
Cohors Breucorum was an important Roman castrum located in western Mauretania Caesariensis.

Cohors Breucorum was an important Roman castrum located in western Mauretania Caesariensis.
The castrum was created under Septimius Severus emperor in the third century. It served as a Roman station and fort on a new military road called "Nova Praetentura", that was created in order to expand to the south the Roman controlled territories in western Mauretania and connect this region to Volubilis [1]
Under the reign of Septimius Severus, presumably in 201 AD, the Romans occupied vast territories in the Oran region, moving the limes established by the Antonines to the south and creating a new frontier line with a new military road: the "Nova praetentura".....this road, connecting with the previous frontier from Rapidum, including the Ouarsenis and the mountains of Frenda and, through the urban centers of Usinaza (Saneg), Cohors Breucorum (Takhemaret), Altava (Ouled-Mimoun), Pomaria (Tlemcem), progressively approached westward to the Mediterranean coast, only a distance of about thirty kilometers from Numerum Syrorum (Lalla Maghnia)M. A. Ruiu [2]
The name was given because it was under the control of the Cohors of the "Breuci", a tribe from ancient Illyria, stationed there (like the cohors from Roman Syria were stationed in nearby Numerus Syrorum.
The castrum had a small "vicus" located nearby, that had nearly 1500 inhabitants and that survived for a few centuries the removal of the Roman legionaries (that probably happened at the end of the third century). With the Arab invasion in the seventh century the "vicus" disappeared.
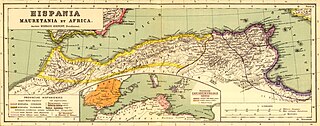
Mauretania is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It stretched from central present-day Algeria westwards to the Atlantic, covering northern Morocco, and southward to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants, seminomadic pastoralists of Berber ancestry, were known to the Romans as the Mauri and the Masaesyli.

Numidia was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in what is now Algeria and a smaller part of Tunisia and small part of Libya in the Maghreb. The polity was originally divided between Massylii in the east and Masaesyli in the west. During the Second Punic War, Masinissa, king of the Massylii, defeated Syphax of the Masaesyli to unify Numidia into one kingdom. The kingdom began as a sovereign state and later alternated between being a Roman province and a Roman client state.

Siga was a Berber and Roman port located near what is now Aïn Témouchent, Algeria. Under the Roman Empire, it was part of western Mauretania Caesariensis, bordering Mauretania Tingitana.

Mauretania Caesariensis was a Roman province located in what is now Algeria in the Maghreb. The full name refers to its capital Caesarea Mauretaniae, in order to distinguish it from neighboring Mauretania Tingitana, which was ruled from Tingis.

Mauretania Sitifensis was a Roman province in Africa Proconsularis. The capital was Setifis.
Cohors secunda Gallorum veterana equitata was a mixed infantry and cavalry regiment of the Auxilia corps of the Imperial Roman army. It was stationed, in the 2nd and 3rd centuries, in a fort near Hadrian's Wall in Britain.
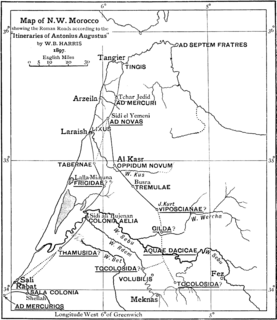
Roman roads in Morocco were the western roads of Roman Africa.

Aiadava was a Dacian town in the Remesiana region, present day Bela Palanka, Serbia.

Thamusida was a Berber, Carthaginian, and Roman river port that was near the present-day towns of Kénitra and Mehdia in Morocco. Under the Roman Empire, it formed a part of the province of Mauretania Tingitana.

Altava was an ancient Roman-Berber city in present-day Algeria. It served as the capital of the ancient Berber Kingdom of Altava. During the French presence, the town was called Lamoriciere. It was situated in the modern Ouled Mimoun near Tlemcen.

Uzinaza is an ancient Roman-Berber city located in present-day Algeria. It is located in the modern commune of Saneg.
Masuna or Massonas ruled the Mauro-Roman Kingdom during the early sixth century as King of the Moors and Romans. Masuna is the earliest recorded ruler of this kingdom, which is assumed to have been established by the local Berber chieftains and rulers following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire and loss of Roman control over Mauretania. His reign would see the arrival of the forces of the Eastern Roman Empire in Northern Africa, with which he allied himself, and the fall of the Vandal Kingdom.

Auzia was a Roman-Berber colonia in present-day Sour El-Ghozlane, Algeria. The area was located around 150 km south-east of Algiers, in the ancient province of Mauretania Caesariensis.

Rapidum was a Roman settlement and fort located in Mauretania Caesariensis, nearly 100 km south of Icosium (Algiers).

Castellum Tingitii, also called Castellum Tingitanum, was a Roman colonia in Mauretania Caesariensis, and corresponds to present-day Chlef in Algeria.
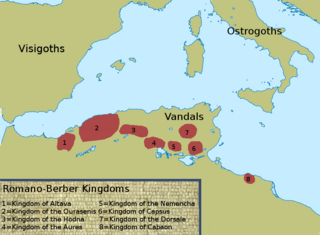
The Kingdom of Altava was an independent Berber kingdom centered on the city of Altava in present-day northern Algeria. The Kingdom of Altava was a successor state of the previous Mauro-Roman Kingdom which had controlled much of the ancient Roman province of Mauretania Caesariensis. This Kingdom collapsed following Eastern Roman military campaigns to decrease its influence and power after Garmul invaded the Exarchate of Africa.

Castra Nova was a Roman-era city and diocese in Mauretania, Africa Proconsulare. The town is identified with the stone ruins at Mohammadia, Mascara in modern Algeria. It is now a Roman Catholic titular see.

Aquae Calidae was a Roman colony of the Roman province of Mauretania Caesariensis. The Roman city has been identified with ruins at Hammam Righa in the wilaya of Chlef, Algeria, North Africa.

Castellum Dimmidi was a Roman castrum located in the south of the Mauretania Caesariensis

The Mauro-Roman Kingdom was an independent Christian Berber kingdom centered on the city of Altava which controlled much of the ancient Roman province of Mauretania Caesariensis, located in present-day northern Algeria. The kingdom was first formed in the fifth century as Roman control over the province weakened and Imperial resources had to be concentrated elsewhere, notably in defending the Italian Peninsula itself from invading Germanic tribes.