
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others. The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all pesticide use globally. Most pesticides are used as plant protection products, which in general protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. In general, a pesticide is a chemical or biological agent that deters, incapacitates, kills, or otherwise discourages pests. Target pests can include insects, plant pathogens, weeds, molluscs, birds, mammals, fish, nematodes (roundworms), and microbes that destroy property, cause nuisance, or spread disease, or are disease vectors. Along with these benefits, pesticides also have drawbacks, such as potential toxicity to humans and other species.

Silent Spring is an environmental science book by Rachel Carson. Published on September 27, 1962, the book documented the environmental harm caused by the indiscriminate use of DDT, a pesticide used by soldiers during WW2. Carson accused the chemical industry of spreading disinformation, and public officials of accepting the industry's marketing claims unquestioningly.

Insecticides are pesticides used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Acaricides, which kill mites and ticks, are not strictly insecticides, but are usually classified together with insecticides. The major use of Insecticides is agriculture, but they are also used in home and garden, industrial buildings, vector control and control of insect parasites of animals and humans. Insecticides are claimed to be a major factor behind the increase in the 20th-century's agricultural productivity. Nearly all insecticides have the potential to significantly alter ecosystems; many are toxic to humans and/or animals; some become concentrated as they spread along the food chain.

A pesticide poisoning occurs when pesticides, chemicals intended to control a pest, affect non-target organisms such as humans, wildlife, plants, or bees. There are three types of pesticide poisoning. The first of the three is a single and short-term very high level of exposure which can be experienced by individuals who die by suicide, as well as pesticide formulators. The second type of poisoning is long-term high-level exposure, which can occur in pesticide formulators and manufacturers. The third type of poisoning is a long-term low-level exposure, which individuals are exposed to from sources such as pesticide residues in food as well as contact with pesticide residues in the air, water, soil, sediment, food materials, plants and animals.

Carbaryl is a chemical in the carbamate family used chiefly as an insecticide. It is a white crystalline solid previously sold under the brand name Sevin, which was a trademark of the Bayer Company. The Sevin trademark has since been acquired by GardenTech, which has eliminated carbaryl from most Sevin formulations. Union Carbide discovered carbaryl and introduced it commercially in 1958. Bayer purchased Aventis CropScience in 2002, a company that included Union Carbide pesticide operations. Carbaryl was the third-most-used insecticide in the United States for home gardens, commercial agriculture, and forestry and rangeland protection. As a veterinary drug, it is known as carbaril (INN).
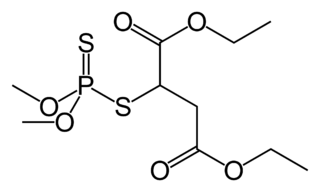
Malathion is an organophosphate insecticide which acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. In the USSR, it was known as carbophos, in New Zealand and Australia as maldison and in South Africa as mercaptothion.

Chlorpyrifos (CPS), also known as chlorpyrifos ethyl, is an organophosphate pesticide that has been used on crops, animals, and buildings, and in other settings, to kill several pests, including insects and worms. It acts on the nervous systems of insects by inhibiting the acetylcholinesterase enzyme. Chlorpyrifos was patented in 1966 by Dow Chemical Company.

Pest control is the regulation or management of a species defined as a pest; such as any animal, plant or fungus that impacts adversely on human activities or environment. The human response depends on the importance of the damage done and will range from tolerance, through deterrence and management, to attempts to completely eradicate the pest. Pest control measures may be performed as part of an integrated pest management strategy.

Paraquat (trivial name; ), or N,N′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride (systematic name), also known as methyl viologen, is an organic compound with the chemical formula [(C6H7N)2]Cl2. It is classified as a viologen, a family of redox-active heterocycles of similar structure. This salt is one of the most widely used herbicides. It is quick-acting and non-selective, killing green plant tissue on contact. It is also toxic (lethal) to human beings and animals due to its redox activity, which produces superoxide anions. It has been linked to the development of Parkinson's disease and is banned in 58 countries.
Pesticides vary in their effects on bees. Contact pesticides are usually sprayed on plants and can kill bees when they crawl over sprayed surfaces of plants or other areas around it. Systemic pesticides, on the other hand, are usually incorporated into the soil or onto seeds and move up into the stem, leaves, nectar, and pollen of plants.

An agrochemical or agrichemical, a contraction of agricultural chemical, is a chemical product used in industrial agriculture. Agrichemical refers to biocides and synthetic fertilizers. It may also include hormones and other chemical growth agents.

Agricultural wastewater treatment is a farm management agenda for controlling pollution from confined animal operations and from surface runoff that may be contaminated by chemicals in fertilizer, pesticides, animal slurry, crop residues or irrigation water. Agricultural wastewater treatment is required for continuous confined animal operations like milk and egg production. It may be performed in plants using mechanized treatment units similar to those used for industrial wastewater. Where land is available for ponds, settling basins and facultative lagoons may have lower operational costs for seasonal use conditions from breeding or harvest cycles. Animal slurries are usually treated by containment in anaerobic lagoons before disposal by spray or trickle application to grassland. Constructed wetlands are sometimes used to facilitate treatment of animal wastes.

The Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) is a United States federal law that set up the basic U.S. system of pesticide regulation to protect applicators, consumers, and the environment. It is administered and regulated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the appropriate environmental agencies of the respective states. FIFRA has undergone several important amendments since its inception. A significant revision in 1972 by the Federal Environmental Pesticide Control Act (FEPCA) and several others have expanded EPA's present authority to oversee the sales and use of pesticides with emphasis on the preservation of human health and protection of the environment by "(1) strengthening the registration process by shifting the burden of proof to the chemical manufacturer, (2) enforcing compliance against banned and unregistered products, and (3) promulgating the regulatory framework missing from the original law".

Aldicarb is a carbamate insecticide which is the active substance in the pesticide Temik. It is effective against thrips, aphids, spider mites, lygus, fleahoppers, and leafminers, but is primarily used as a nematicide. Aldicarb is a cholinesterase inhibitor which prevents the breakdown of acetylcholine in the synapse. Aldicarb is considered "extremely hazardous" by the EPA and World Health Organization and has been banned in more than 100 countries. In case of severe poisoning, the victim dies of respiratory failure.

Endosulfan is an off-patent organochlorine insecticide and acaricide that is being phased out globally. It became a highly controversial agrichemical due to its acute toxicity, potential for bioaccumulation, and role as an endocrine disruptor. Because of its threats to human health and the environment, a global ban on the manufacture and use of endosulfan was negotiated under the Stockholm Convention in April 2011. The ban took effect in mid-2012, with certain uses exempted for five additional years. More than 80 countries, including the European Union, Australia, New Zealand, several West African nations, the United States, Brazil, and Canada had already banned it or announced phase-outs by the time the Stockholm Convention ban was agreed upon. It is still used extensively in India and China despite laws against its use. It is also used in a few other countries. It is produced by the Israeli firm Makhteshim Agan and several manufacturers in India and China. On May 13, 2011, the India Supreme Court ordered a ban on the production and sale of endosulfan in India, pending further notice.
Neonicotinoids are a class of neuro-active insecticides chemically similar to nicotine, developed by scientists at Shell and Bayer in the 1980s.

The Food Quality Protection Act (FQPA), or H.R.1627, was passed unanimously by Congress in 1996 and was signed into law by President Bill Clinton on August 3, 1996. The FQPA standardized the way the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) would manage the use of pesticides and amended the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act and the Federal Food Drug and Cosmetic Act. It mandated a health-based standard for pesticides used in foods, provided special protections for babies and infants, streamlined the approval of safe pesticides, established incentives for the creation of safer pesticides, and required that pesticide registrations remain current.

Acephate is an organophosphate foliar and soil insecticide of moderate persistence with residual systemic activity of about 10–15 days at the recommended use rate. It is used primarily for control of aphids, including resistant species, in vegetables and in horticulture. It also controls leaf miners, caterpillars, sawflies, thrips, and spider mites in the previously stated crops as well as turf, and forestry. By direct application to mounds, it is effective in destroying imported fire ants.

The environmental effects of pesticides describe the broad series of consequences of using pesticides. The unintended consequences of pesticides is one of the main drivers of the negative impact of modern industrial agriculture on the environment. Pesticides, because they are toxic chemicals meant to kill pest species, can affect non-target species, such as plants, animals and humans. Over 98% of sprayed insecticides and 95% of herbicides reach a destination other than their target species, because they are sprayed or spread across entire agricultural fields. Other agrochemicals, such as fertilizers, can also have negative effects on the environment.
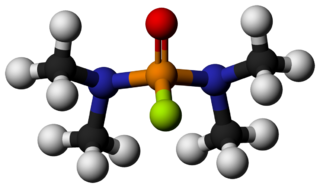
Dimefox, also known as TL-792 or T-2002, is a highly toxic organophosphate insecticide. In its pure form it is a colourless liquid with a fishy odour. Dimefox was first produced in 1940 by the group of Gerhard Schrader in Germany. It was historically used as a pesticide, but has been deemed obsolete or discontinued for use by the World Health Organization due to being an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase. It is not guaranteed that all commercial use of this compound ceased, but in most countries it is no longer registered for use as a pesticide. It is considered an extremely hazardous substance as defined by the United States Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act.

















