Churchill Falls Airport | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summary | |||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||
| Owner/Operator | Churchill Falls (Labrador) Corp. | ||||||||||
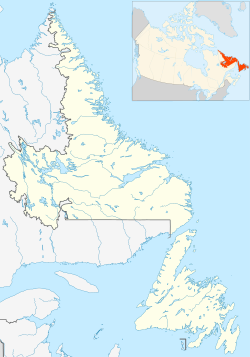
| Location | Churchill Falls, Newfoundland and Labrador | ||||||||||
| Time zone | AST (UTC−04:00) | ||||||||||
| • Summer (DST) | ADT (UTC−03:00) | ||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 1,437 ft / 438 m | ||||||||||
| Coordinates | 53°33′45″N064°06′21″W / 53.56250°N 64.10583°W | ||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Sources: Canada Flight Supplement [1] Environment Canada [2] Transport Canada [3] | |||||||||||
Churchill Falls Airport( IATA : ZUM, ICAO : CZUM) is owned and operated by Churchill Falls Labrador Corporation Limited. Provincial Airlines provides regularly scheduled passenger service at the airport, which handled about 1,400 passengers annually over between 2000 and 2003. The airport is located 4 nautical miles (7.4 km; 4.6 mi) northwest of Churchill Falls, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada.
Contents
Four small structures are the only buildings, as the airport has no formal terminal.