arkansas. It is among the smallest bats in eastern North America and is known for its small feet and black face-mask. Until recently, all North American small-footed Myotis were considered to be "Myotis leibii". The western population is now considered to be a separate species, Myotis ciliolabrum. The Eastern small-footed bat is rare throughout its range, although the species may be locally abundant where suitable habitat exists. Studies suggest white-nose syndrome has caused declines in their populations. However, most occurrences of this species have only been counted within the past decade or two and are not revisited regularly, making their population status difficult to assess. Additionally, most bat populations in the Eastern U.S. have been monitored using surveys conducted in caves and mines in the winter, but Eastern small-footed bats hibernate in places that make them unlikely to be encountered during these surveys. Perhaps as a result, the numbers of Eastern small-footed bats counted in winter tend to be low and they are relatively variable compared to other species of bats. Many biologists believe the species is stable, having declined little in recent times, but that it is vulnerable due to its relatively restricted geographic range and habitat needs.

The Kolar leaf-nosed bat, or leafletted leaf-nosed bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is endemic to India. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests and caves. It is found in only one cave in India, and its population is less than 200 individuals.
The Bahaman funnel-eared bat is a species of bat in the family Natalidae.
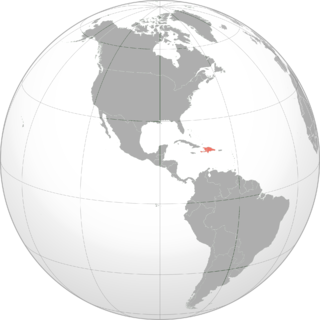
The Hispaniolan greater funnel-eared bat is a species of funnel-eared bat endemic to the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean. First described in 1902, it has a complex taxonomic history, with some authors identifying multiple subspecies, now recognised as the separate species Natalus primus and Natalus jamaicensis, and others considering Natalus major to be itself a subspecies of Natalus stramineus. It lives primarily in caves and feeds on insects.

The Cuban greater funnel-eared bat is a species of funnel-eared bat. It is endemic to a cave in westernmost Cuba. it is a member of the family Natalidae.
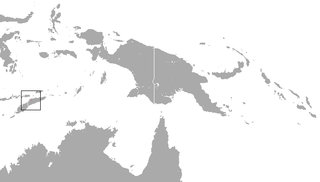
The Timorese horseshoe bat is a species of bat native to Timor-Leste.

The Mexican greater funnel-eared bat is a species of bat found in Central America. While initially and currently described as a species, from 1959–2006 it was considered a subspecies of the Mexican funnel-eared bat, Natalus stramineus.
The Turkestani long-eared bat, Otonycteris leucophaea, is a species of bat found in Asia. Though it was initially described in 1873 as a species, for many years it was considered synonymous with the desert long-eared bat, Otonycteris hemprichii. Recently, it was recognized as a distinct species once again.
Ward's long-eared bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is found in mountainous regions of South Asia and adjoining regions.

















