
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae, a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Earth except glaciers. The world's richest diversity of orchid genera and species is found in the tropics.

The Pleurothallidinae are a neotropical subtribe of plants of the orchid family (Orchidaceae) including 29 genera in more than 4000 species.

Pleione is a small genus of predominantly terrestrial but sometimes epiphytic or lithophytic, miniature orchids. This genus is named after Pleione, mother of the Pleiades, and comprises about 20 species. Common names of this genus include peacock orchid, glory of the east, Himalayan crocus, Indian crocus and windowsill orchid. The genus DiploconchiumSchauer is generally included here. Pleione is abbreviated to Pln in trade journals.

In the botanical classification of plants, Aeridinae Pfitzer is a subtribe of the tribe Vandeae whose representatives all have a monopodial growth habit and do not possess pseudobulbs.

Cypripedioideae is a subfamily of orchids commonly known as lady's slipper orchids, lady slipper orchids or slipper orchids. Cypripedioideae includes the genera Cypripedium, Mexipedium, Paphiopedilum, Phragmipedium and Selenipedium. They are characterised by the slipper-shaped pouches of the flowers – the pouch traps insects so they are forced to climb up past the staminode, behind which they collect or deposit pollinia, thus fertilizing the flower. There are approximately 165 species in the subfamily.

The taxonomy of the Orchidaceae (orchid family) has evolved slowly during the last 250 years, starting with Carl Linnaeus who in 1753 recognized eight genera. De Jussieu recognized the Orchidaceae as a separate family in his Genera Plantarum in 1789. Olof Swartz recognized 25 genera in 1800. Louis Claude Richard provided us in 1817 with the descriptive terminology of the orchids. (See External links below). The next step was taken in 1830-1840 by John Lindley, who recognized four subfamilies. He is generally recognized as the father of orchid taxonomy. The next important step was taken by George Bentham with a new classification, recognizing subtribes for the first time. This classification was first presented in a paper that Bentham read to the Royal Society in 1881. Then it was published in 1883 in the final volume of Genera Plantarum. The next great contributors were Pfitzer (1887), Schlechter (1926), Mansfeld (1937), Dressler and Dodson (1960), Garay (1960, 1972), Vermeulen (1966), again Dressler (1981). and Burns-Balogh and Funk (1986). Dressler's 1993 book had considerable influence on later work.

The Orchidoideae, or the orchidoid orchids, are a subfamily of the orchid family (Orchidaceae) that contains around 3630 species. Species typically have a single (monandrous), fertile anther which is erect and basitonic.

The Oncidiinae is a subtribe within the Orchidaceae that consists of a number of genera that are closely related.

Arethuseae is a mid-sized tribe of orchids in the subfamily Epidendroideae. This tribe was initially categorized by John Lindley in 1840. Its largest subtribes are Arethusinae and Coelogyninae.
Friedrich (Fritz) Wilhelm Ludwig Kränzlin was a botanist associated with the Natural History Museum (BM).

The Vandeae is a large monophyletic tribe within the family of orchids.
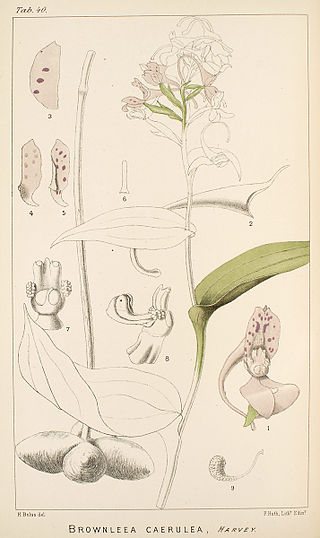
Brownleea is a genus of flowering plants from the family Orchidaceae native to Africa and Madagascar. Eight species are known.
- Brownleea coeruleaHarv. ex Lindl.
- Brownleea galpiniiBolus
- Brownleea graminicolaMcMurtry
- Brownleea macrocerasSond.
- Brownleea maculataP.J.Cribb
- Brownleea mulanjiensisH.P.Linder
- Brownleea parvifloraHarv. ex Lindl.
- Brownleea recurvataSond.
Vargasiella is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It contains two species, both endemic to South America: It has been treated as the only genus in the subtribe Vargasiellinae, but more recently has been included in the subtribe Zygopetalinae.

Pachites is a genus of flowering plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It contains two known species, both endemic to South Africa. One of these, Pachites appressus, is very rare.

× Cambria is a commercial name for intergeneric hybrids among the following genera of orchids of the family Orchidaceae, subfamily Epidendroideae, tribe Cymbidieae and subtribe Oncidiinae:

Dendrobieae is a tribe in the subfamily Epidendroideae, in the family Orchidaceae. The Dendrobieae are mostly tropical, epiphytic orchids which contain pseudobulbs.

Orchideae is a tribe of orchids in the subfamily Orchidoideae. Historically, it was divided into 2 subtribes, Orchidinae and Habenariinae. The subtribe Orchidinae alone contains about 1,800 species. However, although some phylogenetic studies have established the monophyly of the subtribes, the generic boundaries are unclear, with many genera as traditionally circumscribed being paraphyletic or even polyphyletic. Species of genera such as Habenaria and Platanthera have been placed into both subtribes. A 2017 molecular phylogenetic study found that both subtribes did form clades, but did not formally recognize Habenariinae, because of missing genera and uncertainty over generic boundaries. The Asian species of Orchideae, in particular, have been subject to repeated changes of generic placement from 2012 onwards.

Coryciinae is a subtribe of orchids that has been differently defined and placed in the two classification systems that are currently in use for orchids. Genera Orchidacearum, which is currently the definitive work on orchid taxonomy, delimits Coryciinae as consisting of five genera: Disperis, Evotella, Ceratandra, Pterygodium, and Corycium, and it places Coryciinae in the mostly African tribe Diseae, along with four other subtribes: Brownleeinae, Huttonaeinae, Disinae, and Satyriinae. The genera of Coryciinae are small to medium in size and the number of species in each genus is as follows: Disperis (78), Pterygodium (19), Corycium (15), Ceratandra (6), and Evotella (1).

Disinae is a subtribe of orchids that has been differently defined and placed in the two classification systems that are currently in use for orchids. Genera Orchidacearum, which is currently the definitive work on orchid taxonomy, delimits Disinae as consisting of two closely related genera, Disa and Schizodium, and it places Disinae in the mostly African tribe Diseae, along with four other subtribes: Brownleeinae, Huttonaeinae, Coryciinae, and Satyriinae. In the classification for orchids that was published by Chase et alii in 2015, Schizodium was placed in synonymy under Disa, while Pachites and Huttonaea were transferred to Disinae. In Genera Orchidacearum, Pachites and Satyrium form the subtribe Satyriinae, and Huttonaea is the sole genus in the subtribe Huttonaeinae. The transfer of Pachites and Huttonaea to Disinae by Chase et alii (2015) was done with considerable doubt, and was based upon uncertainty about the relationships of these two genera. In 2009, a molecular phylogenetic study found only weak statistical support for a sister relationship between Huttonaea and Disa.
















