
The Battle of Antietam, or Battle of Sharpsburg particularly in the Southern United States, was a battle of the American Civil War fought on September 17, 1862, between Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia and Union Gen. George B. McClellan's Army of the Potomac near Sharpsburg, Maryland and Antietam Creek. Part of the Maryland Campaign, it was the first field army–level engagement in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War to take place on Union soil. It was the bloodiest day in American history, with a combined tally of 22,717 dead, wounded, or missing.

The Army of the Potomac was the principal Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was created in July 1861 shortly after the First Battle of Bull Run and was disbanded in June 1865 following the surrender of the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in April.

George Bentham was an English botanist, described by the weed botanist Duane Isely as "the premier systematic botanist of the nineteenth century". Born into a distinguished family, he initially studied law, but had a fascination with botany from an early age, which he soon pursued, becoming president of the Linnaean Society in 1861, and a fellow of the Royal Society in 1862. He was the author of a number of important botanical works, particularly flora. He is best known for his taxonomic classification of plants in collaboration with Joseph Dalton Hooker, his Genera Plantarum (1862–1883). He died in London in 1884.

There were four formations in the Union Army designated as III Corps during the American Civil War.

Coelogyne is a genus of over 200 sympodial epiphytes from the family Orchidaceae, distributed across India, China, Indonesia and the Fiji islands, with the main centers in Borneo, Sumatra and the Himalayas. They can be found from tropical lowland forests to montane rainforests. A few species grow as terrestrials or even as lithophytes in open, humid habitats. The genera BolborchisLindl., HologynePfitzer and PtychogynePfitzer are generally included here. The genus is abbreviated Coel. in trade journals.

Bahiopsis parishii known commonly as Parish goldeneye or shrubby goldeneye, is a North American species of flowering shrubs in the sunflower family.

Allium parishii is an uncommon species of wild onion known by the common name Parish's onion. It is native to the Mojave Desert and Sonoran Deserts of California and Arizona. It grows on open dry, rocky slopes at elevations of 900–1,400 m (3,000–4,600 ft).
Atriplex parishii is an uncommon species of saltbush known by the common names Parish's saltbush and Parish's brittlescale. It is native to central and southern California where it can occasionally be found along the immediate coastline, and the Channel Islands. Its distribution extended historically into the western edges of the Mojave Desert and Baja California and it may still exist there.

Dendrobium parishii is a species of orchid native to Asia.

Coelogyne cristata is an epiphytic orchid that comes from cool, moist areas of the eastern Himalayas and Vietnam. It blooms every spring, before the snow begins to melt. Its genus name Coelogyne originates from two Greek words, koilos (“hollow”) and gyne (“woman”), because of the orchid’s pistil. Cristata takes its species name from crista, the Latin word for “comb”, because of the look of the flower’s lip.

Grusonia parishii is a species of cactus known by the common names matted cholla and Parish club cholla. It is native to the Mojave and Sonoran Deserts of California and Arizona.
Tauschia parishii is a species of flowering plant in the carrot family known by the common name Parish's umbrellawort. It is endemic to California.
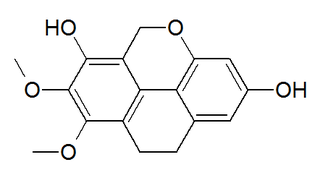
Coelogin is a phenanthrenoid found in the high altitude Himalayan orchid Coelogyne cristata. This molecule has a phenanthro[4,5-bcd]pyran structure.
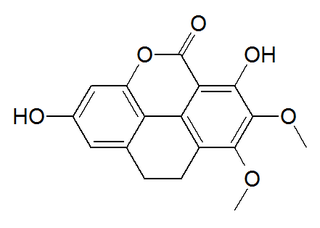
Coeloginin is a phenanthrenoid found in the high altitude Himalayan orchid Coelogyne cristata. This molecule has a phenanthro[4,5-bcd]pyrone structure.

Coeloginanthrin is a phenanthrenoid found in the orchid Coelogyne cristata.
Samuel Bonsall Parish (1838–1928) was a California botanist and curator of the herbarium at Stanford University. A number of plants were named in his honor, including Allium parishii, Atriplex parishii, Boechera parishii, Chaenactis parishii, Cheilanthes parishii, Delphinium parishii ssp. pallidum, Delphinium parishii ssp. parishii, Ericameria parishii, Erigeron parishii, Eriogonum parishii, Eschscholzia parishii, Euphorbia parishii, Galium parishii, Grusonia parishii, Heuchera parishii, Lycium parishii, Malacothamnus parishii, Mimulus parishii, Orobanche parishii ssp. brachyloba, Orobanche parishii ssp. parishii, Perideridia parishii, Phacelia parishii, Plagiobothrys parishii, Puccinellia parishii, Silene parishii, Solanum parishii, Stipa parishii, Symphoricarpos parishii, Tauschia parishii, Trichostema parishii, Viguiera parishii, and others.
Ericameria parishii is a western North American species of flowering plants in the daisy family.

George W. Hooker was an American Civil War veteran who received the Medal of Honor. In 1862 Hooker captured 116 Confederate soldiers along with their colonel and company colors by himself. For this action he was awarded the Medal of Honor. Hooker was elected in 1879 and 1880 as department commander of the Grand Army of the Republic in Vermont. He was also elected as Brattleboro's representative in the Vermont General Assembly, to which he was re-elected in 1882.

Charles Samuel Pollock Parish (1822–1897) was an Anglo-Indian clergyman and botanist who served as chaplain to the forces of the Honourable East India Company in Burma. With his wife Eleanor he collected and painted plants, chiefly orchids, identifying and naming a number of species new to science. Several species are named in his honour.















