Ultraviolet (UV) light is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs, Cherenkov radiation, and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights.

Oxybenzone or benzophenone-3 or BP-3 is an organic compound belonging to the class of aromatic ketones known as benzophenones. It takes the form of pale-yellow crystals that are readily soluble in most organic solvents. It is widely used in sunscreen formulations, plastics, toys, furniture finishes, and other products to limit UV degradation. In nature, it can be found in various flowering plants (angiosperms). The compound was first synthesised in Germany by chemists König and Kostanecki in 1906.

Sunscreen, also known as sunblock, sun lotion or sun cream, is a photoprotective topical product for the skin that helps protect against sunburn and prevent skin cancer. Sunscreens come as lotions, sprays, gels, foams, sticks, powders and other topical products. Sunscreens are common supplements to clothing, particularly sunglasses, sunhats and special sun protective clothing, and other forms of photoprotection.
4-Aminobenzoic acid (also known as para-aminobenzoic acid or PABA because the two functional groups are attached to the benzene ring across from one another in the para position) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4CO2H. PABA is a white solid, although commercial samples can appear gray. It is slightly soluble in water. It consists of a benzene ring substituted with amino and carboxyl groups. The compound occurs extensively in the natural world.
In high energy physics experiments, an absorber is a block of material used to absorb some of the energy of an incident particle in an experiment. Absorbers can be made of a variety of materials, depending on the purpose; lead, tungsten and liquid hydrogen are common choices. Most absorbers are used as part of a particle detector; particle accelerators use absorbers to reduce the radiation damage on accelerator components.
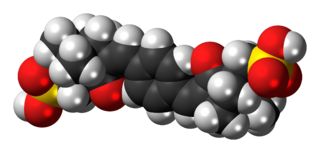
Ecamsule is an organic compound which is added to many sunscreens to filter out UVA rays. It is a benzylidene camphor derivative, many of which are known for their excellent photostability.

Avobenzone is an organic molecule and an oil-soluble ingredient used in sunscreen products to absorb the full spectrum of UVA rays.

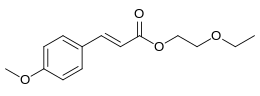
Octyl methoxycinnamate or ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate (INCI) or octinoxate (USAN), trade names Eusolex 2292 and Uvinul MC80, is an organic compound that is an ingredient in some sunscreens and lip balms. It is an ester formed from methoxycinnamic acid and 2-ethylhexanol. It is a liquid that is insoluble in water.

Retinyl palmitate, or vitamin A palmitate, is the ester of retinol (vitamin A) and palmitic acid, with formula C36H60O2. It is the most abundant form of vitamin A storage in animals.

UV filters are compounds, mixtures, or materials that block or absorb ultraviolet (UV) light. One of the major applications of UV filters is their use as sunscreens to protect skin from sunburn and other sun/UV related damage. After the invention of digital cameras changed the field of photography, UV filters have been used to coat glass discs fitted to camera lenses to protect hardware that is sensitive to UV light.

Octocrylene is an organic compound used as an ingredient in sunscreens and cosmetics. It is an ester formed by the Knoevenagel condensation of 2-ethylhexyl cyanoacetate with benzophenone. It is a viscous, oily liquid that is clear and colorless.

2-Ethylhexyl salicylate also known as octisalate or octyl salicylate, is an organic compound used as an ingredient in sunscreens and cosmetics to absorb UVB (ultraviolet) rays from the sun. It is an ester formed by the condensation of salicylic acid with 2-ethylhexanol. It is a colorless oily liquid with a slight floral odor.
Hydrolyzed jojoba esters are the hydrolysate of jojoba esters derived by acid, enzyme or other method of hydrolysis. Hydrolyzed jojoba esters are commonly used in cosmetic formulations.

Homosalate is an organic compound used in some sunscreens. It is made by the Fischer–Speier esterification of salicylic acid and 3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexanol, the latter being a hydrogenated derivative of isophorone. Contained in 45% of U.S. sunscreens, it is used as a chemical UV filter. The salicylic acid portion of the molecule absorbs ultraviolet rays with a wavelength from 295 nm to 315 nm, protecting the skin from sun damage. The hydrophobic trimethyl cyclohexyl group provides greasiness that prevents it from dissolving in water.
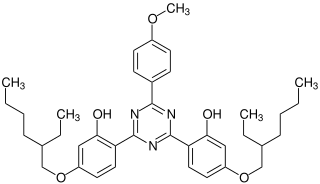
Bemotrizinol is an oil-soluble organic compound that is added to sunscreens to absorb UV rays. It is marketed as Parsol Shield, Tinosorb S, and Escalol S.

Bisoctrizole is a phenolic benzotriazole that is added to sunscreens to absorb UV rays. It is a broad-spectrum ultraviolet radiation absorber, absorbing UVB as well as UVA rays. It also reflects and scatters UV.

Kaempferia galanga, commonly known as kencur, aromatic ginger, sand ginger, cutcherry, is a monocotyledonous plant in the ginger family, and one of four plants called galangal. It is found primarily in open areas in Indonesia, southern China, Taiwan, Cambodia, and India, but is also widely cultivated throughout Southeast Asia.

Amiloxate is an organic molecule used as UV filter in sunscreen products. It is approved for use in the European Union and is undergoing regulatory evaluation in the United States.
A Certified Organic Sunscreen, also known as Petrochemical-Free Sunscreen, is a third party certified sunscreen product consisting of certified and approved organic ingredients, with typically zinc oxide acting as the photo-protector. An organic sunscreen is verified and approved by a certifier to international or national organic standards, such as NSF/ANSI 305 and USDA organic, which define production and labelling requirements for personal care products containing organic ingredients. These standards are complemented by existing sunscreen regulatory bodies such as the FDA that regulate the efficacy of the sunscreen, safety and permitted ingredients. Generally speaking, sunscreen has photo-protective properties that reduce the risk of skin cancer and ageing with relation to the SPF value and proper application.