
Chlorophyta is a taxon of green algae informally called chlorophytes. The name is used in two very different senses, so care is needed to determine the use by a particular author. In older classification systems, it is a highly paraphyletic group of all the green algae within the green plants (Viridiplantae) and thus includes about 7,000 species of mostly aquatic photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. In newer classifications, it is the sister clade of the streptophytes/charophytes. The clade Streptophyta consists of the Charophyta in which the Embryophyta emerged. In this latter sense the Chlorophyta includes only about 4,300 species. About 90% of all known species live in freshwater. Like the land plants, green algae contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b and store food as starch in their plastids.

The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of unicellular algae found in freshwater and moist terrestrial environments, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. The stated number of species in the group varies from about 14 to 26. Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants, they form the Archaeplastida.

The chlorarachniophytes are a small group of exclusively marine algae widely distributed in tropical and temperate waters. They are typically mixotrophic, ingesting bacteria and smaller protists as well as conducting photosynthesis. Normally they have the form of small amoebae, with branching cytoplasmic extensions that capture prey and connect the cells together, forming a net. They may also form flagellate zoospores, which characteristically have a single subapical flagellum that spirals backwards around the cell body, and walled coccoid cells.

Charales is an order of freshwater green algae in the division Charophyta, class Charophyceae, commonly known as stoneworts. Depending on the treatment of the genus Nitellopsis, living (extant) species are placed into either one family (Characeae) or two. Further families are used for fossil members of the order. Linnaeus established the genus Chara in 1753.

The green algae are a group of chlorophyll-containing autotrophic eukaryotes consisting of the phylum Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister group that contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as a sister of the Zygnematophyceae. Since the realization that the Embryophytes emerged within the green algae, some authors are starting to include them. The completed clade that includes both green algae and embryophytes is monophyletic and is referred to as the clade Viridiplantae and as the kingdom Plantae. The green algae include unicellular and colonial flagellates, most with two flagella per cell, as well as various colonial, coccoid (spherical), and filamentous forms, and macroscopic, multicellular seaweeds. There are about 22,000 species of green algae, many of which live most of their lives as single cells, while other species form coenobia (colonies), long filaments, or highly differentiated macroscopic seaweeds.

Eustigmatophytes are a small group of eukaryotic forms of algae that includes marine, freshwater and soil-living species.

The prasinophytes are a group of unicellular green algae. Prasinophytes mainly include marine planktonic species, as well as some freshwater representatives. The prasinophytes are morphologically diverse, including flagellates with one to eight flagella and non-motile (coccoid) unicells. The cells of many species are covered with organic body scales; others are naked. Well studied genera include Ostreococcus, considered to be the smallest free-living eukaryote, and Micromonas, both of which are found in marine waters worldwide. Prasinophytes have simple cellular structures, containing a single chloroplast and a single mitochondrion. The genomes are relatively small compared to other eukaryotes . At least one species, the Antarctic form Pyramimonas gelidicola, is capable of phagocytosis and is therefore a mixotrophic algae.
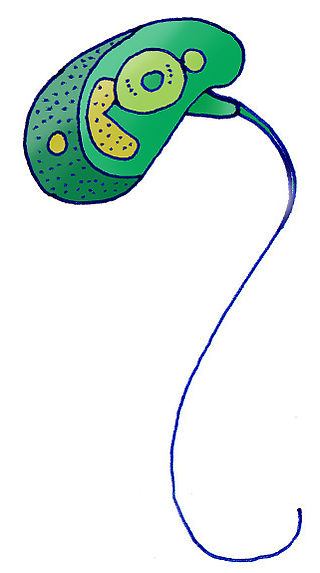
Mamiellales are an order of green algae in the class Mamiellophyceae. Their cells and flagella are covered with spiderweb-like scales of several types. Some species lack scales but possess pigments similar to those of the scale-bearing species.
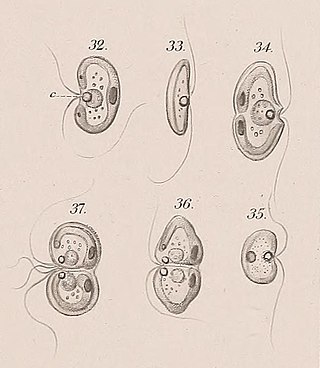
Nephroselmis is a genus of green algae. It has been placed in the family Nephroselmidaceae, although a 2009 study suggests that it should be separated into its own class, Nephroselmidophyceae. One species can be an endosymbiont of Hatena arenicola.
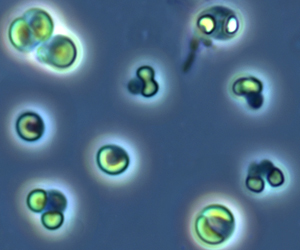
Picocystis is a monotypic genus of green algae, the sole species is Picocystis salinarum. It is placed within its own class, Picocystophyceae in the division Chlorophyta.

Prasinoderma is a genus of green algae in the phylum Prasinodermophyta. Both species in the genus are unicellular, but P. coloniale forms loose sticky colonies.

Bolidophyceae is a class of photosynthetic heterokont picophytoplankton, and consist of less than 20 known species. They are distinguished by the angle of flagellar insertion and swimming patterns as well as recent molecular analyses. Bolidophyceae is the sister taxon to the diatoms (Bacillariophyceae). They lack the characteristic theca of the diatoms, and have been proposed as an intermediate group between the diatoms and all other heterokonts.

Chlorokybus is a multicellular (sarcinoid) genus of basal green algae or charophyte. It has been classified as the sole member of the family Chlorokybaceae, which is the sole member of the order Chlorokybales, in turn the sole member of the class Chlorokybophyceae. It grows on soil and rock surfaces, and is rare.
Mesostigma is a genus of unicellular biflagellate freshwater green algae, with a single species Mesostigma viride, covered by an outer layer of basket‐like scales instead of a cell wall. AlgaeBase classifies it as the only genus in the family Mesostigmataceae, the only family in the order Mesostigmatales, the only order in the class Mesostigmatophyceae. It is now considered to be one of the earliest diverging members of green plants/algae (Viridiplantae).

Picophagea, also known as Synchromophyceae, is a class of photosynthetic stramenopiles. The chloroplast of the Synchromophyceae are surrounded by two membranes and arranged in a way where they share the outer pair of membranes. The entire chloroplast complex is surrounded by an additional two outer membranes.

Triparma is a genus of unicellular algae in the family Triparmaceae in the order Parmales. They form siliceous plates on the cell surface that aid in identification. Triparma is distinguished by its possession of three shield plates, three triradiate girdle plates, a triradiate girdle plate with notched ends, and a small ventral plate. It was first described by Booth & Marchant in 1987 and the holotype is Triparma columacea.

The Parmales are an order of marine microalgae within the Bolidophyceae class. They are found worldwide and characterized by a cell wall composed of 5-8 interlocking silica plates with distinct forms. They were initially thought to be loricate choanoflagellates but were shown to be a separate phyla entirely upon the discovery of chloroplasts, placing it among the photosynthetic stramenopiles.

Tetraparma is a genus of unicellular algae in the family Triparmaceae in the order Parmales. They form siliceous plates on the cell surface that aid in identification. Tetraparma is distinguished by its possession of three shield plates that may have everted rims, three triradiate girdle plates, a triradiate dorsal plate with notched ends, and a large ventral plate. It was first described by Booth & Marchant in 1987 and the holotype is Triparma columacea.

Chloropicophyceae is a class of green algae in the division Chlorophyta that, along with Picocystophyceae, coincides with the traditional "prasinophyte clade VII". Chloropicophyceae has a single order, Chloropicales with a single family, Chloropicaceae.

Chloropicon is a genus of green algae in the class Chloropicophyceae.
















