
Gall wasps, also traditionally calledgallflies, are hymenopterans of the family Cynipidae in the wasp superfamily Cynipoidea. Their common name comes from the galls they induce on plants for larval development. About 1,300 species of this generally very small creature are known worldwide, with about 360 species of 36 different genera in Europe and some 800 species in North America.

The cabbage moth is primarily known as a pest that is responsible for severe crop damage of a wide variety of plant species. The common name, cabbage moth, is a misnomer as the species feeds on many fruits, vegetables, and crops in the genus Brassica. Other notable host plants include tobacco, sunflower, and tomato, making this pest species particularly economically damaging.

Luthrodes pandava also called the Plains Cupid or cycad blue, is a species of lycaenid butterfly found in South Asia, Myanmar, United Arab Emirates, Indochina, Peninsular Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, Java, Sumatra and the Philippines. They are among the few butterflies that breed on cycads, known for their leaves being toxic to most vertebrates.

Catopsilia pomona, the common emigrant or lemon emigrant, is a medium-sized pierid butterfly found in Asia and parts of Australia. The species gets its name from its habit of migration. Some early authors considered them as two distinct species Catopsilia crocale and Catopsilia pomona.

Curetis bulis, the bright sunbeam, is a species of butterfly belonging to the lycaenid family. It is found in Asia.

Athyma nefte, the colour sergeant, is a species of brush-footed butterfly found in tropical South and Southeast Asia.

Rhaphigaster nebulosa, common name mottled shieldbug, is a species of stink bug in the family Pentatomidae.

Andricus kollari, also known as the marble gall wasp, is a parthenogenetic species of wasp which causes the formation of marble galls on oak trees. Synonyms for the species include Cynips kollari, Andricus quercusgemmae, A. minor, A. indigenus and A. circulans.
Chrysonotomyia is a genus of hymenopteran insects of the family Eulophidae.

Leptocybe invasa, the blue gum chalcid wasp or eucalyptus gall wasp, is a chalcid wasp which is the only species in the monotypic genus Leptocybe in the subfamily Tetrastichinae, of the family Eulophidae. It is a gall wasp which causes the formation of galls on a number of species of Eucalyptus, it was described in 2004 after galls were found in river red gums in the Mediterranean and Middle East and has since been found to be a widespread species where its host trees are planted. It is indigenous to Australia.

Neuroterus numismalis is a gall wasp that forms chemically induced leaf galls on oak trees. It has both bisexual and agamic (parthenogenetic) generations and forms two distinct galls on oak leaves, the silk button gall and blister gall. The galls can be very numerous with more than a thousand per leaf.

Biorhiza pallida, also known as the oak apple gall wasp, is a gall wasp species in the family Cynipidae. This species is a member of the tribe Cynipini: the oak gall wasp tribe. Cynipini is the tribe partially responsible for the formation of galls known as oak apples on oak trees. These are formed after the wasp lays eggs inside the leaf buds and the plant tissues swell as the larvae of the gall wasp develop inside. This wasp has a widespread distribution within Europe.

Indothemis carnatica, the black marsh skimmer, or light-tipped demon, is a species of dragonfly in the family Libellulidae. It is found in India, Sri Lanka and Thailand.

Tamarixia radiata, the Asian citrus psyllid parasitoid, is a parasitoid wasp from the family Eulophidae which was discovered in the 1920s in the area of northwestern India (Punjab), now Pakistan. It is a parasitoid of the Asian citrus psyllid, an economically important pest of citrus crops around the world and a vector for Citrus greening disease.
Baeoentedon balios, the balios wasp, is a species of chalcid wasp which was first described from China in 2014. It is a parasitoid of whiteflies of the family Aleyrodidae.
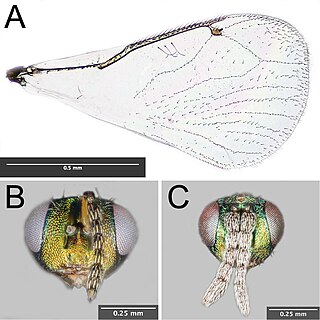
Euderus set, the crypt-keeper wasp, is a tiny chalcid wasp from the family Eulophidae from the United States, described in 2017 as a parasitoid of the gall wasp Bassettia pallida. The description of its life cycle has attracted widespread publicity.
Bassettia pallida is a species of gall wasp found in the Southern United States. This species was described by American entomologist William Harris Ashmead in 1896. B. pallida reproduces asexually in galls it induces on oak trees. The parasite Euderus set, a eulophid wasp, has B. pallida as a host and manipulates its behavior.

Meromacrus gloriosus, the Glorious Elegant, is a species of syrphid fly in the family Syrphidae. Originally described from Mexico by Frank Hull in 1941 this black and yellow wasp mimic has since been observed in many locations in Texas and New Mexico.

Neuroterus saltatorius, also known as the jumping gall wasp, is a species of oak gall wasp. It is found in North America, where it induces galls on a variety of oak trees, including Oregon oak, valley oak, California scrub oak, blue oak, and leather oak.

Chrysonotomyia corynata is a species of parasitoid wasp in the family Eulophidae. It was first described in 2004 from specimens collected in Mexico, specifically the states of Coahuila, Guanajuato, Michoacán, Oaxaca, Puebla and Zacatecas. The overall color of the body is pale yellow with darker brown markings on the top of the thorax. Its biology is unknown.


















