
 |
| Part of a series on the |
| Military of ancient Rome |
|---|
The Classis Flavia Moesica ("Flavian Fleet of Moesia") was the Roman Empire's fleet on the lower Danube river, near the Black Sea.

 |
| Part of a series on the |
| Military of ancient Rome |
|---|
The Classis Flavia Moesica ("Flavian Fleet of Moesia") was the Roman Empire's fleet on the lower Danube river, near the Black Sea.
The Classis Moesica was established sometime between 20 BC and 10 AD. It was based in Noviodunum and controlled the Lower Danube from the Iron Gates to the northwestern Black Sea as far as the Crimea. [1] The honorific Flavia, awarded to it and to the Classis Pannonica, may indicate its reorganization by Vespasian around 75 AD. [2] After Domitian (in 85 AD) it was headquartered in Sexaginta Prista. After Trajan's conquest of Dacia, during which the Classis Moesica provided logistical support, its base was moved to Noviodunum. The fleet also included several secondary ports, like Novae, Oescus and Tomis (modern Constanta). From 41 AD detachments were stationed in Crimea and Tyras.
In a series of Roman provinces a river forms the border of the Empire. In Europe this is the case for the provinces on the Rhine and the Danube. We know of three provincial fleets here, the classis Germanica, the classis Pannonica and the classis Moesica. Although one could conclude from their names that their areas of operations stretched over both provinces bearing their corresponding name, this was not the case. Thus, so-called military diplomas clearly show for the classis Pannonica and the classis Moesica that they belonged to the army of Pannonia Inferior and Moesia Inferior respectively. [3]
The Classis Moesica lasted until the beginning of the fifth century, being later assimilated within the Byzantine navy. [4]
The attested ships used by the Moesian fleet were mainly the ubiquitous liburnae used by most Roman provincial fleets, of which two names survive: "Armata" & "Sagita".
In Scythia Minor, during late Antiquity there were marines ( muscularii ) [5] of legio II Herculia at "Inplateypegiis" and sailors (nauclarii) at Flaviana. [6]

Moesia was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. Moesian Province was first administered by governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballia'. It included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Albania, northern parts of North Macedonia, Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobruja and small parts of Southern Ukraine.

Limes is a term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimiting system of Ancient Rome marking the borders of the Roman Empire. The term has been extended in modern times to refer to the frontier defences in other parts of the empire, such as in the east and in Africa.

Germania Inferior was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the 4th century AD, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium.

The Roman provinces were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as governor.

Praeses is a Latin word meaning "placed before" or "at the head". In antiquity, notably under the Roman Dominate, it was used to refer to Roman governors; it continues to see some use for various modern positions.
The naval forces of the ancient Roman state were instrumental in the Roman conquest of the Mediterranean Basin, but it never enjoyed the prestige of the Roman legions. Throughout their history, the Romans remained a primarily land-based people and relied partially on their more nautically inclined subjects, such as the Greeks and the Egyptians, to build their ships. Because of that, the navy was never completely embraced by the Roman state, and deemed somewhat "un-Roman".

Legio V Macedonica was a Roman legion. It was probably originally levied in 43 BC by consul Gaius Vibius Pansa Caetronianus and Gaius Julius Caesar Octavianus. It was based in the Balkan provinces of Macedonia, Moesia and Dacia. In the Notitia Dignitatum records from beginning of the fifth century, the legion was still stationed in Dacia, with detachments stationed in the east and Egypt.
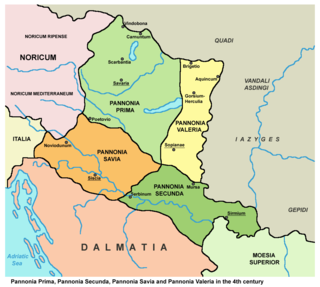
Pannonia Prima was an ancient Roman province. It was formed in the year 296, during the reign of Emperor Diocletian. Previously, it was a part of the province of Pannonia Superior, which, along with Pannonia Inferior, was gradually divided into four administrative units: Pannonia Prima, Pannonia Secunda, Valeria, and Savia. This transition was completed by the time of Constantine. According to the Notitia Dignitatum, Pannonia Prima was governed by a Praeses.

Dacia Ripensis was the name of a Roman province in the northern Balkan peninsula, immediately south of the Middle Danube. Its capital was Ratiaria. It was a district less urban than neighbouring Dacia Mediterranea and more militarized; "military camps and forts, rather than cities, were typical of the province". Besides Ratiaria, Oescus was the major settlement.

The Diocese of Dacia was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, in the area of modern western Bulgaria, central Serbia, Montenegro, Kosovo, northern Albania and northern North Macedonia. It was subordinate to the Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum. Its capital was at Serdica.

Ratiaria was a city founded by the Moesians, a Daco-Thracian tribe, in the 4th century BC, along the river Danube. In Roman times it was named Colonia Ulpia Traiana Ratiaria.

The Moesian Limes is the modern term given to a linked series of Roman forts on the northern frontier of the Roman province of Moesia along the Danube between the Black Sea shore and Pannonia and dating from the 1st century AD. It was the eastern section of the so-called Danubian Limes and protected the Roman provinces of Upper and Lower Moesia south of the river. The eastern section is often called the limes Scythiae minoris as it was located in the late Roman province of Scythia Minor.
Thracia or Thrace is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical and Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek Diadochi ruler Lysimachus, but became a client state of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire as the Sapaean kingdom. Roman emperor Claudius annexed the kingdom as a Roman province in 46 AD.

Capidava was originally an important Geto-Dacian centre on the right bank of the Danube. After the Roman conquest, it became a civil and military centre in the province of Moesia Inferior and part of the defensive frontier system of the Moesian Limes along the Danube.

Noviodunum ad Istrum was a Roman city that developed around the legionary fortress and naval port near the present town of Isaccea. It was in the Roman province of Moesia and was the headquarters of the Roman Danube fleet located on the lower Danube and, from the 4th century AD, the headquarters of the Legio I Iovia (Scythica).
Ancient navies had a large impact on the navies of today. The outcomes of battles between ancient navies have been studied by the military to learn tactics that would help in their conquests. The ships that these civilizations created were what many ship designs were based on and allowed the vessels to become better built. The Punic Wars are some of the most notorious wars in history, and the naval vessels and tactics used in all three became a major part of naval military history.

Moesia Prima was a frontier province of the Late Roman Empire, situated in the central parts of present-day Serbia, along the south bank of the Danube River. Provincial capital was Viminacium, near modern Kostolac in Serbia).
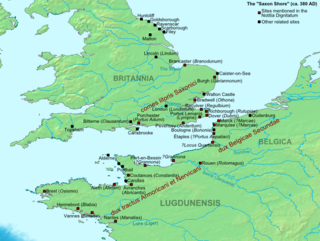
The Dux Belgicae secundae was a senior officer in the army of the Late Roman Empire who was the commander of the limitanei and of a naval squadron on the so-called Saxon Shore in Gaul.

Classiarii referred to all military personnel and personnel assigned to the maneuvering of ships or their construction/maintenance, as part of the Roman navy, an integral part of the Roman army.

The Classis Pontica was a provincialis fleet, established initially by Augustus and then by Nero on a permanent basis. It was tasked with guarding the southern Pontus Euxinus, coordinating with the neighboring fleet of Mesia, the Classis Flavia Moesica.