
Convolvulaceae, known commonly as the bindweed or morning glory family, is a family of about 60 genera and more than 1,650 species of mostly herbaceous vines, but also trees, shrubs and herbs, and also including the sweet potato and a few other food tubers.
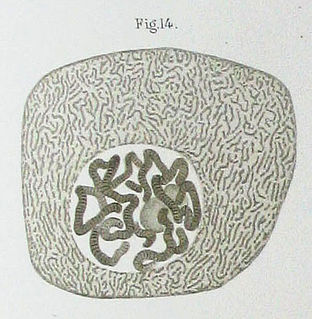
Polytene chromosomes are large chromosomes which have thousands of DNA strands. They provide a high level of function in certain tissues such as salivary glands of insects

The Chironomidae comprise a family of nematoceran flies with a global distribution. They are closely related to the Ceratopogonidae, Simuliidae, and Thaumaleidae. Many species superficially resemble mosquitoes, but they lack the wing scales and elongated mouthparts of the Culicidae. An example of mosquito-resembling species is Tokunagayusurika akamusi.

Chironomus plumosus, also known as the buzzer midge, is a species of nonbiting midge (Chironomidae) that occurs throughout areas in the Northern Hemisphere.

Chironomus is a genus of nonbiting midges in the subfamily Chironominae of the bloodworm family, Chironomidae, containing several cryptic species that can only be distinguished by experts based on the characteristics of their giant chromosomes. The larvae of several species inhabit the profundal zone where they can reach relatively high densities. They use a combination of hemoglobin-like proteins and undulatory movements in their burrows to obtain oxygen in poorly oxygenated habitats.

Psectrotanypus is a genus of non-biting midges in the subfamily Tanypodinae of the bloodworm family Chironomidae. Psectrotanypus varius is known to occur in very polluted waters with only few other accompanying species such as Chironomus plumosus.
Chironomus riparius, also known as Chironomus thummi and commonly known as the harlequin fly, is a species of non-biting midge. Their larvae are known by the common name of blood worm due to their red colouration. It is common in both North America and Europe. The species was described in 1804 by Johann Wilhelm Meigen. C. riparius has been used extensively as a model for genome structure analysis in insects and is also used in toxicology tests and functional developmental genetic studies. Both their adult and larval forms have been implicated as disease vectors but are also an important part of freshwater food chains.
Gammaentomopoxvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Poxviridae, in the subfamily Entomopoxvirinae. Lepidoptera and orthoptera insects serve as natural hosts. There are currently six species in this genus including the type species Chironomus luridus entomopoxvirus.

Chironomus zealandicus, commonly known as the New Zealand midge, common midge, or non-biting midge, is an insect of the Chironomidae family. The worm like larvae known to fisherman and a common name as blood worm due to its red color and elongated blood gills.
Chironomus ochreatus is a species in the family Chironomidae ("midges"), in the order Diptera ("flies").
Chironomus tuberculatus is a species of midge in the family Chironomidae.

Chironomus crassicaudatus is a species of midge in the family Chironomidae.
Chironomus atrella is a species of midge in the family Chironomidae.
Chironomus atroviridis is a species of midge in the family Chironomidae.
Chrysotoxum chinook is a species of syrphid fly in the family Syrphidae.

Glyptotendipes barbipes is a species of midge in the family Chironomidae. It is found in Europe.
Chironomus whitseli is a species of midge in the family Chironomidae.
Chironomus annularius is a species of non-biting midge in the family Chironomidae. It is usually found in regions with bodies of fresh water but can be found in almost every environment. It tends to form "hotspots" around specific areas. The species is distinguished by the size of its chromosomes and the lack of a proboscis.
Animal Ethics is a nonprofit organization formed to promote discussion and debate around issues in animal ethics and to provide information and resources for animal advocates. They also do outreach work in several countries on the issue of speciesism. Their aim is to create a world where moral consideration is extended to all sentient beings. The organization's website covers topics such as speciesism, sentience, veganism and wild animal suffering and has content translated into several languages.







