
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes. The name typically refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, drenching sweats, unintended weight loss, itching, and constantly feeling tired. The enlarged lymph nodes are usually painless. The sweats are most common at night.

Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes. Early on, there are typically no symptoms. Later, non-painful lymph node swelling, feeling tired, fever, night sweats, or weight loss for no clear reason may occur. Enlargement of the spleen and low red blood cells (anemia) may also occur. It typically worsens gradually over years.

The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society (LLS), a 501(c)(3) charitable organization founded in 1949, is a voluntary health organization dedicated to fighting blood cancer world-wide. LLS funds blood cancer research on cures for leukemia, lymphoma, Hodgkin's disease, and myeloma. It provides free information and support services, and it advocates for blood cancer patients and their families seeking access to quality and affordable care.

Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma is a rare cancer of the immune system's T-cells caused by human T cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1). All ATL cells contain integrated HTLV-1 provirus further supporting that causal role of the virus in the cause of the neoplasm. A small amount of HTLV-1 individuals progress to develop ATL with a long latency period between infection and ATL development. ATL is categorized into 4 subtypes: acute, smoldering, lymphoma-type, chronic. Acute and Lymphoma-type are known to particularly be aggressive with poorer prognosis.

Tanespimycin is a derivative of the antibiotic geldanamycin that is being studied in the treatment of cancer, specifically in younger patients with certain types of leukemia or solid tumors, especially kidney tumors.

Bortezomib, sold under the brand name Velcade among others, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma. This includes multiple myeloma in those who have and have not previously received treatment. It is generally used together with other medications. It is given by injection.

Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) is a plasma cell dyscrasia in which plasma cells or other types of antibody-producing cells secrete a myeloma protein, i.e. an abnormal antibody, into the blood; this abnormal protein is usually found during standard laboratory blood or urine tests. MGUS resembles multiple myeloma and similar diseases, but the levels of antibodies are lower, the number of plasma cells in the bone marrow is lower, and it rarely has symptoms or major problems. However, since MGUS can lead to multiple myeloma, which develops at the rate of about 1.5% a year, or other symptomatic conditions, yearly monitoring is recommended.

Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment (pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medicine, targeted therapy blocks the growth of cancer cells by interfering with specific targeted molecules needed for carcinogenesis and tumor growth, rather than by simply interfering with all rapidly dividing cells. Because most agents for targeted therapy are biopharmaceuticals, the term biologic therapy is sometimes synonymous with targeted therapy when used in the context of cancer therapy. However, the modalities can be combined; antibody-drug conjugates combine biologic and cytotoxic mechanisms into one targeted therapy.
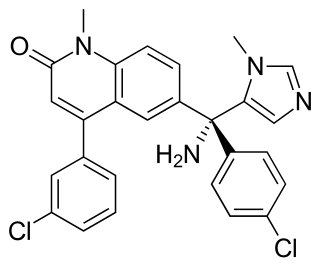
Tipifarnib is a farnesyltransferase inhibitor. Farnesyltransferase inhibitors block the activity of the farnesyltransferase enzyme by inhibiting prenylation of the CAAX tail motif, which ultimately prevents Ras from binding to the membrane, rendering it inactive.
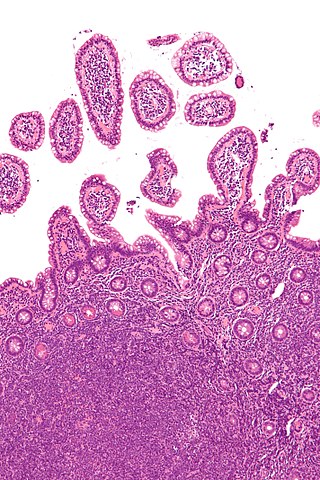
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a type of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, comprising about 6% of cases. It is named for the mantle zone of the lymph nodes where it develops. The term 'mantle cell lymphoma' was first adopted by Raffeld and Jaffe in 1991.
In hematology, plasma cell dyscrasias are a spectrum of progressively more severe monoclonal gammopathies in which a clone or multiple clones of pre-malignant or malignant plasma cells over-produce and secrete into the blood stream a myeloma protein, i.e. an abnormal monoclonal antibody or portion thereof. The exception to this rule is the disorder termed non-secretory multiple myeloma; this disorder is a form of plasma cell dyscrasia in which no myeloma protein is detected in serum or urine of individuals who have clear evidence of an increase in clonal bone marrow plasma cells and/or evidence of clonal plasma cell-mediated tissue injury. Here, a clone of plasma cells refers to group of plasma cells that are abnormal in that they have an identical genetic identity and therefore are descendants of a single genetically distinct ancestor cell.

Plasma cell leukemia (PCL) is a plasma cell dyscrasia, i.e. a disease involving the malignant degeneration of a subtype of white blood cells called plasma cells. It is the terminal stage and most aggressive form of these dyscrasias, constituting 2% to 4% of all cases of plasma cell malignancies. PCL may present as primary plasma cell leukemia, i.e. in patients without prior history of a plasma cell dyscrasia or as secondary plasma cell dyscrasia, i.e. in patients previously diagnosed with a history of its predecessor dyscrasia, multiple myeloma. The two forms of PCL appear to be at least partially distinct from each other. In all cases, however, PCL is an extremely serious, life-threatening, and therapeutically challenging disease.
Milatuzumab is an anti-CD74 humanized monoclonal antibody for the treatment of multiple myeloma non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.

Omacetaxine mepesuccinate is a pharmaceutical drug substance that is indicated for treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).

Leukemia & Lymphoma is a peer-reviewed medical journal published by Informa Healthcare. It covers basic and clinical aspects of hematologic malignancies. The editors-in-chief are Aaron Polliack, Koen Van Besien, and John Seymour.
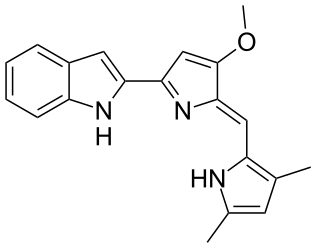
Obatoclax mesylate, also known as GX15-070, is an experimental drug for the treatment of various types of cancer. It was discovered by Gemin X, which was acquired by Cephalon, which has since been acquired by Teva Pharmaceuticals. Several Phase II clinical trials were completed that investigated use of obatoclax in the treatment of leukemia, lymphoma, myelofibrosis, and mastocytosis.
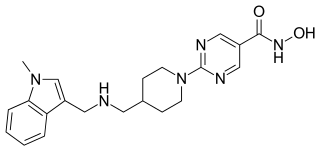
Quisinostat is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of cancer. It is a "second generation" histone deacetylase inhibitor with antineoplastic activity. It is highly potent against class I and II HDACs.
Expert Review of Hematology is a MEDLINE-indexed, peer-reviewed, international medical journal publishing review articles and original papers on all aspects of hematology. It is part of the Expert Review series, published by Informa.

Selinexor sold under the brand name Xpovio among others, is a selective inhibitor of nuclear export used as an anti-cancer medication. It works by blocking the action of exportin 1 and thus blocking the transport of several proteins involved in cancer-cell growth from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm, which ultimately arrests the cell cycle and leads to apoptosis. It is the first drug with this mechanism of action.
Selective inhibitors of nuclear export are drugs that block exportin 1, a protein involved in transport from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm. This causes cell cycle arrest and cell death by apoptosis. Thus, SINE compounds are of interest as anticancer drugs; several are in development, and one (selinexor) has been approved for treatment of multiple myeloma as a drug of last resort.















