
A ketene is an organic compound of the form R′R″C=C=O, where R and R' are two arbitrary monovalent chemical groups. The name may also refer to the specific compound ethenone H
2C=C=O, the simplest ketene.
Chemically, an aldehyde is a compound containing a functional group with the structure −CHO, consisting of a carbonyl center with the carbon atom also bonded to hydrogen and to any generic alkyl or side chain R group,. The functional group itself is known as an aldehyde or formyl group.

Osmium tetroxide (also osmium(VIII) oxide) is the chemical compound with the formula OsO4. The compound is noteworthy for its many uses, despite its toxicity and the rarity of osmium. It also has a number of unusual properties, one being that the solid is volatile. The compound is colourless, but most samples appear yellow. This is most likely due to the presence of the impurity OsO2, which is yellow-brown in colour.

An acetal is a functional group with the connectivity R2C(OR')2). Here, the R groups can be organic fragments (a carbon atom, with arbitrary other atoms attached to that) or hydrogen, while the R' groups must be organic fragments not hydrogen. The two R' groups can be equivalent to each other (a "symmetric acetal") or not (a "mixed acetal"). Acetals are formed from and convertible to aldehydes or ketones and have the same oxidation state at the central carbon, but have substantially different chemical stability and reactivity as compared to the analogous carbonyl compounds. The central carbon atom has four bonds to it, and is therefore saturated and has tetrahedral geometry.
In organic chemistry, transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic group R″ of an ester with the organic group R′ of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. The reaction can also be accomplished with the help of other enzymes, particularly lipases.
In chemistry, a hydration reaction is a chemical reaction in which a substance combines with water. In organic chemistry, water is added to an unsaturated substrate, which is usually an alkene or an alkyne. This type of reaction is employed industrially to produce ethanol, isopropanol, and butan-2-ol.
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups. An aliphatic diol is also called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified.

Sodium periodate is an inorganic salt, composed of a sodium cation and the periodate anion. It may also be regarded as the sodium salt of periodic acid. Like many periodates it can exist in two different forms: sodium metaperiodate, which has the formula NaIO4, and sodium orthoperiodate, normally this means sodium hydrogen periodate (Na2H3IO6) but the fully reacted sodium orthoperiodate salt, Na5IO6, can also be prepared. Both salts are useful oxidising agents.
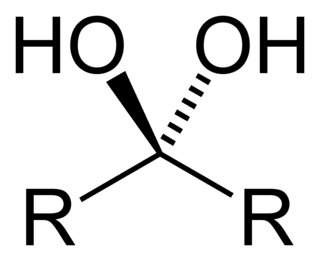
A geminal diol is any organic compound having two hydroxyl functional groups (-OH) bound to the same carbon atom. Geminal diols are a subclass of the diols, which in turn are a special class of alcohols. Most of the geminal diols are considered unstable.

Tetrapropylammonium perruthenate (TPAP or TPAPR) is the chemical compound described by the formula N(C3H7)4RuO4. Sometimes known as the Ley–Griffith reagent, this ruthenium compound is used as a reagent in organic synthesis. This salt consists of the tetrapropylammonium cation and the perruthenate anion, RuO−
4.

Endosulfan is an off-patent organochlorine insecticide and acaricide that is being phased out globally. The two isomers, endo and exo, are known popularly as I and II. Endosulfan sulfate is a product of oxidation containing one extra O atom attached to the S atom. Endosulfan became a highly controversial agrichemical due to its acute toxicity, potential for bioaccumulation, and role as an endocrine disruptor. Because of its threats to human health and the environment, a global ban on the manufacture and use of endosulfan was negotiated under the Stockholm Convention in April 2011. The ban has taken effect in mid-2012, with certain uses exempted for five additional years. More than 80 countries, including the European Union, Australia, New Zealand, several West African nations, the United States, Brazil, and Canada had already banned it or announced phase-outs by the time the Stockholm Convention ban was agreed upon. It is still used extensively in India, China despite laws banning it, and few other countries. It is produced by Makhteshim Agan and several manufacturers in India and China. Although, the Supreme Court had, by an order dated 13.05.2011, put a ban on the production and sale of endosulfan in India till further orders.
Dihydroxylation is the process by which an alkene is converted into a vicinal diol. Although there are many routes to accomplish this oxidation, the most common and direct processes use a high-oxidation-state transition metal. The metal is often used as a catalyst, with some other stoichiometric oxidant present. In addition, other transition metals and non-transition metal methods have been developed and used to catalyze the reaction.
Triethylborane (TEB), also called triethylboron, is an organoborane (a compound with a B-C bond). It is a colorless pyrophoric liquid. Its chemical formula is (C2H5)3B, abbreviated Et3B. It is soluble in organic solvents tetrahydrofuran and hexane.
Glycol cleavage is a specific type of organic chemistry oxidation. The carbon–carbon bond in a vicinal diol (glycol) is cleaved and instead the two oxygen atoms become double-bonded to their respective carbon atoms. Depending on the substitution pattern in the diol, these carbonyls can be either ketones or aldehydes.
The Corey–Winter olefin synthesis is a series of chemical reactions for converting 1,2-diols into olefins. It is named for the American chemist and Nobelist Elias James Corey and the American-Estonian chemist Roland Arthur Edwin Winter.
A reaction intermediate or an intermediate is a molecular entity that is formed from the reactants and reacts further to give the directly observed products of a chemical reaction. Most chemical reactions are stepwise, that is they take more than one elementary step to complete. An intermediate is the reaction product of each of these steps, except for the last one, which forms the final product. Reactive intermediates are usually short lived and are very seldom isolated. Also, owing to the short lifetime, they do not remain in the product mixture.

The Kuwajima Taxol total synthesis by the group of Isao Kuwajima of the Tokyo Institute of Technology is one of several efforts in taxol total synthesis published in the 1990s. The total synthesis of Taxol is considered a landmark in organic synthesis.

Damascenones are a series of closely related chemical compounds that are components of a variety of essential oils. The damascenones belong to a family of chemicals known as rose ketones, which also includes damascones and ionones. beta-Damascenone is a major contributor to the aroma of roses, despite its very low concentration, and is an important fragrance chemical used in perfumery.
The Criegee oxidation is a glycol cleavage reaction in which vicinal diols are oxidized to form ketones and aldehydes using lead tetraacetate. It is analogous to the Malaprade reaction, but uses a milder oxidant. This oxidation was discovered by Rudolf Criegee and coworkers and first reported in 1931 using ethylene glycol as the substrate.

Pregnanediol glucuronide, or 5β-pregnane-3α,20α-diol 3α-glucuronide, is the major metabolite of progesterone and the C3α glucuronide conjugate of pregnanediol (5β-pregnane-3α,20α-diol). Approximately 15 to 30% of a parenteral dose of progesterone is metabolized into pregnanediol glucuronide. While this specific isomer is referred to as pregnanediol glucuronide and is the most major form, there are actually many possible isomers of the metabolite.











