
Bile, or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver and stored and concentrated in the gallbladder. After eating, this stored bile is discharged into the duodenum.
The bile acid sequestrants are a group of resins used to bind certain components of bile in the gastrointestinal tract. They disrupt the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids by combining with bile constituents and preventing their reabsorption from the gut. In general, they are classified as hypolipidemic agents, although they may be used for purposes other than lowering cholesterol. They are used in the treatment of chronic diarrhea due to bile acid malabsorption.

Deoxycholic acid is a bile acid. Deoxycholic acid is one of the secondary bile acids, which are metabolic byproducts of intestinal bacteria. The two primary bile acids secreted by the liver are cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid. Bacteria metabolize chenodeoxycholic acid into the secondary bile acid lithocholic acid, and they metabolize cholic acid into deoxycholic acid. There are additional secondary bile acids, such as ursodeoxycholic acid. Deoxycholic acid is soluble in alcohol and acetic acid. When pure, it comes in a white to off-white crystalline powder form.

Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), also known as ursodiol, is a secondary bile acid, produced in humans and most other species from metabolism by intestinal bacteria. It is synthesized in the liver in some species, and was first identified in bile of bears of genus Ursus, from which its name derived. In purified form, it has been used to treat or prevent several diseases of the liver or bile ducts.
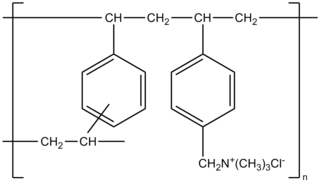
Colestyramine (INN) or cholestyramine (USAN) is a bile acid sequestrant, which binds bile in the gastrointestinal tract to prevent its reabsorption. It is a strong ion exchange resin, which means it can exchange its chloride anions with anionic bile acids in the gastrointestinal tract and bind them strongly in the resin matrix. The functional group of the anion exchange resin is a quaternary ammonium group attached to an inert styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer.

Enterohepatic circulation refers to the circulation of biliary acids, bilirubin, drugs or other substances from the liver to the bile, followed by entry into the small intestine, absorption by the enterocyte and transport back to the liver. Enterohepatic circulation is an especially important concept in the field of toxicology as many lipophilic xenobiotics undergo this process causing repeated liver damage.

Cholestasis is a condition where bile cannot flow from the liver to the duodenum. The two basic distinctions are an obstructive type of cholestasis where there is a mechanical blockage in the duct system that can occur from a gallstone or malignancy, and metabolic types of cholestasis which are disturbances in bile formation that can occur because of genetic defects or acquired as a side effect of many medications. Classification is further divided into acute or chronic and extrahepatic or intrahepatic.

Bile bears, sometimes called battery bears, are bears kept in captivity to harvest their bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder, which is used by some traditional Asian medicine practitioners. It is estimated that 12,000 bears are farmed for bile in China, South Korea, Laos, Vietnam, and Myanmar. Demand for the bile has been found in those nations as well as in some others, such as Malaysia and Japan.
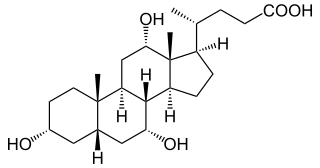
Cholic acid, also known as 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid is a primary bile acid that is insoluble in water, it is a white crystalline substance. Salts of cholic acid are called cholates. Cholic acid, along with chenodeoxycholic acid, is one of the two major bile acids produced by the liver, where it is synthesized from cholesterol. These two major bile acids are roughly equal in concentration in humans. Derivatives are made from cholyl-CoA, which exchanges its CoA with either glycine, or taurine, yielding glycocholic and taurocholic acid, respectively.

Chenodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid. Salts of this carboxylic acid are called chenodeoxycholates. Chenodeoxycholic acid is one of the main bile acids. It was first isolated from the bile of the domestic goose, which gives it the "cheno" portion of its name.

Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile salts.
Postcholecystectomy syndrome (PCS) describes the presence of abdominal symptoms after a cholecystectomy.

Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase also known as cholesterol 7-alpha-monooxygenase or cytochrome P450 7A1 (CYP7A1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP7A1 gene which has an important role in cholesterol metabolism. It is a cytochrome P450 enzyme, which belongs to the oxidoreductase class, and converts cholesterol to 7-alpha-hydroxycholesterol, the first and rate limiting step in bile acid synthesis.

The biliary tract, refers to the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts, and how they work together to make, store and secrete bile. Bile consists of water, electrolytes, bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids and conjugated bilirubin. Some components are synthesized by hepatocytes, the rest are extracted from the blood by the liver.

The G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1 (GPBAR1) also known G-protein coupled receptor 19 (GPCR19), membrane-type receptor for bile acids (M-BAR) or TGR5 as is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPBAR1 gene.

Ileal sodium/bile acid cotransporter, also known as apical sodium–bile acid transporter (ASBT) and ileal bile acid transporter (IBAT), is a bile acid:sodium symporter protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC10A2 gene.

Fibroblast growth factor 19 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGF19 gene. It functions as a hormone, regulating bile acid synthesis, with effects on glucose and lipid metabolism. Reduced synthesis, and blood levels, may be a factor in chronic bile acid diarrhea and in certain metabolic disorders.

Sodium/bile acid cotransporter also known as the Na+-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) or liver bile acid transporter (LBAT) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC10A1 (solute carrier family 10 member 1) gene.

SeHCAT is a drug used in a clinical test to diagnose bile acid malabsorption.
Bile acid malabsorption (BAM), known also as bile acid diarrhea, is a cause of several gut-related problems, the main one being chronic diarrhea. It has also been called bile acid-induced diarrhea, cholerheic or choleretic enteropathy, bile salt diarrhea or bile salt malabsorption. It can result from malabsorption secondary to gastrointestinal disease, or be a primary disorder, associated with excessive bile acid production. Treatment with bile acid sequestrants is often effective.

















